Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
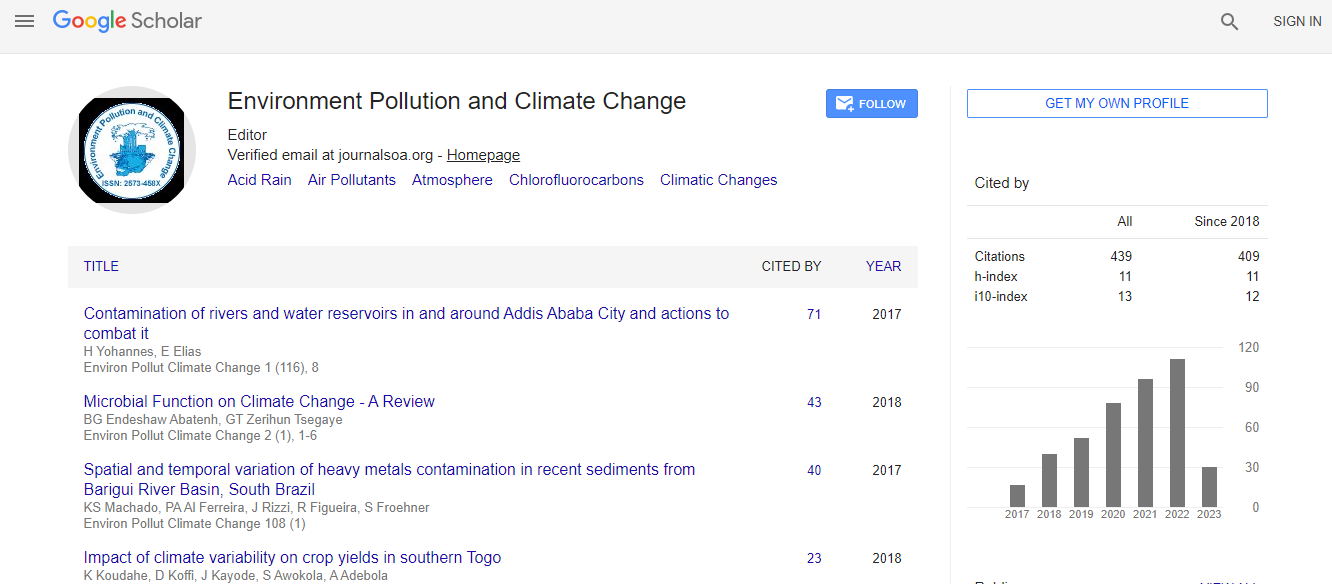
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 672
Environment Pollution and Climate Change received 672 citations as per Google Scholar report
Environment Pollution and Climate Change peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Share This Page
Population Status and Ecology of the Steno-Endemic Fairy Shrimp Chirocephalus sibyllae Cottarelli and Mura, 1975 Inhabiting a Mountain Temporary Pond (Central Italy)
Global Summit on Environmental Health
Maria Gaetana Barelli
University of Perugia, Italy
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Environ Pollut Climate Change
Abstract
High-elevation ephemeral waters are sentinels of climate change, as they quickly respond to decreasing precipitation levels and increasing air temperatures. Fairy shrimps are among the most threatened invertebrates in ephemeral waters, as they are extremely vulnerable to habitat loss. Chirocephalus sibyllae is a fairy shrimp endemic to the Palazzo Borghese temporary pond, located within Sibillini Mountains National Park (Central Italy). The aims of the present study were to: (i) evaluate the physicochemical characteristics of C. sibyllae habitat, with special reference to climate changes over twenty years; (ii) document the life history, size, and abundance of C. sibyllae; and (iii) document the coexisting zooplankton fauna in Palazzo Borghese pond. The zooplankton community was monitored fortnightly, during the filling phases of the pond, from April 2019 to June 2021, using an 80 �¼m mesh net, within transects of known length. On each sampling occasion, physicochemical parameters were measured, and water-level fluctuations and pond surface area were recorded. Compared to what was reported in the literature, in the last two years the wet phase of the Palazzo Borghese pond was shorter, and the pool dried up much earlier than in the past. The water quality was good and reflected the typical characteristics of high-mountain oligotrophic ponds. According to the extreme unpredictability of environmental features, the zooplankton community was composed of a very limited number of species, adapted to face drought conditions for most of the year. The year 2019 was configured as the season with the most favorable conditions for the development of C. sibyllae; in 2020, the short duration of the pond did not allow the species to complete its life cycle. Climate change seems to pose the main threat to the species, considering that the progressive increase in air temperatures and the decrease in snowfall will, likely, lead to increasingly shorter filling phases of its habitat.Biography
Barelli Maria Gaetana is a science professor at the G. Peano scientific high school in Monterotondo, Rome. He has participated since 2019 in the monitoring study of the Chirocephalus marchesonii Lago di Pilato Monti Sibillini and the Chirocephaus sibyllae Laghetto of Palazzo Borghese Monti Sibillini Italy, with the research group of the University of Perugia coordinated by Prof. Lorenzoni. You are the guide of the Sibillini National Park.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi