Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
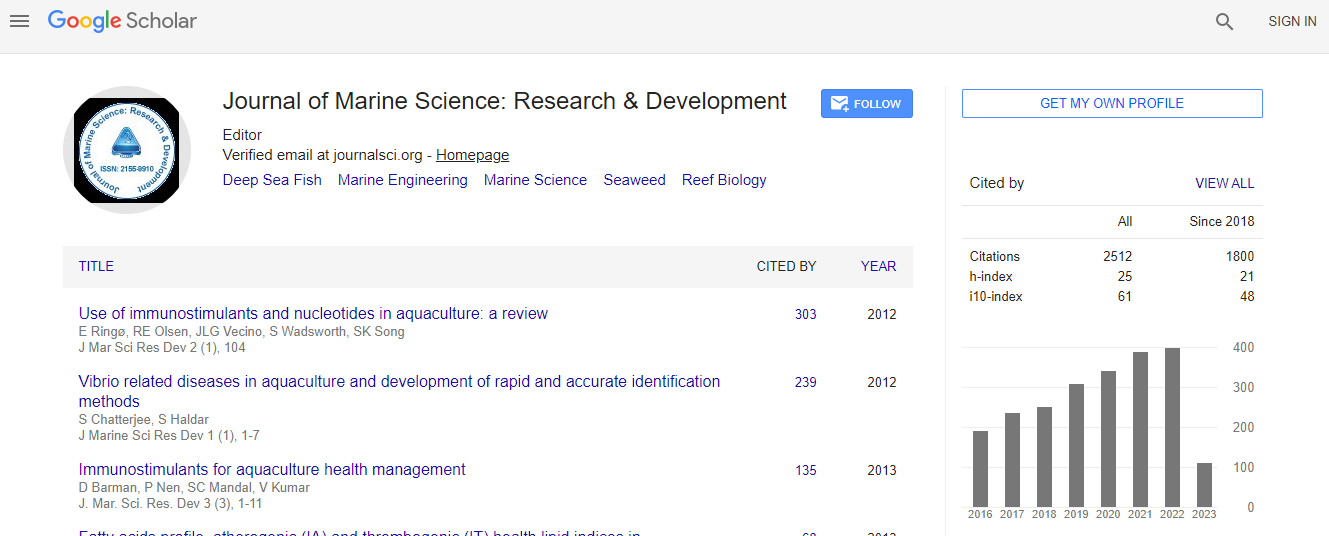
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effects of several seaweed extract on rhizoid formation of the red algae Porphyra suborbiculata
3rd International Conference on Oceanography
Mehader Getachew Desta and Yong-Ki Hong
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: J Marine Sci Res Dev
Abstract
Marine algae and invertebrates are major fouling organisms causing considerable structural and economic damage to man-made structures such as ship hulls and aquaculture nets. Most antifouling techniques have relied on organotin or heavy metals based paints that act as broad spectrum toxins to target and non-target marine organisms. So, naturally occurring antifouling compounds are the most promising alternatives to prevent the attachment of fouling organisms. Therefore, in this study we have investigated the anti-attachment and enhancing activities of 18 seaweed extracts against the known fouling species of red algae, Porphyra suborbiculata. At both tested concentrations of 20 and 200 ���¼g/mL culture medium. Hizikia fusiformis extract showed the highest inhibitory effect on the rhizoid production, rhizoid growth and germinated and juvenile blade growth. Also, extracts from Ulva pertusa, Enteromorpha linza, Undaria pinnatifida, Sargassum horneri, Ecklonia cava showed significant growth inhibition activities (P<0.01). In contrast, the Codium fragile extract enhanced the rhizoid production with same concentrations. Also H. fusiformis methanol extract inhibited the growth of the spores from both U. pertusa and U. pinnatifida and reduced the attachment of the diatoms Naviculata annexa and Nitzchia pungens (P<0.05). Among the five fractions isolated from the H. fusiformis extract, ethyl acetate, chloroform-methanol and chloroforml fractions have shown significant inhibitory activities against the growth of the P. suborbiculata spore. In open silca-gel-column fractionation of this extract, among the five elutes collected the highest inhibition of the P. suborbiculata spore was found in the acetonirile fraction. The isolation of the purified inhibitory compound was done by RP-HPLC at 220 nm after choosing ethanol and acetonirile as mobile phases based on RP-TLC result.Biography
Mehader Getachew Desta is MSc student in Pukyong National University, Fisheries College (Department of Biotechnology), Busan, Republic of Korea. She has been working on isolation of bioactive anti-fouling compounds from different seaweed species. Currently, she is purifying anti-fouling compounds from the brown seaweed H. fusiformis

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi