Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
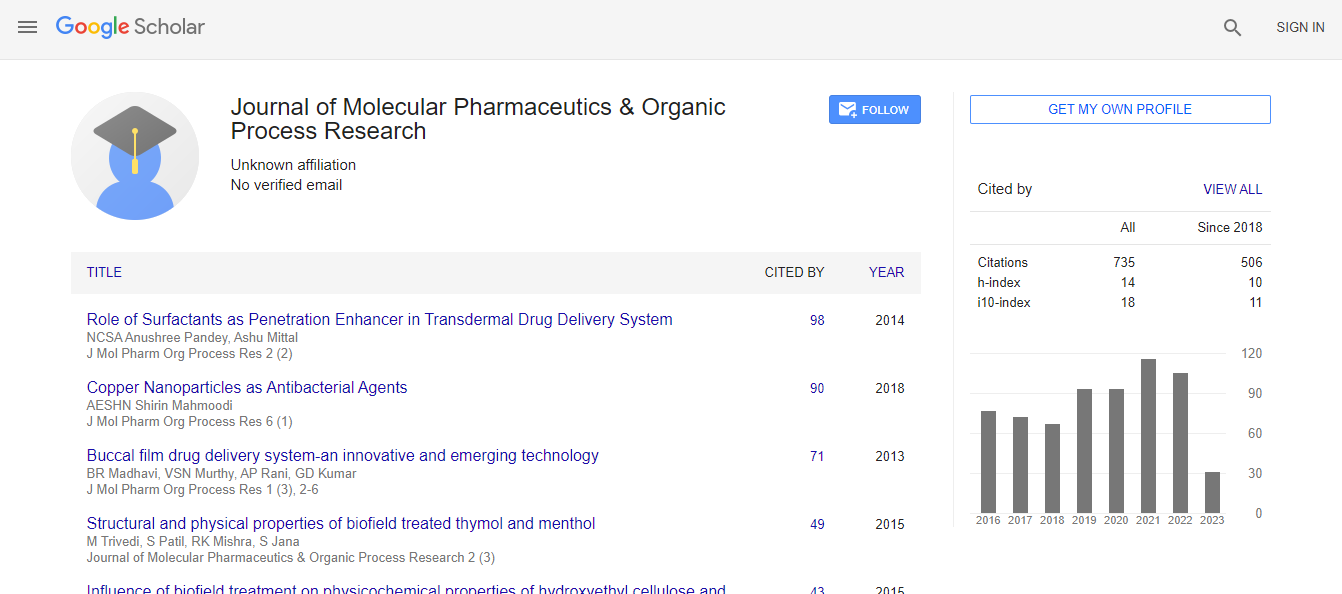
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1057
Journal of Molecular Pharmaceutics & Organic Process Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Academic Keys
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Share This Page
Medication dosing and body weight
2nd International Conference on Pharmaceutical Formulations and API
Maha A. AlMolaiki
King Abdulaziz Medical City-Central Region-Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs, Saudi Arabia
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Mol Parm Org Process Res
Abstract
Patient's weight is a crucial consideration in medication dosage since the size of the body affects the concentration of the drug in body fluids and at the site of action. Dose calculation based on body weight became standard for certain medications dosing. Dosing based on patient├ó┬?┬?s specific weight makes the drug quantity administered specific to the patient being treated. When a drug is absorbed into the bloodstream, it is rapidly circulated through the body. Blood is circulated for about one minute on average. As the blood recirculates, the drug moves from the bloodstream into the body├ó┬?┬?s tissues for example: fat, muscle, and brain tissue. Once absorbed, most drugs do not spread equally throughout the body. In the body, water soluble drugs tends to stay within the blood and surrounding tissues, while fat soluble drugs tend to concentrate in fatty tissues. Other drugs concentrate mainly in only one small part of the body for example: iodine concentrates mainly in the thyroid gland; because the tissues have a special attraction for affinity and the ability to retain that drug. Factors Affecting Drug distribution are plasma protein binding, physicochemical properties of the medication (lipophilicity, hydrophilicity), tissue blood flow and membrane transporters. Body composition in a normal body weight and obese patients, 20% from normal body weight is adipose weight and 80% lean weight, however, 40% from obese patient weight is adipose tissue and 60% is lean weight. Hydrophilic drugs excreted by renal clearance, has low volume of distribution, low Intracellular penetration and high extracellular distribution in comparison to lipophilic drugs that are excreted by hepatic clearance has high volume of distribution, high Intracellular penetration and low extracellular distribution.Biography
Maha A. AlMolaiki, B.Sc., Pharm.D, SSC-PhP-IMP, Internal Medicine Clinical Pharmacist, Pharmaceutical Care Services, King Abdulaziz Medical City, Ministry of National Guard Health Affairs, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, Department of Pharmacy Practice, College of Pharmacy, King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi