Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
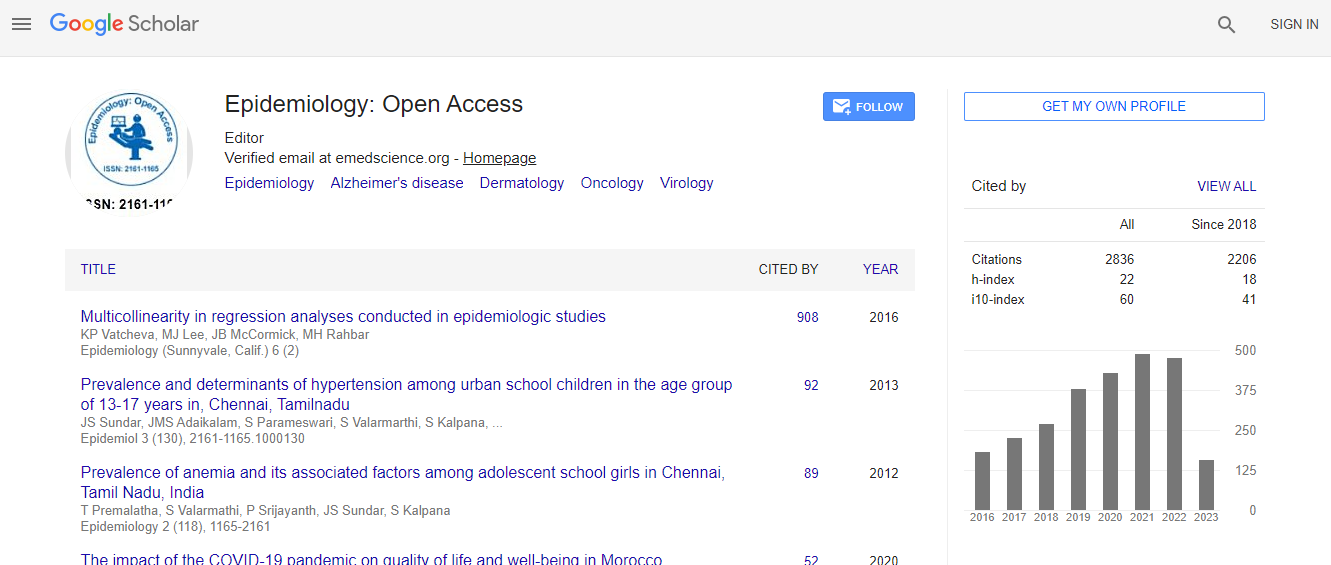
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Efficacy of various medicines for Giardiasis treatment. A comparative study. Initial results
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Wojciech Ozimek
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Giardia lamblia is a common intestinal parasite in the Poland and a frequent cause of diarrheal illness throughout the world.
Despite the recognition of G. Lamblia clinical and epidemiological illness for the last over 50 years, and the millions infected
worldwide, there have been few reviews of therapy for this infection and no definitive treatment protocols have been published.
In addition, only a few of agents have been used in therapy, and the agents which are available may vary in significantly in
efficacy and have adverse effects or be contraindicated in certain clinical situations. Also, growing resistance may play a role
in some infections. When evaluating the clinical efficacy of agents used against Giardia, it is difficult to compare studies. They
vary as to entry methodology (whether randomization was done and if treatment was blinded or open), population studied
(children, adults, symptomatic and/or asymptomatic patients), outcome measures (clinical efficacy and/or stool negativity),
and duration of follow-up. Nevertheless, conclusions may be drawn from the studies when viewed as a whole, and statements
can be made about the relative efficacy of the agents. This paper will review the efficacy of agents currently used for the
treatment of Giardiasis in our medical center. The total of 480 patients with giardiasis were treated with eight of the medicines
most commonly used for this infection. All drugs were used in their usual posologic schedules. The cure rates achieved with
furazolidone, nifuratelum, metronidazole, nimorazole, ornidazole, tinidazole, nitazoxanide and albendazole were, respectively,
63%, 65%, 65%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 94%, 96% and 96%, while in a control group given no medication stools of only 35% of the
patients became negative. Side effects were of minor importance in patients treated with nimorazole, ornidazole, tinidazole,
nitazoxanide and albendazole, and were somewhat more frequent and severe in those treated with furazolidone, nifuratelum
and metronidazole.
Biography
Wojciech Ozimek is a MD Paediatrician, Independent lecturer, researcher and media expert in parasitic and vector-borne diseases in Warsaw, Masovian District,
Poland.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi