Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
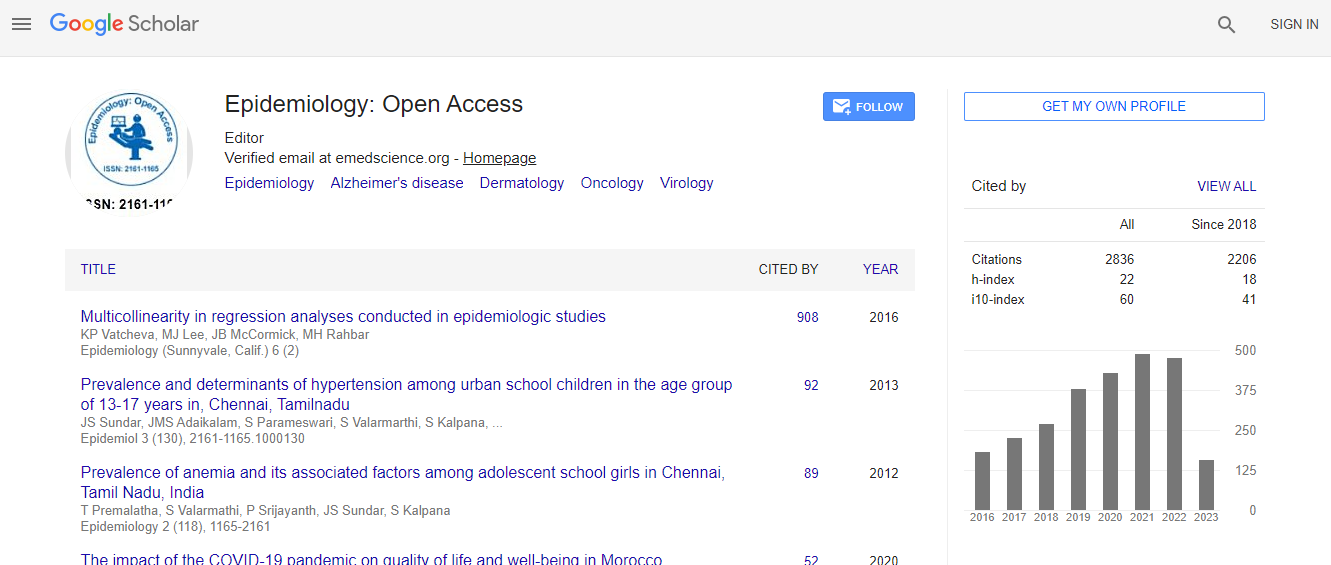
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Genome-wide interaction study of alcohol consumption on blood pressure: The Korean genome and epidemiology study (koges) Ansan and Ansung study
8th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Youngjun Kim, Jihye Kim, Bermseok Oh and Mi Kyung Kim
Hanyang University, KoreaKyung Hee University, KoreaCheil General Hospital and Womens Healthcare Center, Korea
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Background: Heavy alcohol drinking is a known risk factor for hypertension, however, little is known about the interaction of gene-alcohol consumption on the blood pressure. We carried out the Genome-wide gene-environment interaction (GEI) analysis in order to find significant SNPs that interacted alcohol consumption on blood pressure. Methods: The data were from the Ansan-Ansung community-based cohort in Korean genome and epidemiology study (KoGES) consisting of epidemiologic data and genome-wide SNPs data among 10,030 study participants aged 40-69 years old. Gene-alcohol interaction analysis on blood pressure was analyzed by multiple linear regression in PLINK in men study participants. The blood pressure was represented by two traits of systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP). 10% False Discovery Rate (FDR) was considered to determine significant SNPs in this analysis. Results: The 15 index SNPs showed significant interaction (10% FDR, P< 9.07e-07) with alcohol consumption on DBP in men participants. Conclusion and Discussion: Among the 15 findings in this analysis, two index SNPs, rs1297184 (LGR5) and rs78333128 (RSPO3) were known to be involved Renin-angiotensin system on blood pressure regulation. However, there have been no reports about its interaction with alcohol consumption on blood pressure. Thus, this finding could contribute to explain blood pressure regulation by interaction of gene-alcohol consumption. Recent Publications: 1. Marmot, M.G., et al. (1994), Alcohol and blood pressure: the INTERSALT study. Bmj, 308(6939): p. 1263-1267. 2. Cho, Y.S., et al. (2009), A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nature genetics 41: 527–534. 3. Benjamini, Y. and Y. Hochberg (1995), Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the royal statistical society. Series B (Methodological): p. 289-300. 4. Shaikh, L.H., et al. (2015), LGR5 activates noncanonical Wnt signaling and inhibits aldosterone production in the human adrenal. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 100(6): E836-E844. 5. Tomaschitz, A., et al. (2010), Aldosterone and arterial hypertension. Nature Reviews Endocrinology, 6(2): p. 83.Biography
Youngjun Kim has his expertise in evaluation and passion in improving the public health and wellbeing. He works in Cheil General Hospital & Women's Healthcare Center as a researcher and studies epidemiology in doctoral course.
E-mail: episomal@hanyang.ac.kr

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi