Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
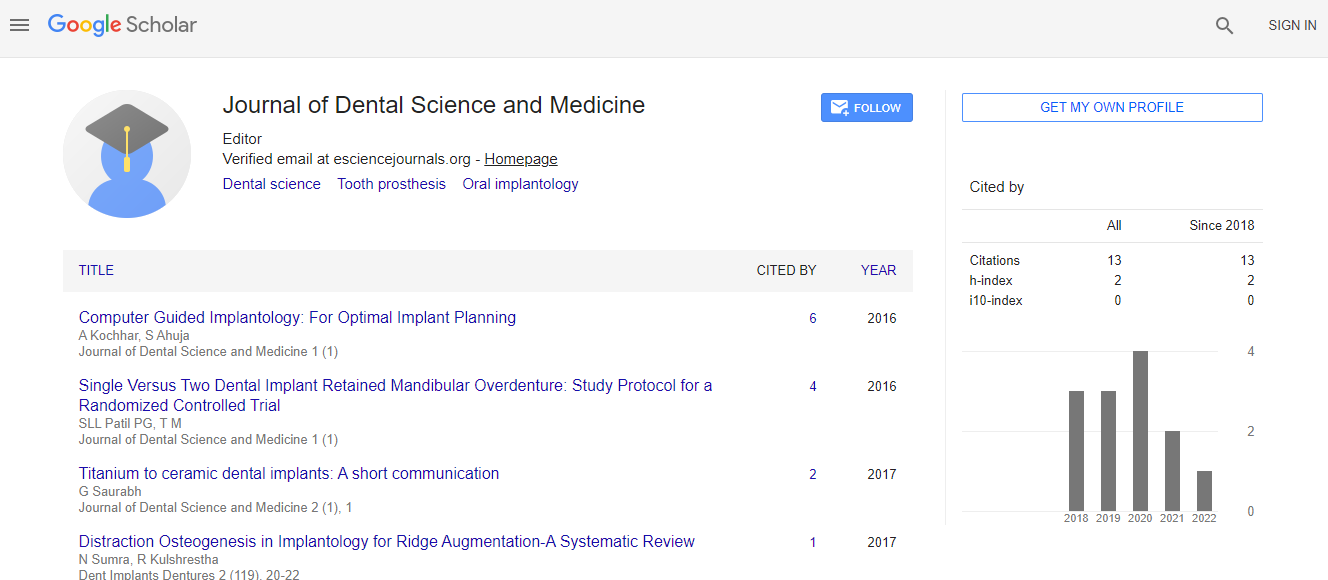
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 13
Journal of Dental Science and Medicine received 13 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Effect of Thymoquinone on Odontogenesis of Human Dental Pulp Cells
4th Annual Meeting on Cosmetic Dentistry & Orofacial Myology & 7th Annual Meeting on Pedodontics and Geriatric Dentistry
Dr. Hanadi Alwafi
Pediatric Dentist and Special Health Care Need, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Dent Sci Med
Abstract
Thymoquinone (TQ), the active component of Nigella sativa, is well known for its several beneficial effects against various diseases. However, its impact on the odontogenesis of normal human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) has not been studied before. Purpose: the aim of the present study is to evaluate the effect of TQ on cell attachment efficiency, proliferation rate, and odontogenesis of HDPCs by screening the phenotypic marker Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and expression of Dentin Sialoprotein (DSP). Methods: Human dental pulp cells were cultured in triplicate using growth media with various TQ concentrations: 5�¼M, 10�¼M, 15�¼M, 30�¼M, and 0�¼M as a control group, at 7 and 21 days. Cell proliferation rates were measured by the optical density of crystal violet dye stained cells. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity was measured by a fluorometric assay. The expression of Dentin Sialoprotein (DSP) was measured by ELISA. Statistical analysis was conducted using SAS software A (version 9.3; SAS Institute, Cary, NC) in a one-way ANOVA test, and Studentâ��s t-test. The data were normalized on per million cells basis. The data were presented as the mean of triplicate tests. Results: Higher cell attachment efficiency was shown in all TQ groups at 16 hours (P<. 0001) except for the 5 �¼M group. A significantly higher cell proliferation rate was demonstrated with low TQ concentration (5 �¼M) at 7 days (P<. 0001) and 21days (P<.0.05). Significantly higher levels of ALP activity were observed in all TQ groups at 7 days (P <0.0001) and 21 days (P <0.0001). DSP expression was significantly down-regulated in all TQ groups at 7 days compared to the control (P <0.05). However, at 21 days, all various TQ concentrations reacted with HDPCs to produce DSP and started to differentiate the same as the control group, except with TQ =15 �¼M, where DSP was significantly down regulated compared to the control group (P<0.0001). Conclusion: This is the first report to investigate optimal TQ concentrations needed to induce HDPC attachment, proliferation, and odontogenic potential. This might lead to the development of new odontogenic treatments having clinical application.Biography
Dr. Hanadi Alwafi has her bachelor’s degree in dental medicine and Surge from King Abdul Aziz University, Jeddah, KSA, in 2000-2001. She joined the Ministry of Health in various cities in KSA for several years. Then She got her Master of Dental Science in 2013 from Tufts University School of Dental Medicine, Boston, USA. After that, she earned her advanced clinical certificate in Pediatric Dentistry and her Doctorate in Pediatric Dentistry from Boston University Henry M. Goldman School of Dental Medicine, Boston, MA, USA. She became a Diplomate of the American Board of Pediatric Dentistry in 2018 and a Fellowship of Royal College of Dentists of Canada in 2021. She worked as an Assistant Professor at Riyadh Elm University and currently working in the private sector in KSA as Pediatric Dentist and Special Health Care Needs.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi