Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
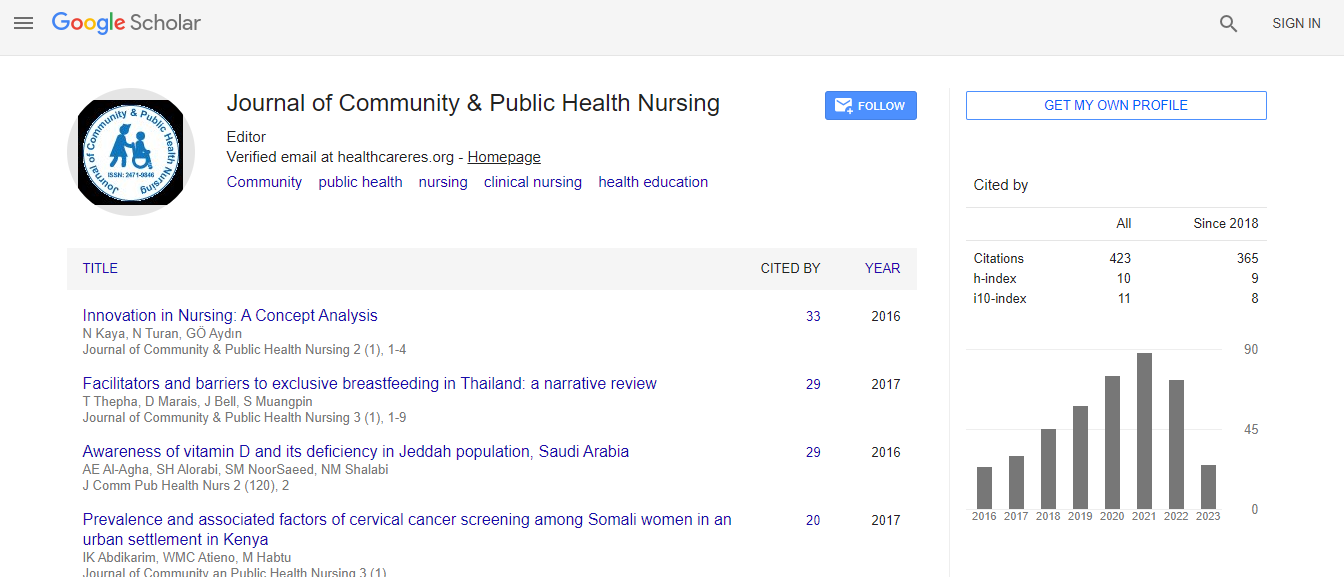
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 739
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Medical staff facing covid-19 disease at the university clinics of Lubumbashi in Dr Congo 2021
World Nursing Congress
Mbutshu Lukuke Hendrick
School of Public Health, University of Lubumbashi, Democratic Republic of Congo
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nurs
Abstract
Abstract Over the past 20 years, the world has experienced several outbreaks of infectious diseases characterized by high speed of transmission, such as a currently with the infectious disease outbreak called COVID-19. This study aimed to determine the prevalence of COVID-19 among healthcare workers; to describe the means of prevention used by these nursing staff and to determine the behavior and attitude towards the disease of these nursing staff of the University Clinics of Lubumbashi. Methods This is a descriptive cross-sectional study from January 1, 2021 to June 31, 2021 among all healthcare providers (doctors and nurses) working at the University Clinics of Lubumbashi. Results Out of 391 caregivers surveyed, including 246 doctors and 145 nurses, we observed a prevalence of 10.99% that is43 caregivers, including 28 doctors, i.e. 65.12% and 15 Nurses or 34.88% whose average age was 40 √?¬Ī6 years, with a predominance of men (56%)that is sex ratio of 1.26 in favor of men. It is important to note that Most cases were diagnose clinically, i.e. 62.79% of cases.The saliva droplets were the mode of contamination of Covid-19the Most experienced by caregivers with 58.14%, followed by physical contact with a rat√?¬© of 39.53%. The wearing of mask and hydro-alcoholic friction were the most cited by caregivers as the most effective means of prevention, which they applied and advised patients. Most of the caregivers were subjected to chloroquine and azythromycin, the others admitted to using the traditional treatment of inhaling the vapors of several wild leaves and trees, in particular: lemon, Mango Is about the out come of the disease, almost -all of the nursing staff were cured, i.e. 97.67% of cases. Conclusion The prevalence of covid-19 disease among caregivers was 10.99%, however it is observed that active screening was not carried out and the cases observed presented almost all of the clinical signs and the clinical diagnosis was used for all cases, hence its under estimation. It would be important to regularly screen exposed caregivers and make personal protective Equipment regularly available and monitor barrier measures. Keywords: Pr√?¬©valence, Nursing Staff, Covid-19.Biography
Mbutshu Lukuke Hendrick completed his doctorate at the age of 47 years at Lubumbashi University, where he is Associate Professor of hospital hygiene at the Public Health School of the same university. He has published more than 25 articles in Pan African, Asian, European and American journals.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi