Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
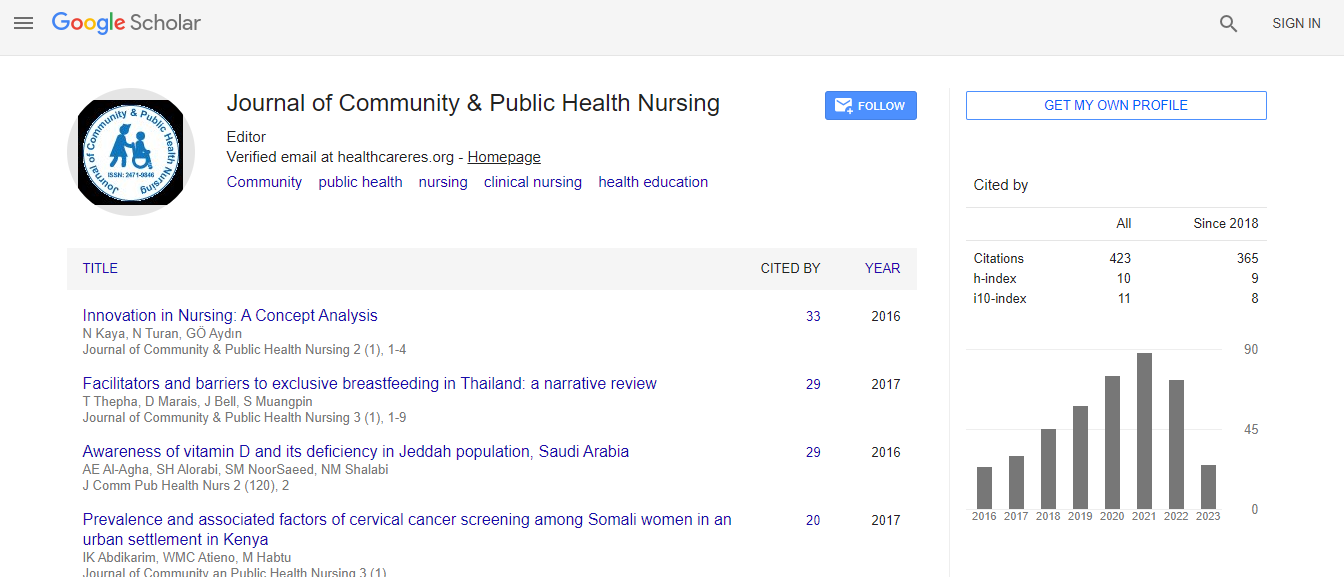
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 739
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing received 739 citations as per Google Scholar report
Journal of Community & Public Health Nursing peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effectiveness of simulation in first year undergraduate nursing students in tertiary education setting
25th World Congress on Nursing & Healthcare
Sujatha Shanmugasundaram
California State University, USA
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Comm Pub Health Nurs
Abstract
Globally, simulation has been considered one of the vital component in nursing curricula. While much innovative pedagogies have taken momentum in imparting the nursing curriculum, simulation has emerged as a significant method that is being adopted to teach clinical courses. Evidence prove that simulation enhances the knowledge and skills of nursing techniques and also it imptoves critical thinking and problem solving skills for the nursing students. It is quite evident that simulation is useful in creating a good learning environment which contributes to safety practice and confidence in the clinical settings. There are various types of simulation techinques utilized in the nursing education such a low-fidelity, high-fidelity, 3D and video unfolding case simulations. Due to rapid changes in clinical placements, patient safety issues and ethical concerns, students’ direct experience with patient care and opportunities to handle problem-based clinical situations have been diminished. Simulation plays an important role in enhancing the students’ knowledge and skills and best prepare them for the clinical practice. Simulation offers the chance to increase the speed of acquisition of clinical skills to a defined level of competence by allowing the opportunity for repetitive practice at the learner’s own pace. Therefore, to conclude, simulation is an effective method of teaching-learning strategy in an undergraduate nursing education curriculum.Biography
E-mail: sujathas@csufresno.edu

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi