Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
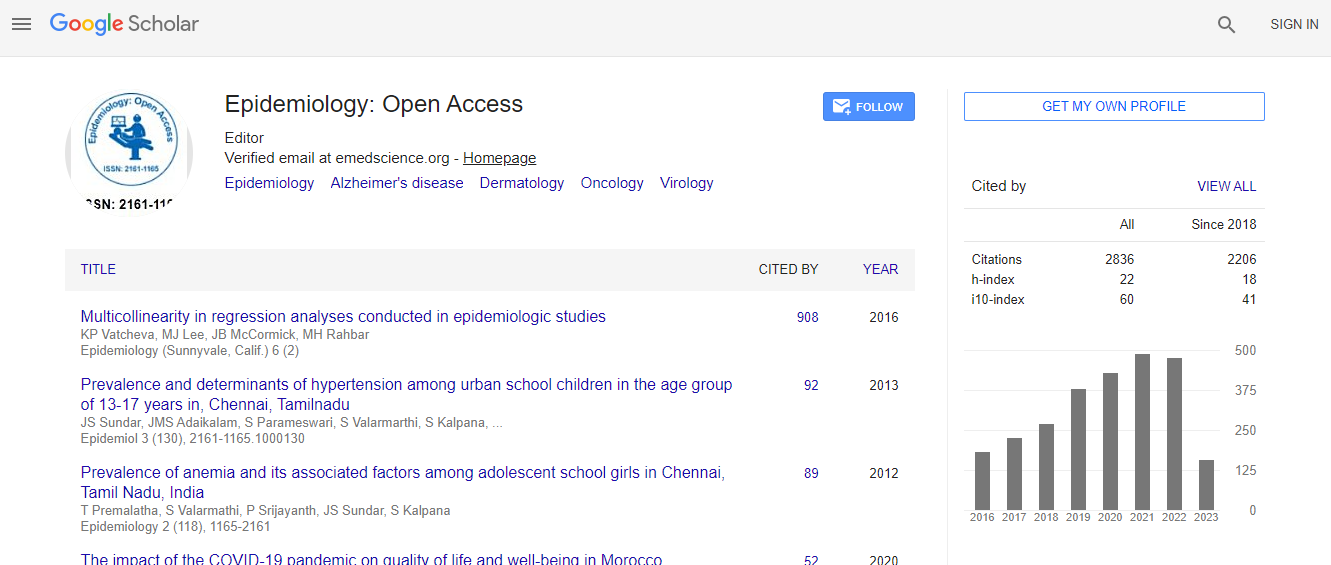
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Development of breast cancer risk prediction models using the UK biobank dataset
8th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Kawthar Al-ajmi
University of Manchester, UK
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
We developed two individualized risk prediction models for breast cancer focusing on the modifiable risk factors using the UK Biobank data. The models have been built based on the menopausal status pre- and post-menopausal. A nested case-control study within the 273,467 female participants was used to develop the models. Bootstrap stepwise regression was employed to identify variables that best fit the models followed by conventional stepwise logistic regressions to confirm the set of variables. We employed machine learning decision tree classification analysis using the significant epidemiological risk factors to fit the trees and explore any interactions. We also used a Mendelian Randomization (MR) approach to seek further factors. A polygenic score of predisposition SNPs that reached GWAS significant p-value was incorporated into both models. Model performance was tested through calibration and discrimination for both models. We applied a cross validation approach of 10 folds to test internal validation. For model external validation, we plan to utilize breast cancer datasets from international cohorts. The model provide risk scores derived from the presence or absence of specific factors and are converted to relative risk estimates to enable the comparison of individual risk to the population risk at the same age group. The models have the potential to help a woman modify her lifestyle. The models will be implemented in the primary care and community based facilities as part of breast cancer prevention initiatives with the main aims of improving cancer education and prevention. Recent Publications: 1. Risk of breast cancer in the UK biobank female cohort and its relationship to anthropometric and reproductive factors, July 2018. (Published) 2. Review of non-clinical risk models to aid prevention of breast cancer. (Accepted for publication) 3. Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Gene Polymorphism and Breast Cancer Risk among Arab Omani Women: A Case- Control Study, July 2012.Biography
Kawthar Al-ajmi is a PhD student at university of Manchester in Epidemiology department. Kawthar has an expertise in statistical genetics, epidemiology and medial laboratory sciences. Her research interests are cancer epidemiology and public health. Kawthar and her supervisory team are developing an epidemiological tool for cancer to be used by public aiding for improving cancer education and prevention in the UK.
E-mail: Kawthar.alajmi@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi