Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
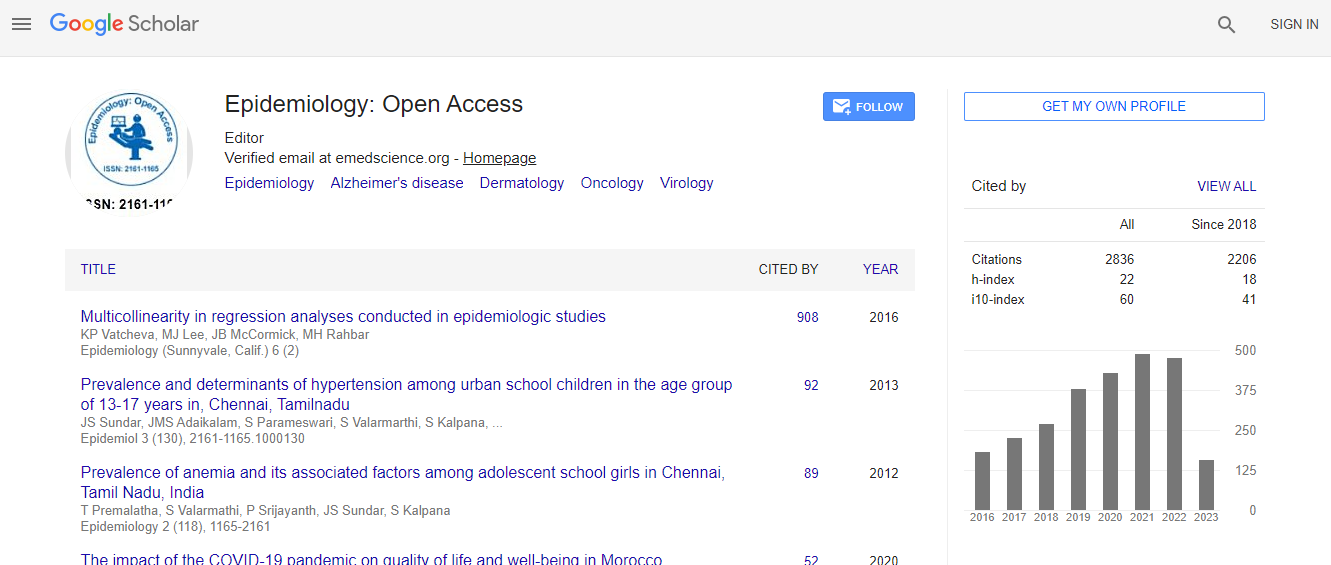
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Characterization of Salmonella bareilly isolates from foodborne outbreaks in Gyeonggi-Do
8th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Nanjoo Park
Gyeonggi-Do Institute of Health & Environment, Republic of Korea
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Among the cases of food poisoning caused by Salmonella in Gyeonggi Province in recent years, Salmonella Bareilly has emerged as a cause of food poisoning since 2014, and it has been continuously detected from 2014 to 2016. Total 21 strains were isolated. In this study, biochemical identification, serotype analysis, and antibiotic resistance of Salmonella bareilly strains isolated from foodborne pathogens annually since 2014 were analyzed. Protein analysis was performed using MALDI-TOF. Various pathogenic genes were detected and PFGE and genetic characteristics were analyzed. All isolates were identified as Salmonella spp. and confirmed by Salmonella bareilly through serotype analysis, and no isolates were found to be resistant to antibiotics. The correlation between Salmonella bareilly using MALDI-TOF was divided into two groups. The pathogenic genes of Salmonella, flgB, ssaK, sseC, sseD, invA, sopE2, sipD and sipB were all detected. As a result of PFGE analysis, it was separated into two clusters. When the PFGE analysis results were compared with the Kores PulsNet Data, the isolated strains in 2014 showed different genotypes from Salmonella Bareilly, which was isolated in Korea. Recent Publications: 1. Kim, K.A., Yong, K.C., Jeong, J.A., Huh, J.W., Hur, E.S., Park, S.H., Choi, Y.S., Yoon, M.H., and Lee, J.B. (2014). Analysis of Epidemiological Characteristics, PFGE Typing and Antibiotic Resistance of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains Isolated from Gyeonggi-do, Korean Journal of Microbiology, 50(4), pp.285-295. 2. Ae-Ri Cho, Hee-Jin Dong, and Seongbeom Cho (2013), Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Salmonella spp. by Using a Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay in Duck Carcass Sample, Korean J. Food Sci. An.Vol. 33(5), pp. 655- 663 3. McDaniel, T. K., Jarvis, K. G., Donnenberg, M. S., and Kaper, J. B. (1995). A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 92, pp.1664-668. 4. Clifford G. Clark (2013), Evaluation of MALDI-TOF mass spectroscopy methods for determination of Escherichia coli pathotypes. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 94, pp.180–191 5. Park SG, Kim MS, Lee YK. (2006). Trend of antimicrobial susceptibility and multiple drug resistance patterns of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis isolated from foodborne patients in Seoul between 2001 and 2005. J Fd Hyg Safety, 21, pp. 23-30.Biography
Nanjoo Park has completed her MD from College of Agriculture and Life Science, Seoul National University (Republic of Korea). She is research scientist for the public health in Gyeonggi-Do Institute of Health and Environment, Republic of Korea. She has published variable domestic papers(subjects; infectious disease, microbiology) in reputed journals and serving as an co-worker in various field.
E-mail: nanjoopark@gg.go.kr

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi