Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
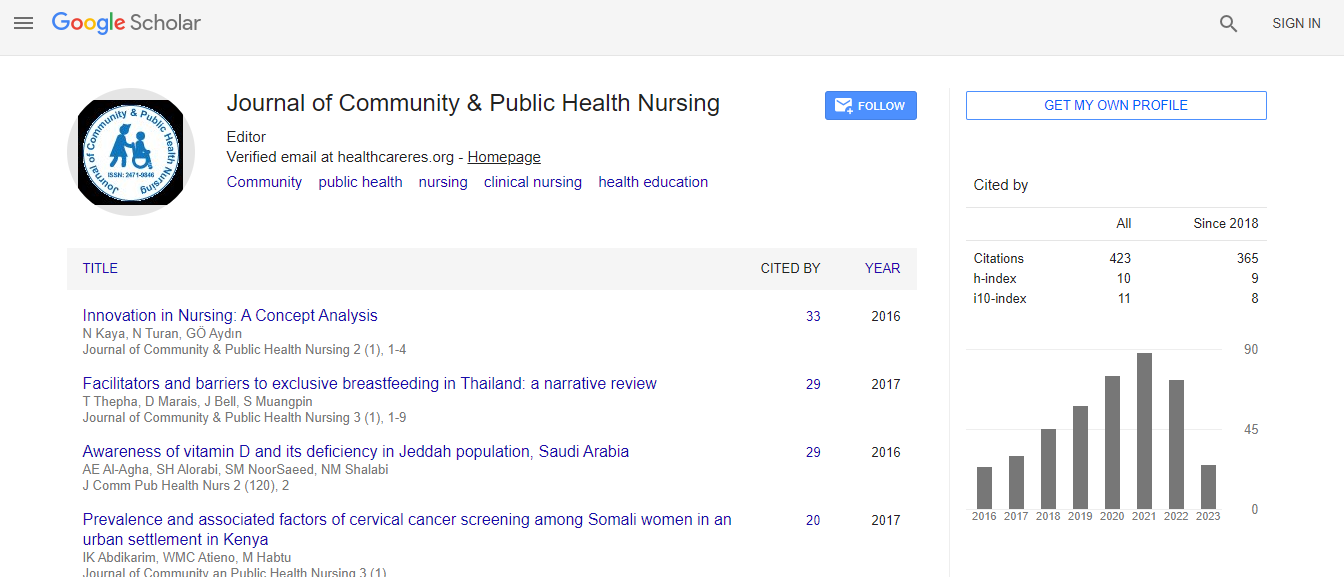
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 739
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Influence of burnout in nurses on patient safety
5th World Congress on Patient Safety, Health Care and Well-being
Dr. Hulya Kocyigit
Sivas Cumhuriyet University, Turkey
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nurs
Abstract
Providing the highest level of patient safety is one of the basic requirements for increasing the quality of nursing care. However, in addition to various factors such as ineffective communication and teamwork, unsuccessful organizational processes and the physical and psychological overload of professionals, the burnout in nurses over time jeopardizes patient safety. There is a relationship between burnout and patient safety based on the work process, personal characteristics, and teamwork. High levels of burnout are associated with external factors such as excessive workload, long working hours, and interpersonal relationships. Professional fatigue, which is one of the most important causes of burnout, negatively affects patient safety. Workload is cited as a determining factor for professional fatigue. Specifically, for healthcare professionals with high burnout rates, high hourly loads had a strong negative impact on patient safety. Higher burnout levels also lead to increased medical errors, patient dissatisfaction, and patient and family complaints. This situation can be explained by emotional fatigue and depersonalization, which triggers the feeling of exhaustion and cynicism in nurses as health professionals, acts distant and cold in the face of patient's needs, and reduces the quality of care. Nurses with little experience have problems with the medical level hierarchy, with nurses and managers who have more years of experience or leadership positions in the service, as well as doctors, and this situation paves the way for them to experience burnout. In this respect, teamwork, which is not based on hierarchy, prevents the development of burnout in nurses and, accordingly, behaviors that will harm patient safety. As part of health professionals who are open to communication, have management support, and fulfill their duties with professional suitability, mutual learning, and teamwork, nurses are likely to feel productive and satisfied and therefore less likely to develop burnout. On the other hand, the development of burnout may result from the lack of a patient safety culture. Burnout can be prevented by developing a positive safety culture towards the patient and providing problem-solving and coping with stressful situations. In addition, burnout of nurses can be prevented by in-service training, using evidencebased clinical practice guidelines, improving technologies used in the service, better working conditions, continuous guidance on infection prevention methods, and better psychological and emotional support to health professionals. In conclusion, preventing burnout in nurses is an important strategy to increase patient safety.Biography
Hulya Kocyigit is currently working as Research Assistant at the Sivas Cumhuriyet Universty. She graduated a doctoral program in the Department of Nursing at the same universty in 2022. She is working on catheter-associated urinary system infections, simulation applications in nursing education, comfort theory ect.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi