Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
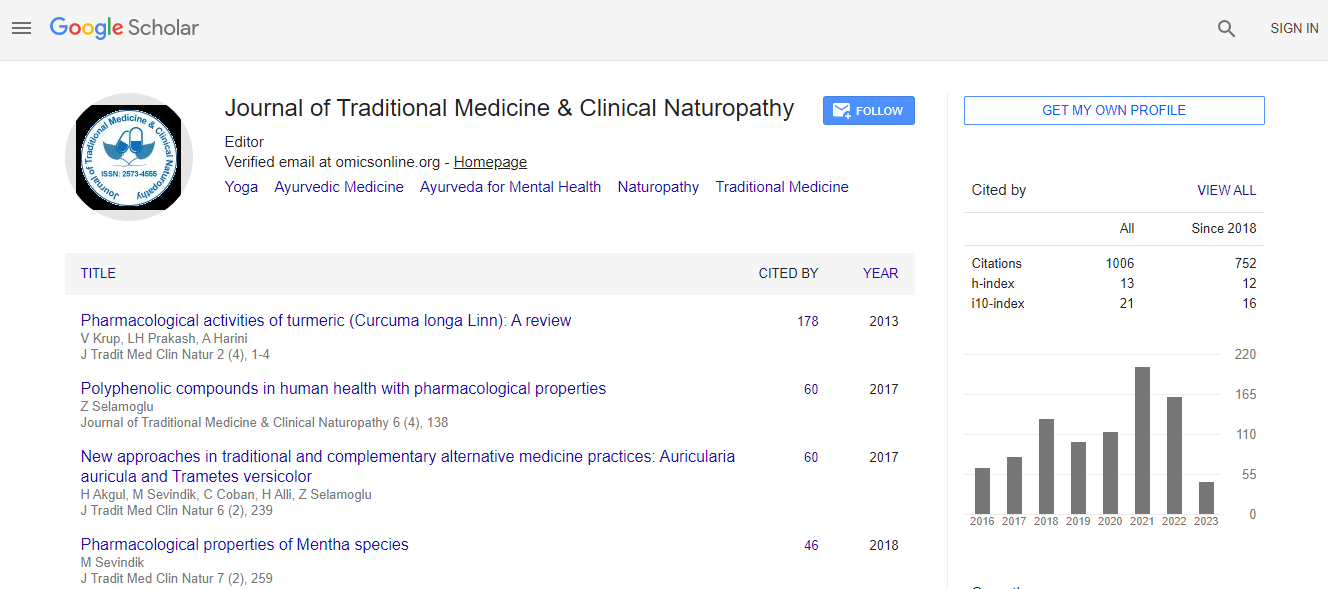
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1504
Journal of Traditional Medicine & Clinical Naturopathy peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Gynura divaricata rich in 3,5-/4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and chlorogenic acid restrains islet cell apoptosis and improves pancreatic function in type-2 diabetic mice
8th International Conference and Exhibition on Traditional & Alternative Medicine
Xiao-Lu Yin, Bing-Qing Xu and Yu-Qing Zhang
School of Biology and Basic Medical Sciences-Soochow University, China
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Tradit Med Clin Natur
Abstract
The aim of this study was to investigate the potential protective effect of Gynura divaricate (GD) in diabetic mice. Gynura divaricata (GD) is a kind of natural products for edible and medicine. The analytical results showed that the methanol extract of GD riches in 10.3% 3,5- or 6.8% 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid and 5.6% chlorogenic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection (HPLC–DAD). After STZ-induced type-2 diabetic mice (male ICR) were orally administered with 1%, 5% and 10% GD diet for four weeks, a series of assays was performed. The hypoglycaemic rate of fasting blood glucose (FBG) reached 41.4% in 10% GD group and the fasting serum insulin in the highest dose GD group has decreased as low as normal group. GD treatment significantly reduced the Glycosylated Serum Protein (GSP) level in diabetic mice. The activities of total Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase were markedly increased; while the Malonaldehyde (MDA) level was decreased in pancreas tissue by treatment of GD. H&E-staining showed that the pathological damage in islets with pancreatic β-cells was ameliorated by GD treatment. An immunohistochemical assay showed that GD promoted marked β-cell regeneration. GD treatment also caused notable increase in GLUT2, GK, MafA, PDX-1 and Bcl-2 as well as reduction in Bax and caspase-3 expression as shown by western blot analysis. In conclusion, GD exerts the pronounced hypoglycemic effect by restraining islet cell apoptosis and improving pancreatic function. Therefore, GD might be a promising food or medicine for the treatment of diabetes.Biography
Xiao-Lu Yin is pursing Master’s degree in Biology from Soochow University. She has published one paper “Mulberry branch bark powder significantly improves hyperglycemia and regulates insulin secretion in type II diabetic mice”.
E-mail: yinxiaolu1881992@163.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi