Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
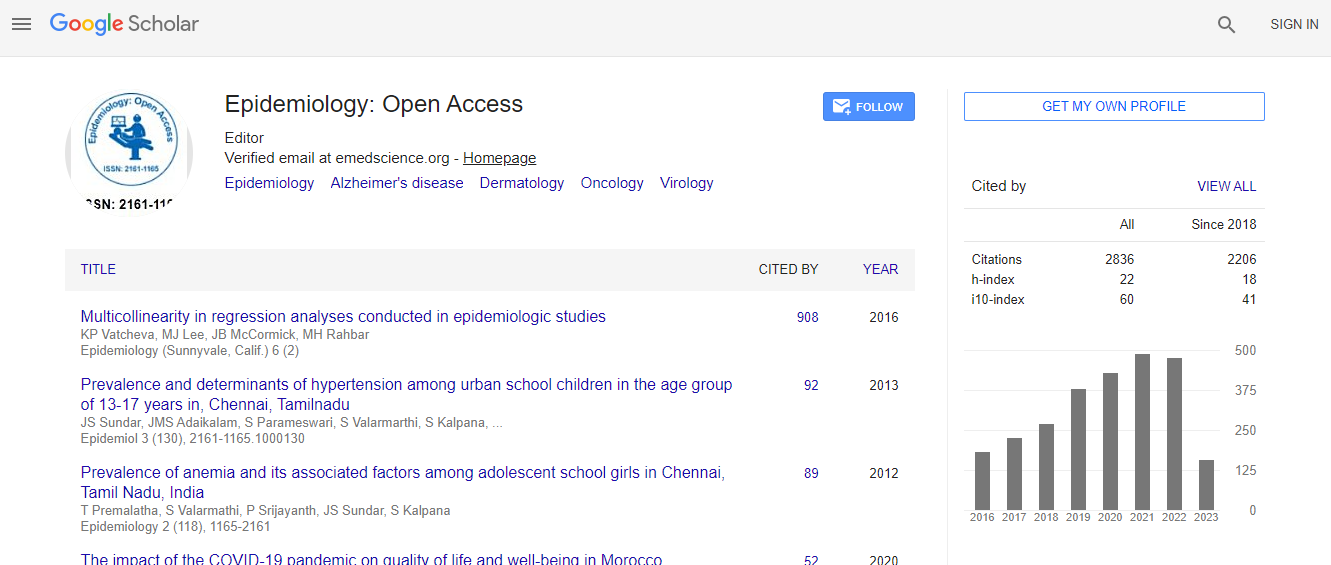
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Measuring the multidimensions of symptoms in people with advanced stages of chronic kidney disease
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Hayfa Almutary1, 2, 3, Ann Bonner1, 3, 4 and Clint Douglas1
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is increasing globally and in Saudi Arabia it affects approximately 8% annual increment of
dialysis population. It is associated with a high symptom burden. Previous studies have largely reported on the prevalence
of symptoms only in the haemodialysis population. This study examined symptom burden across disease stages and treatment
groups in advanced CKD, and their correlation with demographic and clinical factors. Using a cross-sectional design, a
convenience sample of 436 patients with CKD was recruited from three hospitals in Saudi Arabia. The CKD Symptom Burden
Index (CKD-SBI) was used to measure 32 CKD symptoms. Demographic and clinical data were also collected. Of the sample
75.5% were receiving dialysis (haemodialysis, n = 287; peritoneal dialysis, n = 42) and 24.5% were non-dialysis (CKD stage 4,
n = 69; CKD stage 5, n = 38). Average symptom reported was 13.01 ± 7.67. Fatigue and pain were common and burdensome
across all symptom dimensions.Approximately one-third of participants experienced sexual symptoms. Dialysis patients
reported greater symptom burden, especially patients on haemodialysis. Haemodialysis treatment, older age and being female
were independently associated with greater total symptom burden. In conclusion, symptom burden is high among advanced
stages of CKD, particularly among those receiving dialysis. Although fatigue, pain and sexual dysfunction are key contributors
to symptom burden in CKD, these symptoms are often under-recognised and warrant routine assessment. The CKD-SBI offers
a valuable tool to assess symptom burden, leading to the commencement of timely and appropriate interventions.
Biography
Hayfa Almutary has over 12 years’ experience as a registered nurse. She has a master degree of acute care nursing from Queensland University of Technology
(QUT), Australia and Bachelor degree of nursing from King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. She is a Lecturer in nursing school at King Abdulaziz
University. Currently she is a PhD candidate in the School of Nursing at QUT, Australia. Her research of interest is symptom assessment and management in
chronic kidney disease. The primary focus of her PhD research is to explore symptom clusters in advanced stages of CKD in order to improve the quality of
symptom assessment and management among CKD patients. She has three published articles in this field. In addition, one conference paper was presented at the
Renal Society of Australasia Annual Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 2014.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi