Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
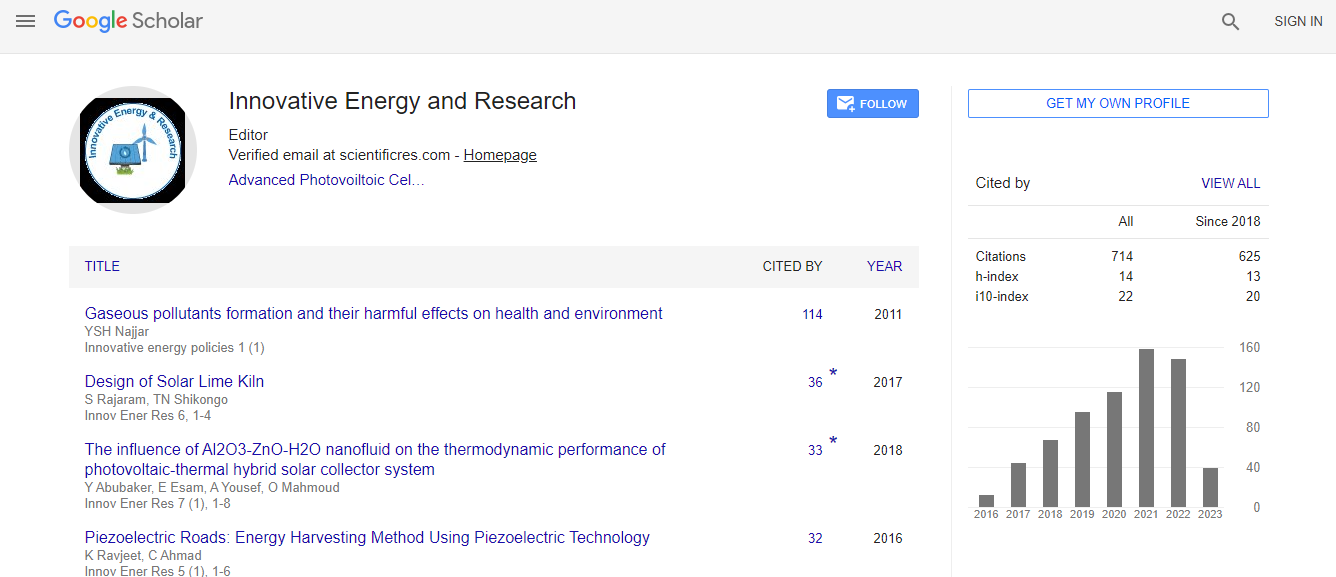
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Multi-striped orthogonal photon-photo carrier-propagation solar cells (MOP3SCs) with new asymmetric redirection waveguides
20th International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Akira Ishibashi
Research Institute for Electronic Science - Hokkaido University, Japan
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
In orthogonal photon-photo carrier propagation solar cell (MOP3SC), photons propagate in the direction orthogonal to that of the photo carriers. Photons being absorbed in the direction vertical to that of the carrier drift/diffusion, tradeoff between photon absorption and carrier collection can be lifted. We can set the stripe-width large enough to absorb all the photons keeping the distance between the p/n electrode distance (= semiconductors layer thickness) short enough to allow most of photo carriers to reach out to the contact metals. Further, by placing those multiple semiconductor stripes, neighboring to each other, with different band-gaps in such an order that the incoming photons first encounter the widest gap semiconductor, then medium-gap ones, and the narrowest at last, we can convert the whole solar spectrum into electricity resulting in high conversion efficiency. The multi-striped solar cell structure is placed at the edge of redirection waveguide in which 3D-propagation photons are redirected to be 2D photons propagating in the waveguide. The waveguide-coupled MOP3SC serves as a concentration photovoltaic system typically operating under a few hundreds to a thousand suns. Using an integrated-paraboloid-sheet as the first layer of the redirection waveguide, we can make the daytime sunlight virtually impinge the rest of the waveguide structure at a right angle. Further, asymmetric waveguide-coupled MOP3SC serves as a highly efficient concentration photovoltaic system thanks to the low temperature rise due to the minimal thermal dissipation and the diffusive light convertibility thanks to the integrated-paraboloid-sheet. The system is also of interest as a high reliability system, because those photons that can damage the bonding of the materials, being converted into electricity already at upstream, never go into the medium or narrow gap semiconductors. Thus, the asymmetric waveguide-coupled MOP3SC would serve as an ultimate high efficiency all-in-one system in the near future. Recent Publications 1. Ishibashi A, White S, Kawaguchi N, Kondo K and Kasai T (2016) Edge-illumination scheme for multi-striped orthogonal photon-photo carrier - propagation solar cells, Int. J. Eng. Tech. Res. 6(1):115-117. 2. Ishibashi A, Kobayashi H, Taniguchi T, Kondo K and Kasai T (2016) Optical simulation for multi-striped orthogonal photon - photo carrier-propagation solar cell (MOP3SC) with redirection waveguide. 3D Research 7:33. 3. Ishibashi A (2016) Orthogonal photon-photo carrier - propagation solar cells, (in Japanese) Energy Devices 3(4): pp. 77-83.Biography
Akira Ishibashi received the BSc, MSc and PhD degrees in Physics in 1981, 1983, and 1990, respectively, all from the University of Tokyo, Japan. During 1982–1983, he was a Research Assistant at LBNL, Berkeley, USA. In 1983, he joined the Research Center of Sony Corporation, Yokohama. He was a Visiting Faculty at Loomis Laboratory, Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1990-1991. In Sony he achieved world-first RT CW operation of blue/green laser diodes using ZnMgSSe, in 1993. He was a Visiting Professor at Center for Interdisciplinary Research, Tohoku University, Japan in 1998. Since 2003 he has been a full Professor in leading Nanostructure Physics Lab in RIES, Hokkaido University, Japan. In 2006, he started Hokkaido University Venture Company, C’sTEC Corp., based on Clean Unit System Platform (CUSP). His main target is to realize high-efficiency solar cells exploiting CUSP that helps people live in a high standard.
E-mail: i-akira@es.hokudai.ac.jp

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi