Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
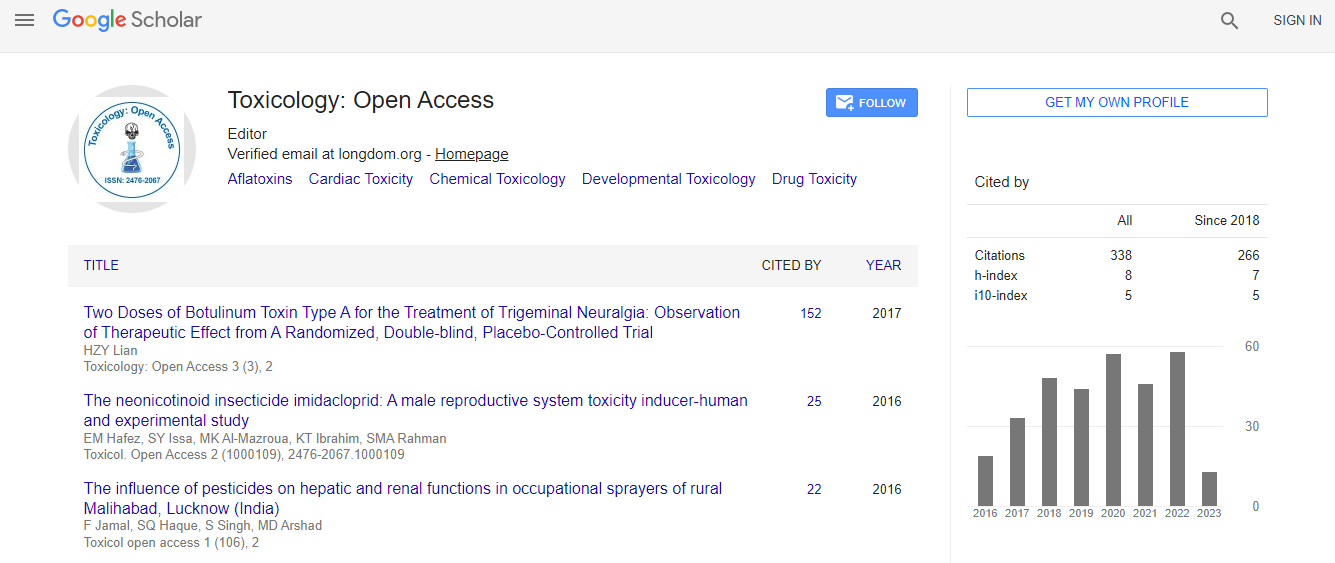
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 336
Toxicology: Open Access received 336 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Evaluation of in vitro degradation rate of hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel cross-linked with 1, 4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (BDDE) using RP-HPLC and UV-Vis spectroscopy
8th World Congress on Toxicology and Pharmacology
Mohammed Al Sibani, Ahmed Al Harassi and Reinhard H H Neubert
Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg, Germany University of Nizwa, Oman
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Toxicol Open Access
Abstract
A hyaluronic acid (HA) was cross-linked with 1, 4-butanediol diglycidyl ether to produce nine BDDE-HA hydrogels. The degradation rates of six hydrogels were evaluated by HPLC and UV-Visible spectroscopy. The percentage amount of N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) obtained after one-day enzymatic digestion to the total amount obtained after complete digestion was an indicative of the degradation rate of each hydrogel. The results were calculated with 95% confidence interval and showed (62.6%�±12.3 w/w), precision value % R.S.D=7.95, average recovery=81.0%, LOD=6.4 �¼g/ml for HPLC and (63.3�±13.9 w/w), precision value %R.S.D=8.83, average recovery=83.1%, LOD=5.4 �¼g/ml for UV method. The two methods showed also good linearity with correlation coefficients (R2) of 0.998 and 0.9995 for HPLC and UV method, respectively. For a comparison purpose, the other three hydrogels were rated using the conventional weight loss method which showed relatively higher degradation rates with an average of (73.4%�±5.7 w/w), %R.S.D=3.13. Statistical analysis revealed that there was no significant difference between HPLC and UV-Visible methods, however, these values differed significantly (p<0.05) from the value obtained from the weight loss method.Biography
Mohammed Al Sibani has completed his Master’s degree in 2008 from Huddersfield University, UK in the field of Analytical Chemistry. Currently, he is a PhD candidate since July 2013 at the Department of Pharmacy, University of Halle-Wittenberg, Germany and his thesis topic is related to the enhancement of stability and viscoelastic properties of HA dermal fillers cross-linked with BDDE. He has worked as an Analysis and Application Technician in mass spectrometry lab at Nizwa University for the last 6 years.
Email: sibanimm@unizwa.edu.om

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi