Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
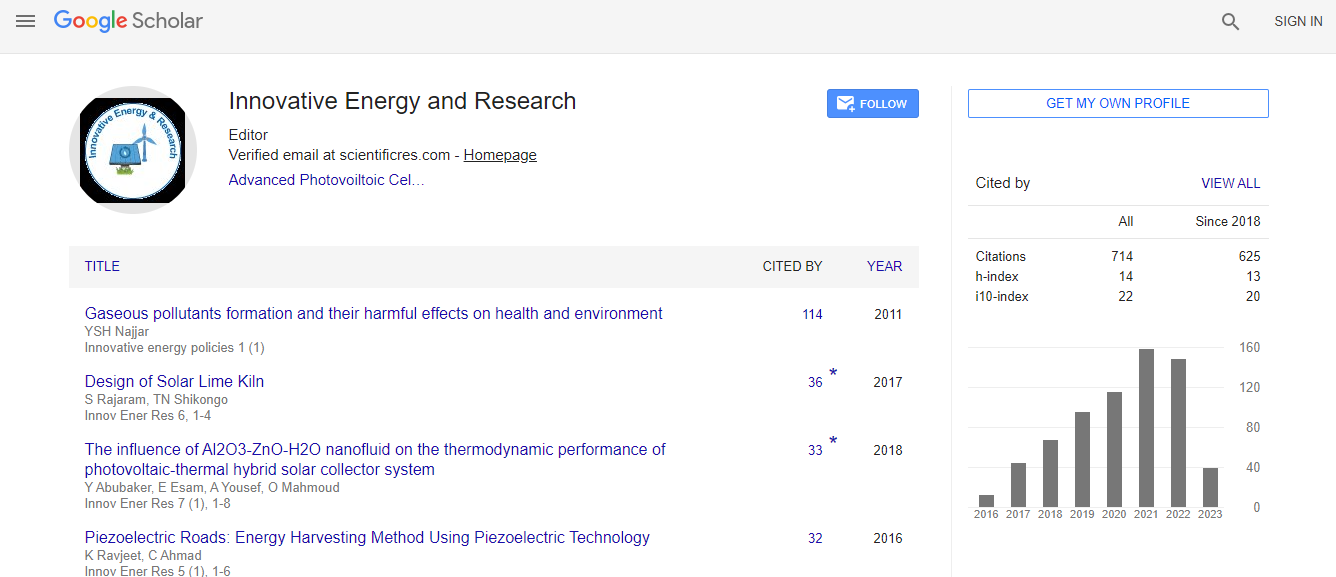
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Photoferroic (ZnSnO3) for photovoltaic applications
20th International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Manikandan Marimuthu and Mukilraj Thayanithi
Anna University, IndiaUniversity of Madras, India
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
In the recent decades, the field of renewable clean energy i.e., solar energy has emerged as an alternative to the traditional power sources. Solar energy is one of the most important resources which have been harvested through Photovoltaic (PV) effect. Photovoltaic effect typically involves two basic processes: generation of electron-hole pairs as and separation of electrons and holes. In semiconductor based solar cell, the generation and separation of electrons and holes usually takes place at a material interface and the maximum open-circuit voltage is equal to the semiconductor band gap. Since there is observation of bulk photovoltaic effect in the ferroelectric materials, the open-circuit voltages exceeds the band gap due to the separation of electron-hole pairs by the built-in potential induced by intrinsic polarization. The bulk photovoltaic effect has been reported in several ferroelectric perovskite oxides, such as Pb(Zr,Ti)O3, BaTiO3 and LiNbO3 family. These oxides have relatively large internal electric fields that could be exploited in photovoltaic applications. Hence, harvesting solar energy from ferroelectrics is still a new field of research and which grew considerable attention in the recent years. Therefore, the LiNbO3 type ZnSnO3 is prepared by hydrothermal method. The prepared ZnSnO3 is explored as photoanode in the solar device and the device performance is tested using I-V characteristics. The photo-physical properties are analyzed and explained using appropriate mechanisms. X-ray diffraction confirms the R3C symmetry of polar ZnSnO3 phase. Scanning electron micrograph shows an agglomeration of square shaped particles. Ferroelectric behaviour is confirmed by P-E loop tracer. Double semicircle, one in the low frequency and other in the relatively high frequency explains the charge transport characteristics between the interfaces of the fabricated device. An open circuit voltage of 0.64 V, a short circuit current density of 1.39 mA/cm2 and a conversion efficiency of 0.5% are obtained for the constructed device. These results show the potential value of ferroelectric ZnSnO3 for use in solar cells, although the efficiency cannot yet compete with semiconductor materials. An effort is hence put forth for the deep understanding on photovoltaic mechanisms in ferroelectric materials.Biography
E-mail: mani7289@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi