Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
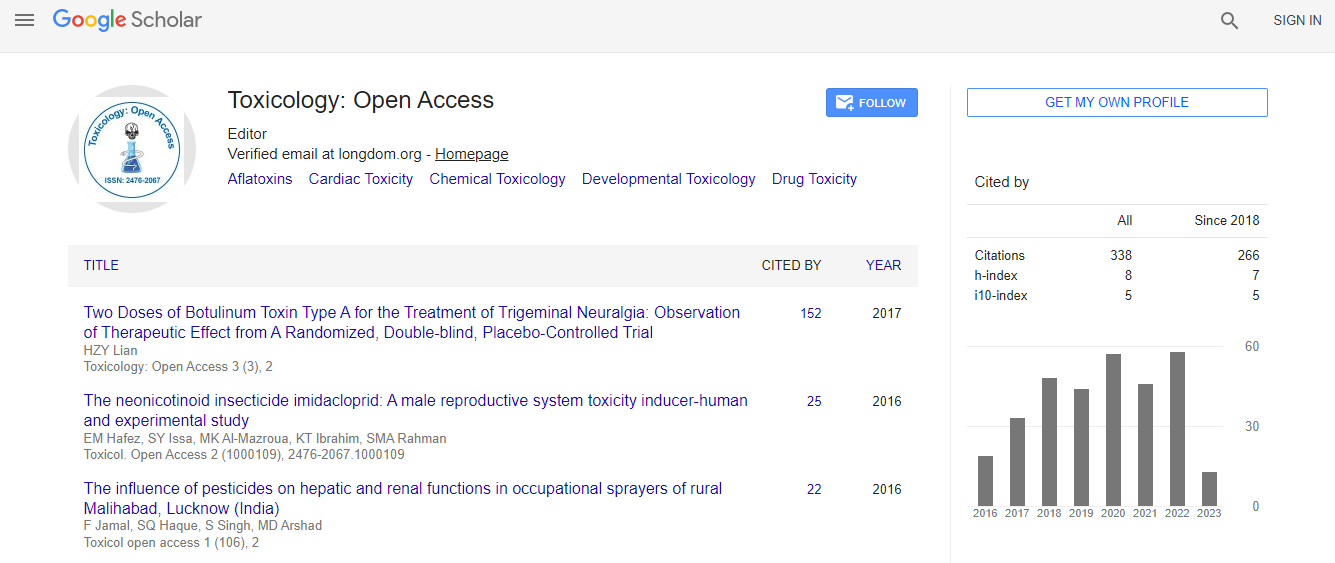
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 336
Toxicology: Open Access received 336 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Investigating brain tissue damage following respiratory contact with carbon nanotubes in rat using isolated lung mitochondria
20th World Congress on Toxicology and Pharmacology
Fatemeh Samiei and Jalal Pourahmad Jaktaji
Iran University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Toxicol Open Access
Abstract
Objective: The main aim of this study is to investigate the lung toxicity following the respiratory contact with Multi-Wall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs) in male Wistar rats.Method: Rats were exposed to 5 mg/m3 MWCNT aerosol in different size and purity for 5 hours/day, 5 days/week for 2 weeks in a whole-body exposure chamber. After two weeks exposure, the rats of all groups was necropsied the animals lungs were removed. Then we separated the left and right lungs and mitochondria of them were isolated and parameters of mitochondrial toxicity including mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase (complex II) activity, generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) collapse, mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release were evaluated.
Result: Our results demonstrated that MWCNTs with different characteristics, in size and purity, significantly (P<0.05) decreased mitochondrial succinate dehydrogenase activity and mitochondrial ROS production. Induced mitochondrial swelling, MMP collapse and cytochrome c release mitochondria and right lung had seen more damage.
Conclusion: We concluded that MWCNTs with different characteristics, in size and purity because damage in varying degrees on the mitochondrial respiratory chain and induce ROS mediated cytotoxicity by directly targeting mitochondria lung tissue. It seems that the right lung has been more damaged due to the larger size of the left lung.
Biography
E-mail: fh.samiei@yahoo.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi