Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
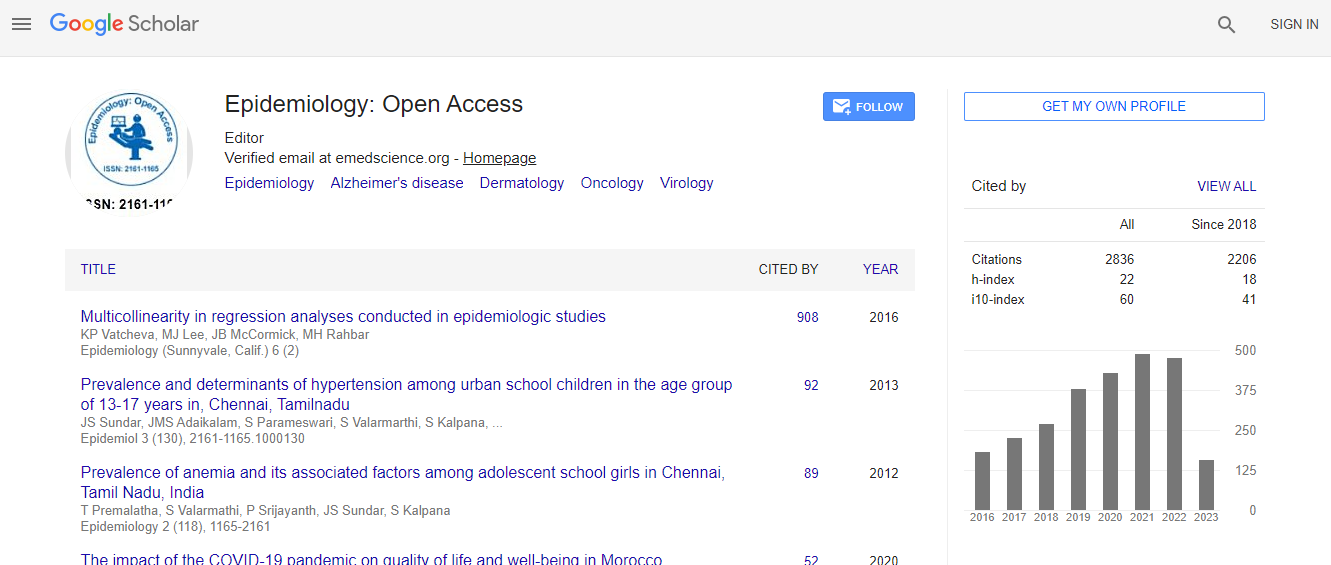
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Marginal models for meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy studies in frequentist and Bayesian framework using rstan and CopulaREMADA
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Nyawira Nyaga Victoria
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Current statistical procedures implemented in general software packages for pooling of diagnostic test accuracy data include
hSROC (Rutter and Gatsonis 2001) regression and the bivariate normal model(BRMA) (Reitsma et al. (2005), Arends
(2006) and Chu and Cole (2006)). However, these models do not report the overall mean. The hSROC model is less intuitive
and therefore less popular while the bivariate normal model has difficulties estimating the correlation parameter when the
number studies in the meta-analysis are small and/or when the between-study variances are relatively large. As a result, the
between study variance estimates from the BRMA are upwardly biased as they are inflated to compensate for the restriction
on correlation parameter (Riley et al 2007). We present advanced statistical methods for meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy
studies and demonstrate the use of different software packages in R or with an R interface together with code, to apply different
model strategies for obtaining appropriate meta-analytic parameter estimates. The focus is on the joint modelling of sensitivity
and specificity using copulas as well as using the concept of sharing random components. To illustrate the methods, we used
classical example of Glas et al.(2003) on diagnostic accuracy of telomerase as urinary tumour marker for diagnosing primary
bladder cancer and a second dataset from a systematic review by Arbyn et al.(2013) that aimed at comparing sensitivity and
specificity of human papillomavirus testing versus repeat cytology for triage of minor cytological cervical lesions.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi