Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
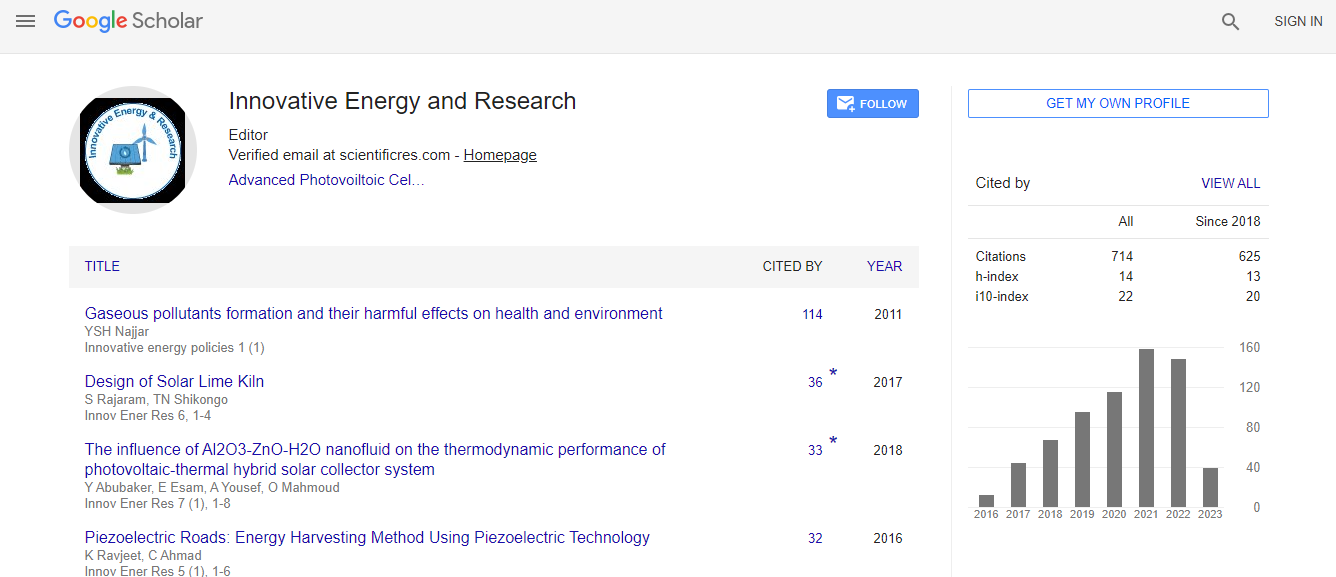
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Interfacial energy materials for flexible, safe batteries: Gummy electrolyte and gummy binder
21st International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
W H Katie Zhong
Washington State University, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
Two conformable interfacial energy materials have been designed and fabricated for battery applications, i.e. gummy electrolyte and gummy binder with a chewing gum-like appearance (thereafter called “gummy” material). Electrolytes play a very important role for battery safety and performance. The gummy electrolyte was demonstrated with beneficial properties, such as high ionic conductivity (liquid electrolyte level), good mechanical properties (solid materials level), and strong adhesion (adhesive level), as well as safety characteristics providing thermal protection for batteries. The other interfacial energy material, the gummy binder, is a dual-conductive adhesive for fabricating high performance battery electrodes. The primary function of conventional electrode binders is “binding” particles in electrodes without directly contributing to the performance of electrodes/batteries, as they cannot conduct electrons and/or ions. The gummy binder possesses high ionic and electronic conductivities, strong adhesion and appropriate mechanical/rheological properties, as well as excellent conformability and processibility. As it is a dual-conductive adhesive, the gummy binder is an effective solution to address the issues that are relevant to the interface weakness and structural instability. Firstly, the adhesive electrode matrix being the continuous phase can provide stable structures and “robust” interfaces via strong adhesion with the active electrode particles (the filler phase). The results enhance the durability of the electrodes and thus the batteries. Secondly, the continuous phase with uniform conductive interfaces provides the base for dual conductive functions (for both ions and electrons) inside the electrodes. Therefore, with such a matrix material, “robust” interfaces, which are defined as stable with high interfacial adhesion and good conductive properties for ion/electron transfer, can be built inside the electrodes. Thirdly, the gummy binder as the conductive continuous phase can also promote heating transport/releasement, thus the safety of the batteries can be improved.Biography
E-mail: Katie_zhong@wsu.edu

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi