Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
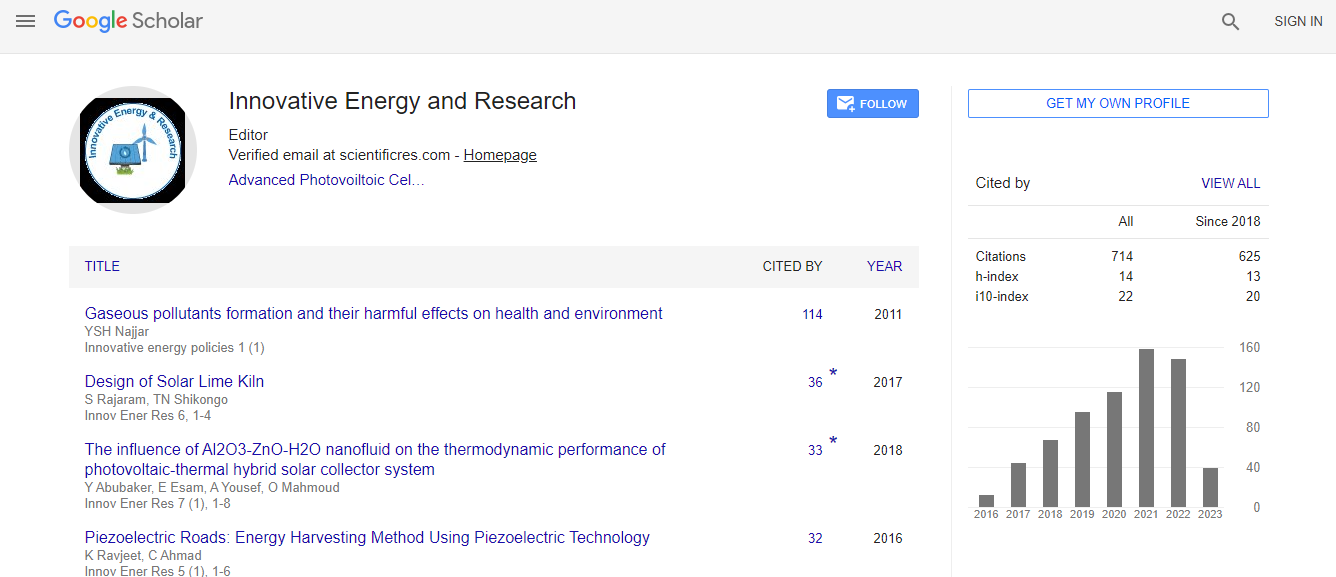
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 712
Innovative Energy & Research received 712 citations as per Google Scholar report
Innovative Energy & Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Electrochemically fabricated substrate dependent smart electrocatalysts Ni-Fe double and Ni-Co-Fe triple hydroxides for efficient water splitting to oxygen and hydrogen
21st International Conference on Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Shahed U M Khan and Meron S Metaferia
Duquesne University, USA
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Innov Ener Res
Abstract
Water electrolysis is a significant method that can utilize renewable energy to produce hydrogen; a fuel that can transform earth towards a clean energy future. Activity of electrocatalysts for water oxidation is fundamental for energy conversion technologies including integrated solar power generating devices and water electrolyzers. In this study we have electrochemically fabricated the naturally abundant and stable electrocatalysts Ni-Fedouble hydroxides, Ni-Fe-Co-triple hydroxides, for efficient splitting of water to oxygen and clean fuel hydrogen. Oxygen-evolution activities of these electrocatalysts were examined in an alkaline solution of KOH. We focused in determining electro-catalytic activity of these double and triple hydroxides electrodeposited on different substrates such as Ni-foam, electrodeposited Ni-Co-oxide on Ni-foam and pressed porous Ni-Co oxide under varying electrodeposition bath composition, electrodeposition time and electrodeposition current and potentials. We found that Ni-Fe-Co triple hydroxide electrodeposited for total of 10 min on pressed porous Ni-Co-oxide sheet acted as a superior electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction during water splitting reaction. This electrocatalyst generated a current density of ~ 100.0 mA cm-2 at an oxygen overpotential of 0.270 volt (= 1.5-volt vs RHE) in 1.0 M KOH at electrolyte temperature of 25°C. However, this triple hydroxide deposited for 7 min generated 81.0 mA cm-2 at the same overpotential, electrolyte concentration and temperature. The synergetic effect of multiple hydroxides and the substrates was mostly responsible for such enhanced electro-catalytic activity. The effect of higher electrolyte temperature was also found to have important role in enhancing the current density because of exponential dependence of reaction rate on temperature. The surface morphology and the composition of these electrocatalysts were determined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopic (EDS) data.Recent Publications
1. Khan S U M, Al-Shahry M and Ingler Jr W B (2002) Efficient Photochemical Water-splitting by Chemically Modified n-TiO2. Science 297:2243-2245.
2. Shabana Y A, El-Sayed M A, El-Maradny A A, Al-Farawati R K, Al-Zobidi M I and Khan S U M (2016) Photocatalytic removal of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) using carbon- modified titanium oxide nanoparticles. Applied Surface Science 365:108–113.
3. Kavil Y N, Shaban Y A, Orif M I, Al-Farawati R, Zobidi M Khan and S U M (2018) Production of methanol as a fuel energy from CO2 present in polluted seawater - a photocatalytic outlook. Open Chem., 16:1089-1098.
4. Frites M, Ingler W B and Khan S U M (2014) A single chip standalone water splitting photoelectrochemical cell. J. Technol. Innov. in Renewable Ener., 3:6-11.
Biography
Shahed U M Khan has his expertise in the synthesis of materials for the electrochemical and photoelectrochemical splitting of water. He published more than 140 papers in various journals including some top ones such “Journal of Physical Chemistry”, “Journal of American Chemical Society”, “Journal of Electrochemical Society”, “Chemical Physics, Applied Physics and Science”. He co-authored books entitled “Quantum Electrochemistry”, “Surface Electrochemistry” and coedited volume 7 of “Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry.” The focus of his research is to synthesize highly stable energy materials based on naturally abundant sources for efficient splitting of water to oxygen and hydrogen, a clean fuel to have carbon footprint free society in the planet Earth.
E-mail: khan@duq.edu

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi