Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
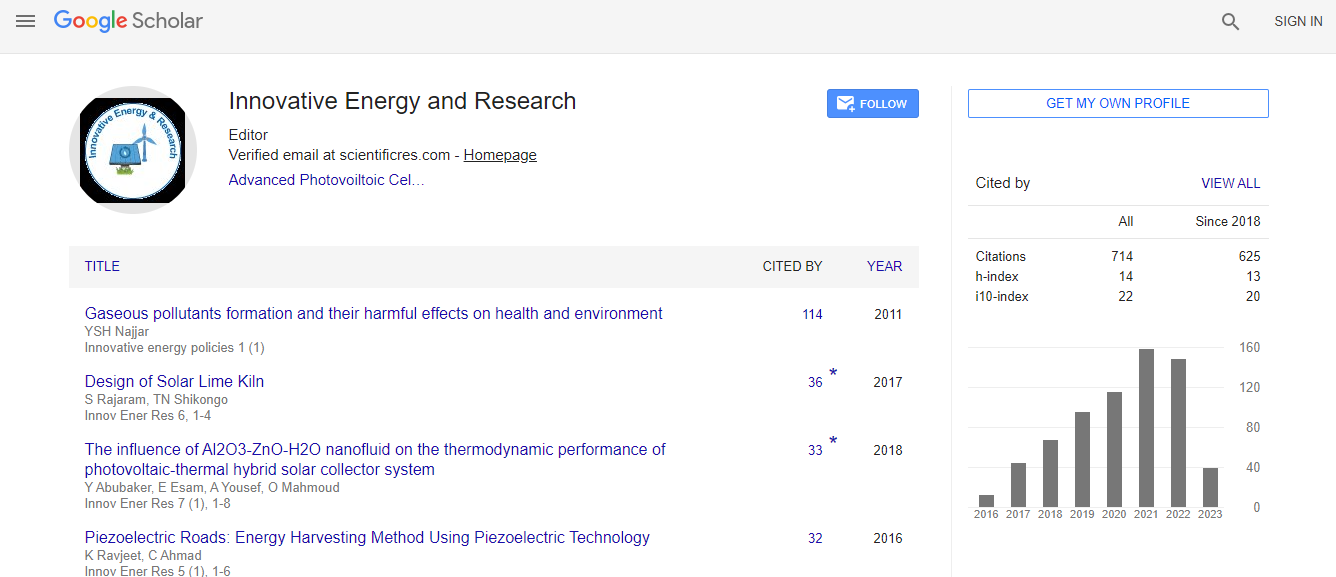
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Highly efficient nano composite electrolyte for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells under room light conditions
Joint Event on 2nd International Conference on Renewable Energy and Resources & Energy Materials and Fuel Cell Research
Shanmuganathan Venkatesan, Chiao-wei Li, I-Ping Liu and Yuh-Lang Lee
National Cheng Kung University, Taiwan
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
Statement of the problem: Dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) are a promising technology owing to their high-power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) under room light conditions and low manufacturing cost with respect to conventional silicon solar cells. Nowadays, the internet of things (IoT) is attracting worldwide technological interest because it delineates associations between various small devices. However, the problems related to power these devices have become significant. Among the several power supply systems, indoor DSSCs will be the most promising for a continuous power supply to IoT devices. In the literature, only a few studies have been reported about the performance of liquid-state DSSCs using iodide electrolytes under room-light conditions. Since relatively few electrons are excited, the recombination of the excited electrons with electrolytes strongly affects the open circuit voltage (Voc) of the DSSCs. In addition, because of the notable decrease in excited holes, less iodide will be required to minimize the holes. These two effects significantly decrease the performance of DSSCs under room light illumination. Methodology: To solve these problems, in this study, new nanocomposite electrolytes (NCEs) were prepared by mixing various metal oxides nanofillers (NFs) and cobalt poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) polymer gel electrolytes (PGEs). These NCEs were utilized to fabricate the quasi-solid-state DSSCs (QS-DSSCs). The performance of QS-DSSCs using MK-2 dye under 200 lux was studied and compared. Findings: The PCE (20.11%) of the QS-DSSCs using 4 wt% ZnO NFs was higher than those of the liquid version (18.91%) and other DSSCs. This was mainly due to the decrease in the capacitance and increase in the recombination resistance of the QSDSSCs using ZnO NFs that contributed to the high Voc of the related DSSC. This cell showed stable, long-term PCE at room temperature (~1000 h). Conclusion: The ZnO/PVDF-HFP NCEs were proven to be efficient and stable for preparing high-performance indoor QSDSSCs.Biography
S Venkatesan received his PhD degree (2009) in chemistry from National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan. He has expertise in preparation, characterization, and utilization of polymer-supported catalysts for efficient and selective organic functional group transformations in the presence of oxygen. He has been utilized these catalysts for the preparation of various chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical sensor and battery applications. In recent years, he has been focused on the fabrication of outdoor and indoor dye-sensitized laboratory and sub-module quasi-solid state dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs). He has successfully assembled these cells after his systematic research in iodide and cobalt-based liquid, polymer, polymer gel electrolytes with and without nanofillers such as nanosized metal oxides, metal carbides, and graphene oxide sponge. In further, he prepared printable electrolytes for DSSCs by altering the viscosity of the polymer electrolytes. These printable electrolytes are beneficial for the role-role-printing process and mass production of DSSCs.
E-mail: venkatkandan@yahoo.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi