Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
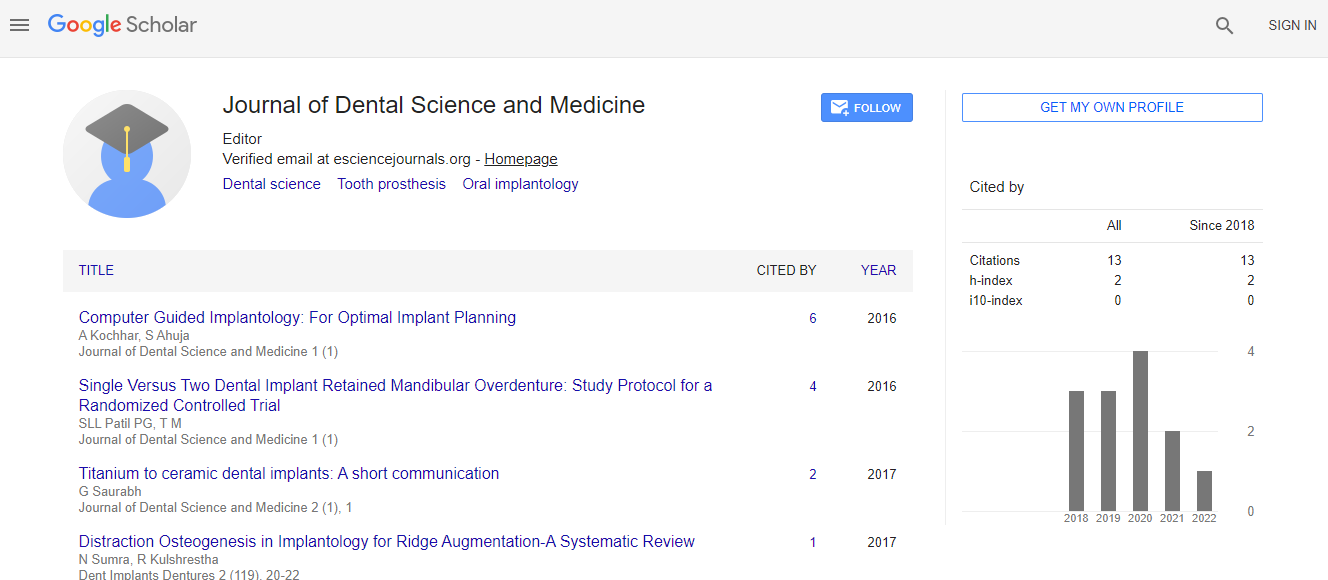
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 13
Journal of Dental Science and Medicine received 13 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Depth of cure of different bulk- fill composites with various color and thickness
3rd Annual Modern Dentistry, Dental Practice and Research Congress & 3rd International Conference on Dental Public Health and Dental Diseases
Maryam Novin Rooz
Department of operative dentistry, School of dentistry, Zanjan University of medical sciences, Zanjan, Iran.
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Dental Science and Medicine
Abstract
Background: In an attempt to fasten and simplify the restoration process, a new class of composite resins, called the bulk fill composite resins have been introduced, which has been claimed to achieve a depth of cure (DOC) of 4 mm without affecting the properties of the material. Purpose: The Purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of different shades, thicknesses and viscosities on the DOC of bulk-fill composites. Materials and method: Four bulk-fill composites [FiltekTM Bulkfill Flowable(FBF),FiltekTM Bulkfill posterior (FBP)Ã?Â?Tetric N-Flow bulkfill(TNF), Tetric N-Ceram bulkfill(TNC)] and a conventional composite, FiltekTM Z250XT Universal(FZ) were evaluated. samples (n=5) were made using two different shades( light and dark ) ,thicknesses (2 and 4 mm ) and viscosities( flowable and sculptable ). Microhardness was conducted on top and bottom surface using Vickers microhardness tester and DOC calculated as the bottom/top ratio. Statistical analysis was done using a mannwhitney test at p<0.05. Results: DOC ranged between 52-95%. FBF composite exhibited the lowest overall hardness numbers. At 2-mm thickness, all the samples achieved an appropriate DOC. However, at 4-mm thickness, only the light shades for FBF and TNF samples achieved a DOC very close to 0.8. At 4-mm thickness, the light shades for FBF, TNF and FZ samples exhibited significantly higher DOC compared to dark shades. For 4-mm-thick samples, DOC of FB )dark and light shades (and DOC of TN (light shade( were different in the flowable type from the sculptable type. Conclusion: Shade and viscosity influence DOC of bulk-fill composites at 4-mm depths. For bulk-fill composites, 20s light curing appears insufficient for 4mm bulk-fill placementBiography
Maryam Novin Rooz is a dentists and Department of operative dentistry, School of dentistry, Zanjan University of medical sciences, Zanjan, Iran.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi