Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
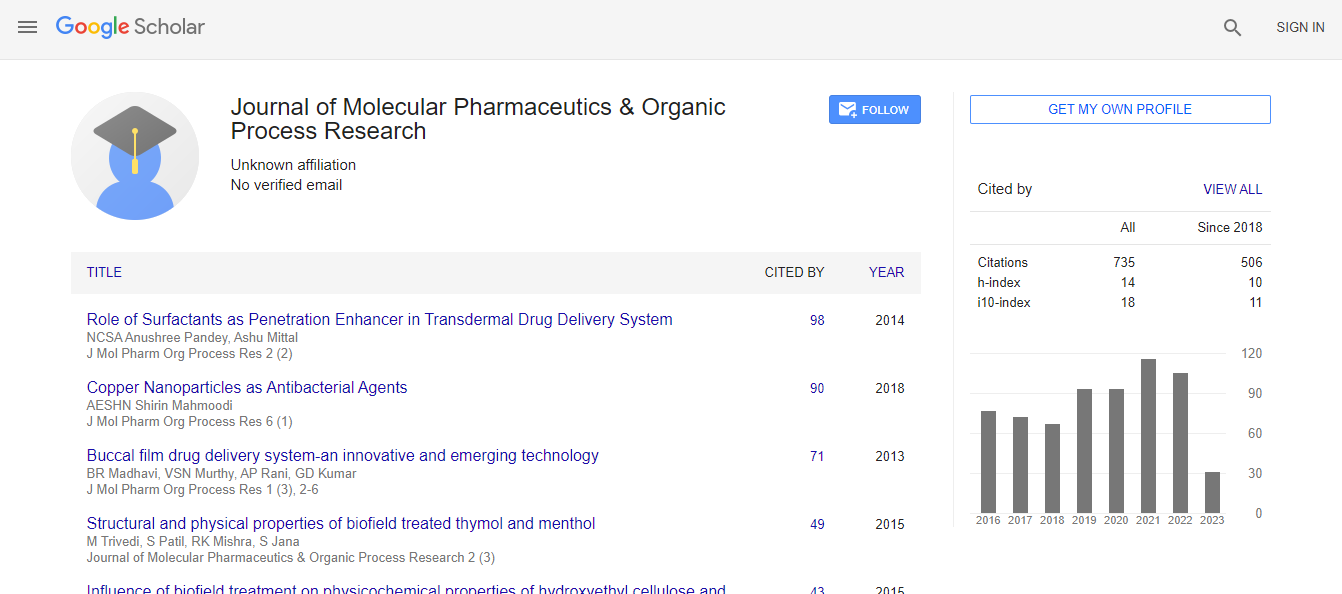
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1057
Journal of Molecular Pharmaceutics & Organic Process Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Academic Keys
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Share This Page
Choosing the correct antiviral for triple epidemic: An in silico approach
3rd World congress on Pharmaceutics, Formulations & Novel Drug Delivery Systems
Emine Erdag*, Nazife Sultanoglu and Cenk Serhan Ozverel
Near East University, Turkey
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Mol Pharm Org Process Res
Abstract
Globally, influenza viruses, Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and SARS-CoV-2 have combined to cause a triple epidemic. Choosing the right antiviral agent to be used in against all three different viruses is very important for reducing overuse of antivirals in patients. Based on the clinical investigations, ten distinct antiviral medications and/or therapeutic candidates that have been employed in COVID-19, RSV and influenza infections were chosen for this study. All 10 different antiviral agents were analyzed to calculate the binding affinities and interactions of ligands with their target viral proteins by using molecular docking approach The RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of the SARS-CoV-2, the PB1-PB2 protein complex of the influenza A virus and the RSV F glycoprotein were chosen as potential viral targets of the molecular docking analysis, respectively. The drug-binding pockets and inhibitory sites were studied, along with the interactions and binding affinities of the ligands. As a result, three of the ten ligands examined had the highest affinity for three viral infections at the docking site of interest. The antiviral drugs with the highest affinities for their targets were AVG-388, Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir. Investigations employing molecular dynamics simulations were also conducted and the results were illustrated via graphs of Root-Mean-Square Deviation (RMSD). The results of the simulation revealed that the affinity remained constant, suggesting that the chosen ligands may function as potent therapeutic agents. In conclusion, in comparison to other ligands, AVG-388, Remdesivir and Nirmatrelvir might be suggested as potent antiviral molecules against the triple epidemic.Biography
Emine Erdag graduated from Near East University Faculty of Pharmacy in 2016 and completed her PhD programme at the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry in 2020. Her doctoral thesis is entitled "Synthesis and Characterization of New 3-Substituted-2(3H) Benzoxazolone Derivatives as Cytotoxic and Antimicrobial Agents". She has been working as a faculty member in the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry since October 2020. Her research interests include medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, organic synthesis, drug design and in silico molecular docking.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi