Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
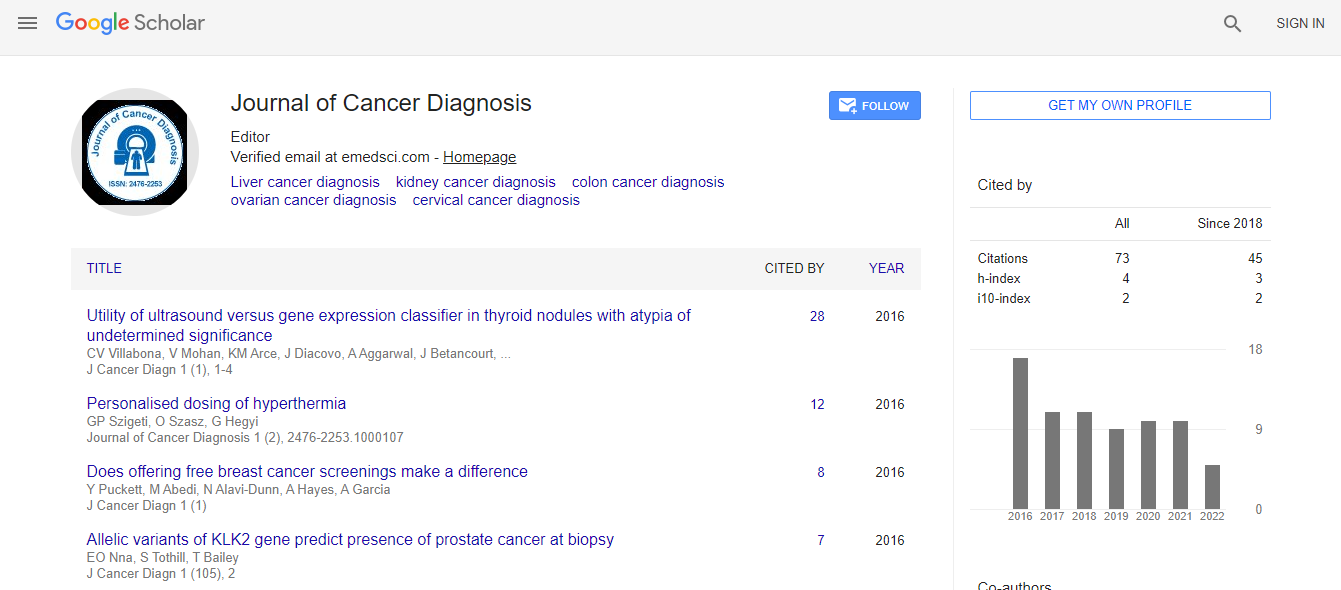
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 95
Journal of Cancer Diagnosis received 95 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Long-term efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma refractory or unsuitable for other therapeutic modalities
Joint Event on International Conference on Cancer Research & Diagnostics & 16th Asia Pacific Biotechnology Congress
Sang Youn Hwang, Seon-Mi Lee, Ki-Jung Jeon, Jung Woo Im, Sang Bu Ahn, Eun Kyeong Ji, Cheol Won Choi and Gwang Mo Yang
Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Republic of Korea
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Cancer Diagn
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to evaluate long-term efficacy and safety of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) for the naive or salvage treatment of inoperable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) were unsuitable for other therapeutic options. Method: The authors reviewed the medical records of 58 patients that were treated by SBRT in our institution when they had HCC without another standard treatment option or complete response of loco-regional therapy between August 2010 and October 2015. All patients SBRT dosages (24-60 Gy from two to eight fractions) were administered according to tumor volume. Survival, response and toxicities were evaluated. Response evaluation was performed according to modified response evaluation criteria for solid tumors. Result: 11 patients were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer A, 25 patients were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer B, 22 patients were Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer C stage. 50 patients had Child-Pugh Class A disease, 8 patients had Class B disease. 26 patients had macrovascular invasion (14 portal vein thrombosis, 4 hepatic vein thrombosis, 8 both venous thrombosis), 3 patients had bile duct invasion. The median greatest tumor dimension was 30 mm (range, 8-170 mm). 49 patients (84.5%) achieved complete response (47 patients within 6 months and 2 patients between 6 and 12 months after complete SBRT), 4 patients (6.9%) had a partial response, 4 patients (6.9%) had stable disease and 1 (1.7%) patient had progression disease. Infield local recurrence was observed in 7 patients (12.1%) and outfield intrahepatic failure was 29 patients (50%) and extrahepatic metastasis was 14 patients (24.1%). The median Overall Survival (OS) was 23 months (range 3-60 months) and the median Progression-Free Survival (PFS) was 7 months (range 1-43 months). Especially 29 patients (50%) have the median OS over 24 months and the median OS of 18 patients with median PFS over 12 months was 35 months (range 18-50 months). Three patients (5.2%) experienced grade 3 gastrointestinal toxicity, 1 patients (1.7%) experienced grade 4 gastric ulcer perforation and 4 patients (6.9%) experienced mild pneumonitis and 1 patient (1.7%) experienced burn requiring skin graft. Three patients (5.2%) experienced grade 3 hepatotoxicity. Conclusion: Our study suggests that SBRT can be effective and safe modality that achieves promising rates of long-term local control and survival in HCC refractory or unsuitable for other therapeutic options, even with vascular or bile duct invasion. A further well controlled, large scaled study to reduce toxicity (especially gastrointestinal and pulmonary and hepatic toxicity) is recommended.Biography
Sang Youn Hwang is currently affiliated to the Department of Internal Medicine and Gastrointestinal Cancer Centre in Dongnam Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences, Republic of Korea.
E-mail: mongmani@hanmail.net

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi