Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
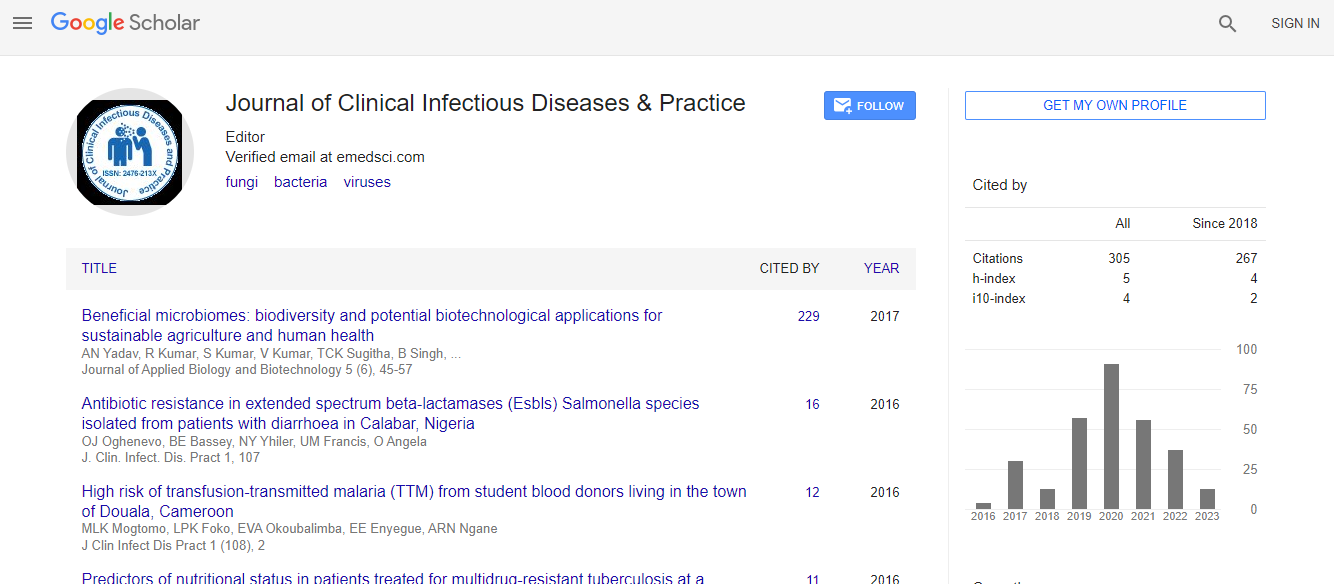
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 531
Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases & Practice peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Google Scholar
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- Publons
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Share This Page
Change in gonadotropins in postmenopausal women: Effects of parity
9th World Congress on Rare Diseases and Orphan Drugs
Ekhator C N, Egbon P O, Ukponahiunsi C A, Okoeguale V E and Koko K
Ambrose Alli University, NigeriaSt Philomena Catholic Hospital, Nigeria
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Clin Infect Dis Pract
Abstract
Introduction: This report assessed the effect of parity on gonadotropins pattern in postmenopausal women. We studied 280 post menopausal women (40 each grouped into nulliparous to para 6). Although there was no significant different in their ages, serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) appeared to correlate negatively with parity. Thus, the levels of gonadotropins may vary with parity in postmenopausal women. Endocrinologically, female aging caused a progressive increase and decrease in FSH and estrogen levels respectively. However, reports showed that FSH secretion varies with individual’s characteristics and only a few studies have investigated the effect of age, body mass index, lifestyle factors and ethnic differences. This report was to assess the effect of parity on gonadotropins changes in postmenopausal women.Materials & Methods: The study was conducted among 280 postmenopausal women attending clinic at Saint Philomena Catholic Hospital in Benin City, Nigeria. They consisted of 40 subjects each with natural menopause transition, devoid of medical, surgical or pathological influence and classified from nulliparous to para 6. After inform consent and approval was given, medical history and blood sample were obtained for serum FSH and luteinizing hormone levels.
Results: The mean age of the women ranges from 56.05±6.91 to 59.25±5.45 years. Nulliparous postmenopausal women had higher FSH (p>0.05) but lower LH (p<0.05) levels compared to porous postmenopausal women. Parity seems to negatively correlate with FSH and LH levels in postmenopausal women.
Discussion: Based on the results, serum gonadotropin levels may vary with parity as with age, BMI, lifestyle and ethnicity.
Recent Publications
1. Burger H, Dudley E, Hopper J, Groome N, Guthrie J, Green A and Dennerstein L (1999) Prospectively measured levels of serum follicle-stimulating hormone, estradiol and the dimeric inhibins during the menopausal transition in a population based cohort of women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 84(11):4025-4030.
2. Manson J M, Sammel M D, Freeman E W and Grisso J A (2001) Racial differences in sex hormone levels in women approaching the transition to menopause. Fertil Steril. 75(2):297-304.
3. Randolph Jr J F, Sowers M F, Gold E B, Mohr B A, Luborsky J, Santoro N, McConnell D S, Finkelstein J S, Korenman S G, Matthews K A, Sternfeld B and Lasley B L (2003) Reproductive hormones in the early menopausal transition: relationship to ethnicity, body size, and menopausal status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88(4):1516-1522.
Biography
Ekhator C N is working as an Associate Professor in the department of Physiology in Ambrose Alli University, Nigeria. He published several articles in many journals. He completed his graduation from University of Ibadan.
E-mail: clemo4real@yahoo.co.uk

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi