Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
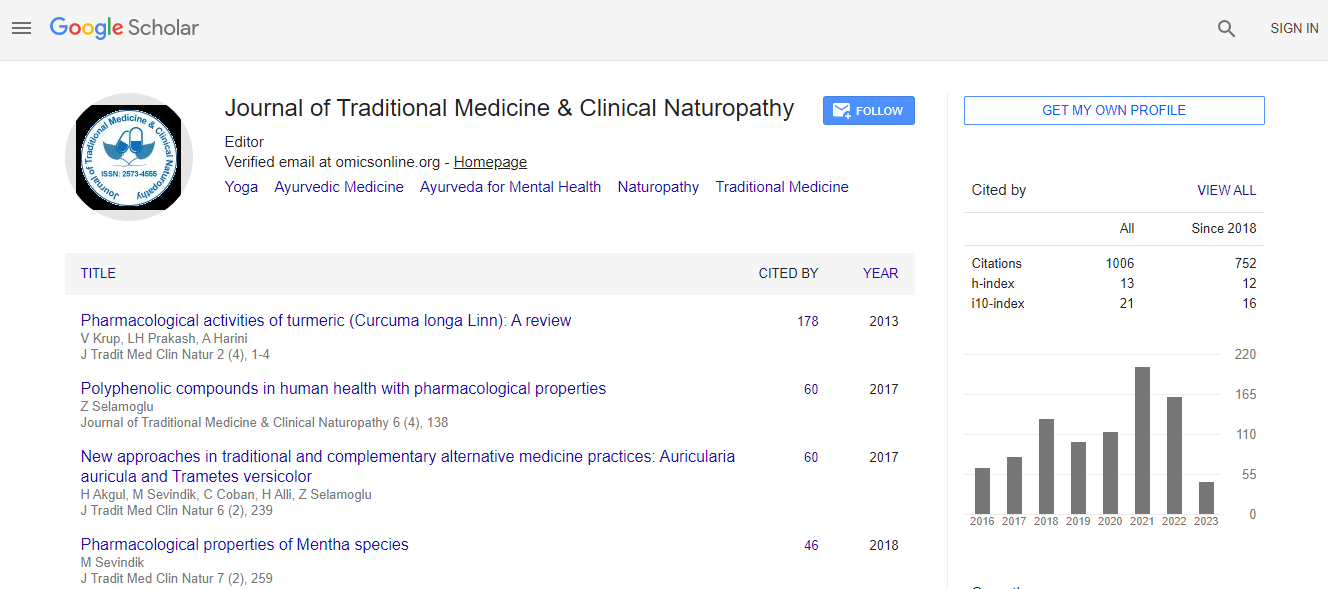
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1504
Journal of Traditional Medicine & Clinical Naturopathy peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Comparison of the effects of carbamyl-�²-methylcholine chloride administered by intravenous, intramuscular and intra-acupuncture point injections
6th International Conference and Exhibition on Traditional & Alternative Medicine
Junhong Gao, Yumin Wang, Jingjing Cui and Xiaochun Yu
China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, China
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: J Tradi Med Clin Natur
Abstract
Objective: To compare the effects of carbamyl-�²-methylcholine chloride (CMCC) administered by intra-acupuncture point injection (IAI), intramuscular injection (IMI), and intravenous injection (IVI), and to analyze the mechanisms. Methods: In the IAI group, CMCC was injected into the Zusanli acupoint (ST 36) immediately after 30-min stimulation by electroacupuncture (EA) at the acupoints, and into the femoral vein and skeletal muscle in IVI and IMI groups, respectively. Intragastric pressure was detected. The plasma concentration of CMCC was measured at various times. Results: The gastric effect of CMCC in the IVI group was enhanced and attenuated more rapidly than in the other groups. In the IAI group, this effect was significantly stronger than that in the IMI group at 2 min and 15 min, but not significantly different between the two groups at 5 min and 30 min. Plasma concentration of CMCC in the IAI group was similar to that in the IVI group at 2 min, but higher than that in the IMI group. The concentration in the IAI group was higher than that in the IV group and similar to that in the IMI group at 5, 15 and 30 min, indicating rapid increase and slower reduction of the plasma concentration of the drug in the IAI group. There was a positive correlation between the plasma concentration of CMCC and intragastric pressure in all groups. Conclusion: The effect of IAI with CMCC was stronger than that of IMI and longer-lasting than that of IVI, which correlated with the blood concentration of CMCC.Biography
Junhong Gao is working as Associate Professor of Institute of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences and Master’s tutor. His research interest is to explore the mechanism of acupuncture and moxibustion and joint administration of acupuncture and drugs. So far totally 3 research projects are/were granted by National Natural Science Foundation of China and Natural Science Foundation of Beijing (as the principal investigator), and more than 40 articles in total were published in reputed journals.
Email: gaojh@mail.cintcm.ac.cn

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi