Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
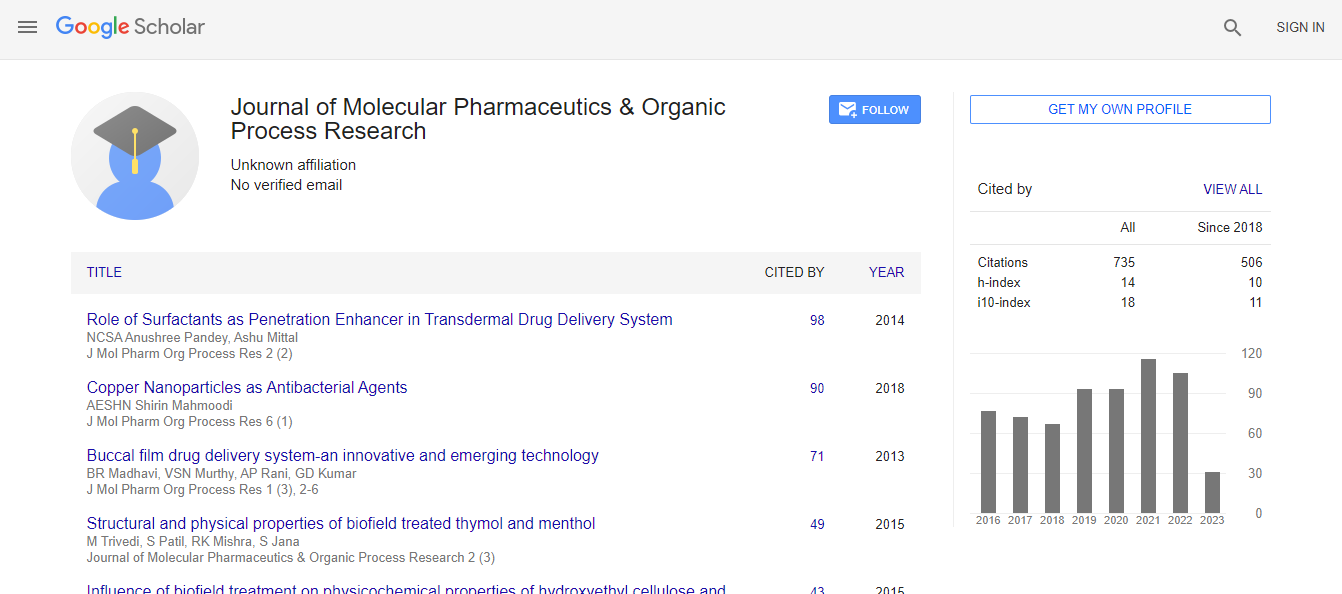
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 1057
Journal of Molecular Pharmaceutics & Organic Process Research peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Academic Keys
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Publons
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Share This Page
Attenuating effect of coumarin-2-aminothiazole against paraquat induced toxicity in rats
2nd International Conference on Pharmaceutical Formulations and API
Ali Sharif*, Saman Shahbaz, Bushra Akhtar and Adeel Arshad
Lahore College for Women University, Pakistan University of Agriculture, Pakistan
ScientificTracks Abstracts: J Mol Parm Org Process Res
Abstract
Background: Several herbicides, especially paraquat, are persistent organic pollutants which cause damage to humans and animals through reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Coumarins are fused benzene and pyrone ring systems with a wide spectrum of bioactivities. The objective of the current investigation was to assess the preventive effect of Coumarin-2-Aminothiazole (C2A) in a rat model of paraquat-induced toxicity. Methodology: Acute oral toxicity was conducted according to the OECD guidelines 425 (limit test). In-vitro anti-oxidant activity was evaluated by DPPH assay. Male rats were divided into 6 groups (n=5). Paraquat (10 mg/ kg BW i.p) was administered to all groups except normal control 2 h prior to the stranded drug and treatment administration. Normal and disease control rats received normal saline whereas treatment groups received 10,20 and 30 mg/kg C2A for 21 days. Levodopa/carbidopa (7 mg/kg) was used as standard therapy. Behavioural tests (elevated plus maze, light/dark box, morris water maze) were performed at 7-day interval during whole study period. The rats were euthanized at day 21. Analysis included Enzyme Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay (ELISA) for measuring levels of inflammatory markers (IL-1b, IL-6 and TNF�?±). Assays for oxidative stress Super-Oxide Dismutase activity (SOD), Catalase (CAT), reduced Glutathione (GSH), Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Nitric Oxide (NO) were also accessed. Neurotransmitters, Dopamine (DA) and Nor-Adrenaline (NA) levels were measured. Computer-aided molecular modeling was used to examine the conformational relationship between the C2A and Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4). Results: C2A revealed no toxicity up to the dose of 2000 mg/kg. C2A exhibited potent anti-oxidant activity with an IC 50 of (82.6 �?¼g/mL) as compared to standard ascorbic acid (37.50 �?¼g/mL). C2A treated groups significantly increased (p<0.05) time spent in open arms and light chamber compared to the disease control group whereas decreased in escape latency (p<0.05) was observed. The findings suggested a decline in inflammatory markers upon treatment with C2A. TNF-ï¡, IL-1ï¢ and IL-6 concentrations were restored (p<0.001) in C2A treated rats. Similar findings were observed for oxidative stress markers. Activities of SOD, CAT and concentration of GSH, MDA and NO were restored (p<0.001) in brain homogenate and serum samples of treated rats. Dopamine and noradrenaline levels were also improved upon treatment with C2A (p<0.001). The docking score of TLR is -5.6 Kcal/mol, C2A demonstrated positive interactions with the relevant proteins' critical amino acid residues. Conclusion Treatment with C2A prevented the paraquat-induced toxicity in the brain due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The main mechanism involved in ameliorating paraquat toxicity in the brain is through reduction of oxidative stress and Neuroinflammation. Keywords: Neurotoxicity, Coumarin 2 aminothiazole, Inflammatory markers, Oxidative stress, Neurotransmitter.Biography
Ali Sharif is from Department of Pharmacology, Institute of Pharmacy, Lahore College for Women University Lahore, Pakistan.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi