Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
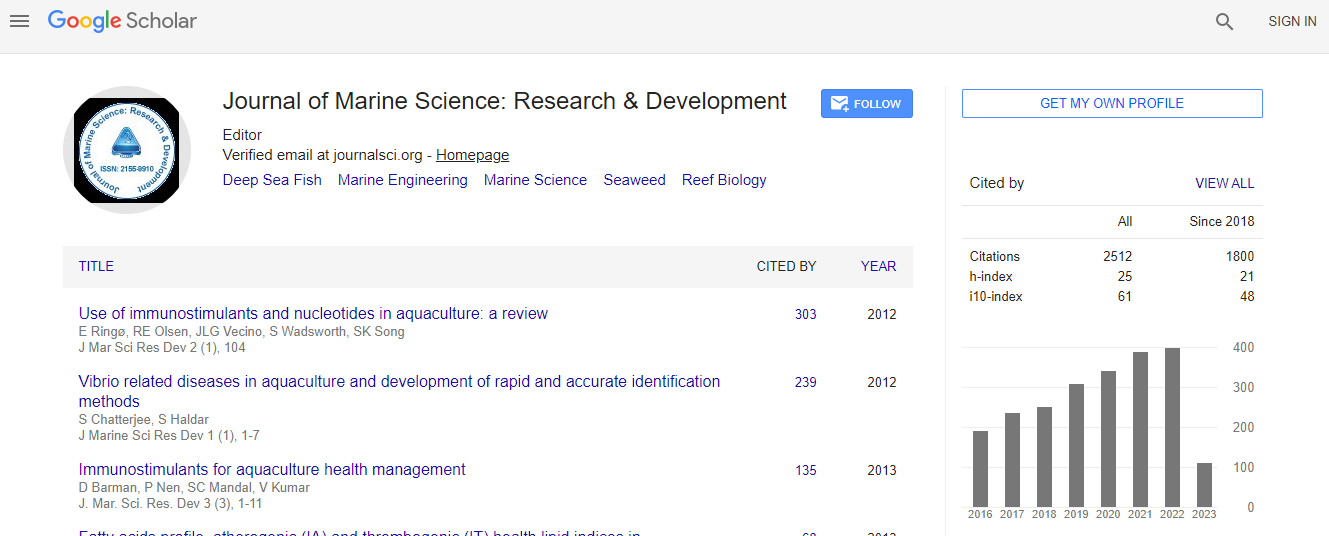
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Hydrodynamic studies of the Vellar estuary, southeast coast of India
4th International Conference on Oceanography & Marine Biology
Mugilarasan M, Venkatachalapthy R and Veerasingam S
Annamalai University, India
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Marine Sci Res Dev
Abstract
Vellar estuary is one of the most prominent and best studied estuary of India in terms of its chemistry and biology, but less studied in terms of its hydrodynamics. In this study, a 2D closed grid high resolution bathymetry was developed using ODOM hydrotrac single beam echo-sounder. Wind, wave, tide and current parameters were measured in upper, middle and lower estuary of the Vellar estuary during southwest monsoon. The tidal signals were analyzed for major harmonic tidal constituents using MIKE-21. A 2D hydrodynamic model was developed with sophisticated software MIKE-21. The depth of the estuary ranged between 0.295 m and 18.235 m with an average of 4.435 m. The maximum wind speed was measured 10 knots and the predominant wave direction was SSW due to the south-westerly wind. The values of wave energy density varied between 0.18 and 1.41 J/m2 and it is relatively high, because the wave action was high during southwest monsoon. Form numbers calculated from the major tidal constituents conformed that the tidal pattern of the Vellar estuary is semi-diurnal. The current speed decreased from the upper estuary to lower estuary. Bottom friction in the Vellar estuary strongly affects the speed of the currents. Hydrodynamic model results show the evolution of the tidal currents over both the incoming and outgoing tides during spring and neap simulations. The hydrodynamic model calibration and validation illustrate the model is capable of accurately predict the hydrodynamics of the Vellar estuary.Biography
Email: mugilarasan.ost@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi