Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
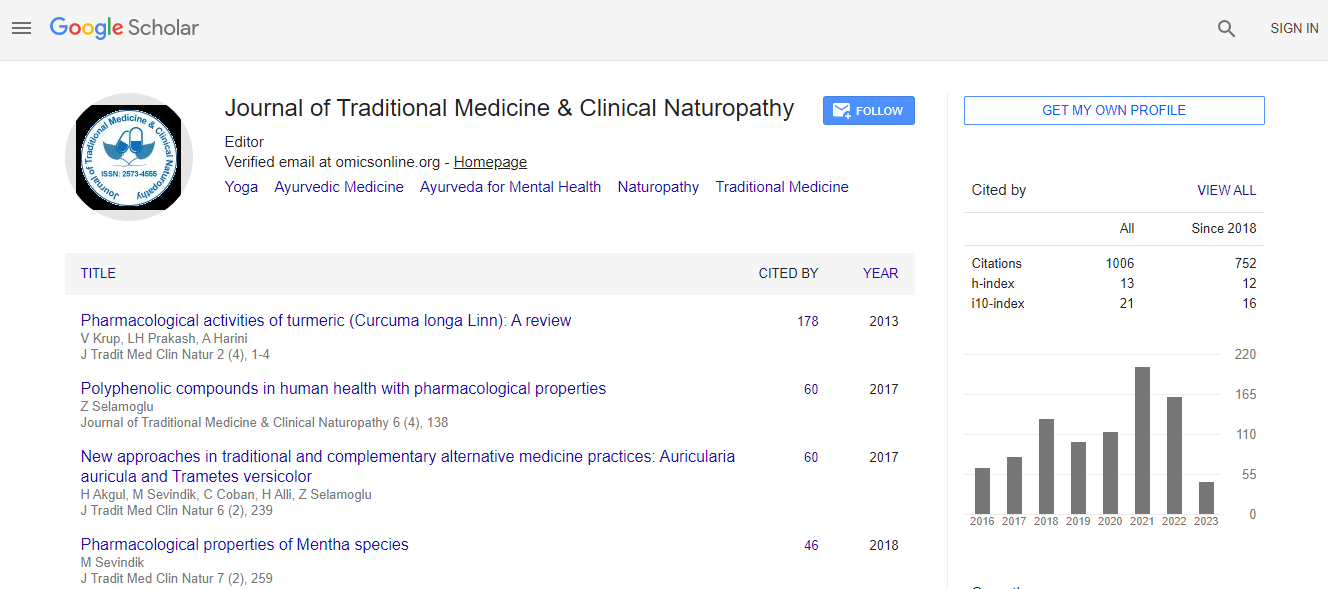
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1504
Journal of Traditional Medicine & Clinical Naturopathy peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Emerging diagnostics and therapeutics for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
12th International Conference on Traditional & Alternative Medicine
Suzanne I. Riskin
Nova Southeastern University, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Tradit Med Clin Natur
Abstract
The obesity epidemic pushed fatty liver disease, which consists of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, to the forefront of the 21st century. Disease work-up is invasive with a liver biopsy or noninvasive using elastography and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) liver enzymes biomarkers. There are no FDA-approved drugs on the market to treat the disease. Alternative medicinal treatments are investigated, which include altering the intestinal microbiota, consuming anti-inflammatory, herbal-based, vitamin-based, and plant-based medications, and following a healthy lifestyle. In this study, databases including Biomedical Reference Collection: Comprehensive, Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health (CINAHL), Google Scholar, and PubMed were used to identify articles pertaining to fatty liver disease (FLD). Articles were less than 10 years old to ensure recent information regarding the disease. Peer review was confirmed using Ulrich’s web. A total of 13 articles were used for this review. In all 13 peer-reviewed articles, the diagnosis of FLD was most commonly done using ALT and AST and lipid profiles. Liver ultrasound, liver FibroScan, and liver biopsy were supplemental tools used to diagnose FLD. Antiinflammatory, herbal-based, vitamin-based, and plant-based medications and healthy gut microbiota had beneficial and therapeutic effects in treating FLD when coupled with healthy lifestyle changes. All medicinal treatments lowered the ALT and AST liver enzymes, lipid profiles (total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein), and liver steatosis scores in studies where ultrasound was used before and after treatment. There were no reported side effects of these treatments. Further investigation is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind the therapeutic effects of treating FLD; however, the medicinal treatments discussed in this review show promising prospects for treating the disease. The treatment options studied may have beneficial impacts in treating FLD patients and may be used in the development of future medications to combat the disease.Biography
Suzanne Riskin, M.D. is an Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine and Foundational Sciences at Nova Southeastern University, Dr. Kiran C. Patel College of Osteopathic Medicine. Dr. Riskin is a full-time faculty member at the Tampa Bay Regional campus and has been there since its opening in 2019. She completed her B.A. from The University of Pennsylvania and M.D. from The University of Miami, Miller School of Medicine. Research interests include medical education, preventative health, cancer prevention, primary care, combating health inequities, and medical humanities. Dr. Riskin has guided student research topics on online studying during COVID, sunscreen application for prevention and vitamin D, and patient education on the treatment of fatty liver disease.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi