Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
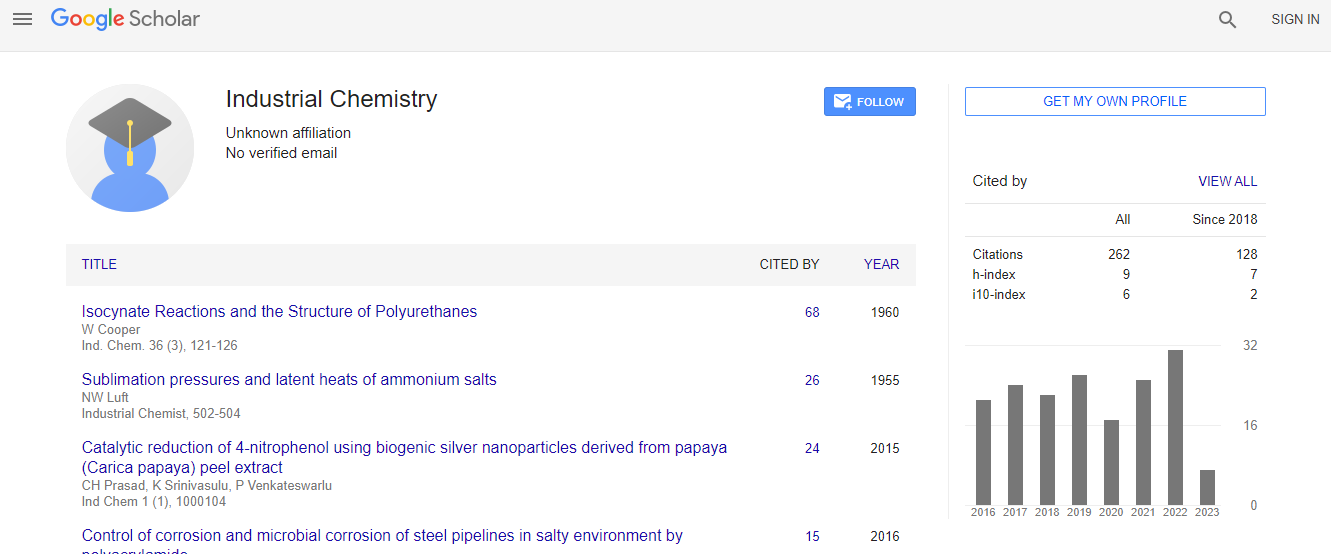
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 262
Industrial Chemistry received 262 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Characterization of the corrosion of oilwell cement exposed to H2S under highsulfur gas reservoir conditions
International Conference on Industrial Chemistry
Tao Gu, Xiaoyang Guo, Xingguo Zhang, Zaoyuang Li, Sheng Huang and Xiaowei Cheng
Southwest Petroleum, P.R. China
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Ind Chem
Abstract
H2S is an acidic and toxic gas and the corrosion of H2S on oilwell cement is considered to be a great challenge for wellbore integrity and environmental safety in the exploitation of high-sulfur gas reservoir. In our work, an unidirectional sample was designed to simulate the actual downhole condition, and the corrosion performances of oilwell cement exposed to humid H2S gas and H2S rich brine were investigated using designed unidirectional samples. Compressive strength, microhardness, porosity, gas permeability, SEM, EDS, and XRD analyses were conducted to compare the dissimilarity of H2S attack in two exposure scenarios. The experimental results show that the corrosion degree of cement exposed to humid H2S gas was lower due to a dense gypsum layer formed on the cement surface; this layer inhibited inward penetration of H2S by blocking diffusion. On the contrary, a porous and loose amorphous silica gel section formed on the headspace of brine-exposed cement for dissolution and migration effects of brine, which facilitated the penetration of H2S to the interior of cement. The degradation mechanism of cement and the effects of exposure scenario on cement properties are proposed.Biography
Dr. Tao Gu obtained his B.Sc. in Polymer Materials and Engineering and M.Sc. in Matericals Science at Southwest Petroleum University (SWPU) in China in 2010 and 2013 respectively. In July 2016, he will be graduated from SWPU with a doctoral degree in Oil & Gas Well Engineering. In the past years, he has been working on Oil & Gas well cementing engineering. His current research interests include durability and corrosion of oil well cement under acid gas conditions and cementing materials and technology for oil-based drilling fluid conditions. Until now, he has published 5 patents applications and 8 papers.
Email: gutaoswpu@163.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi