Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
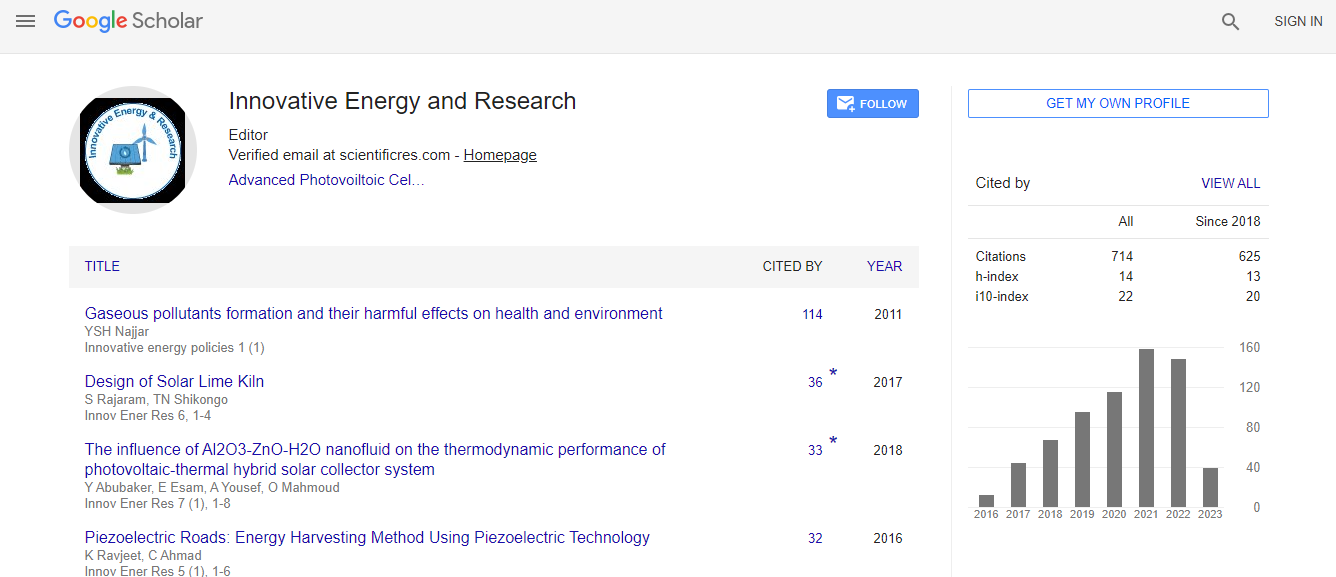
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Magnetic instability in heavily n-doped Fe-based full Heusler compounds: Origin and impact on thermoelectric properties
21st International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Fabio Ricci, Sebastien Lemal, Matthieu J Verstraete and Philippe Ghosez
University of Liege, Belgium
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
Fe2YZ full Heusler compounds, on which first principles on density functional theory (DFT) simulations predict very large thermoelectric power factor (PF), are promising candidates for thermoelectric applications. The building blocks of their interesting thermoelectric properties are the carriers belonging to the Fe-eg orbitals that can be opportunely engineered to maximize PF. These anti-bonding states are represented by a flat band (mainly composed of Fe dx2-y2 character) along the ΓX direction of the Brillouin Zone, related to the highly directional Fe- Fe bond, becoming dispersive along the other directions. This band satisfies the “flat-and-dispersive” requirements proposed by Mahan and Sofo and leads to one-dimensional transport strongly enhancing the PF. However, due to its strongly localized nature, explicit n-doping may induce a Stoner instability driving the system to a half-metallic phase. The present study, performed through DFT using both hybrid functional and GGA+U methods on Fe2YZ1- xAx (Y = Ti, V, Nb, Ta, Z=Al, Si, Sn, Ga and A=Si, P, Sb, Ge) n-doped systems, shows that the appearance of such a magnetic phase is strictly linked to the Fe-eg and Y-site eg orbital hybridization and that it possesses a pure electronic origin, independent on the dopant species. Although the Stoner instability can provide half-metallicity with coupled thermomagnetic responses, the PF is typically reduced in the half-metallic phase due to a reduction of the number of carriers available at the Fermi level. In certain cases, however, the values of the PF are still large (for Fe2TaGa1-xGex or Fe2TiSi1-xPx PF is between 9 and 15 10-3 W K-2 m-1 at 600 K, for example) which stays promising for thermoelectric applications. Going further, we elucidate the possibility to exploit the broader nature of 4d and 5d orbitals at the bottom of the conduction band to overcome the magnetic phase appearance in the doping range of interest.Biography
Fabio Ricci did his PhD on both simulations and experimental measurements on magnetic properties of materials (diluted magnetic semiconductors and soft magnetic materials) by means of the magneto-optical Kerr effect. Subsequently, he worked on theoretical simulations on Fe-based superconductors, principally iron-chalcogenides. He developed and implemented in the ABINIT code the formalism for the non-collinear magnetism in the density functional perturbation theory and, at the same time, started to work on the theoretical engineering of thermoelectric properties of the Fe-based full-Heusler compounds.
E-mail: fabio.ricci@uliege.be

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi