Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
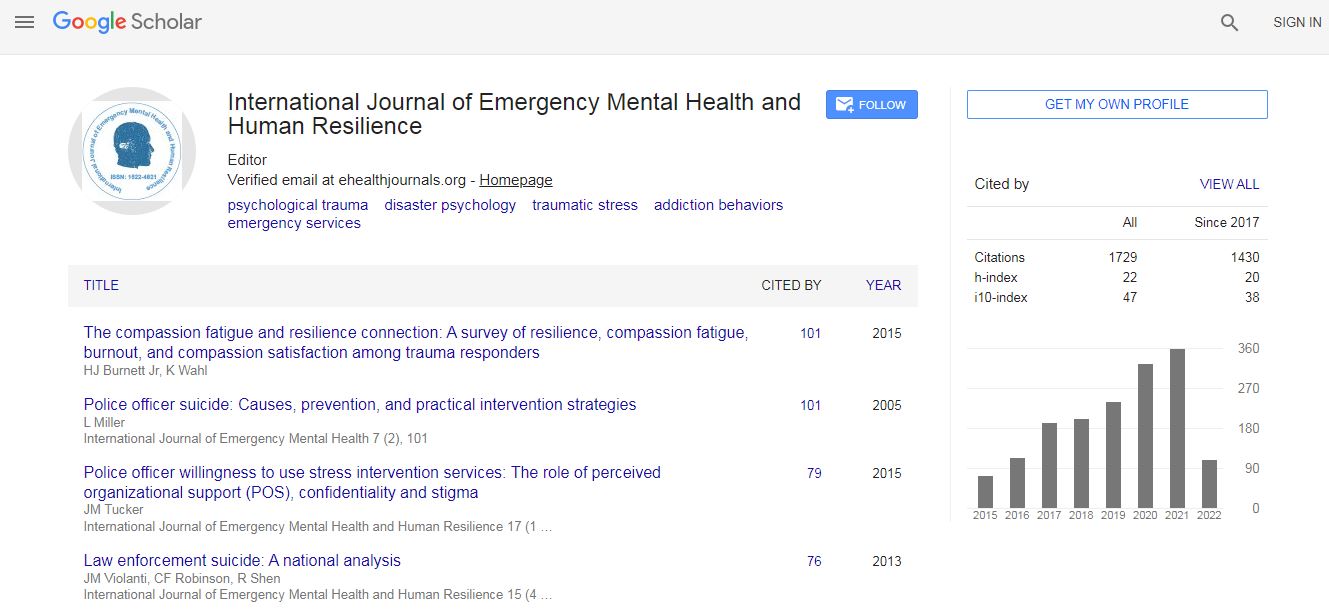
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 4948
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- Publons
- Pubmed
- science Gate
- scispace
- world cat
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
A study to assess resilience of adult family caregivers of patients having schizophrenia and its related disorders, in a selected hospital, New Delhi
5th International Conference on Mental Health and Human Resilience
Bobby Syiemlieh, Y Surbala Devi, Sandhya Gupta and Mamta Sood
AIIMS, Raipur, IndiaAIIMS, New Delhi, India
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Int J Emerg Ment Health
Abstract
Background: Resilience is the process of harnessing biological, psychosocial, structural and cultural resources to sustain wellbeing. If family members are resilient, they can overcome stress associated with providing care for a person having mental illness and preserve their own health and the health of their family.Material & Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was undertaken on 100 adult family caregivers of patient having schizophrenia and its related disorders who were selected consecutively from out-patient clinics of department of psychiatry, in a selected hospital, New Delhi. The data were collected using subject information sheet for caregiver and patient, Connor-Davidson resilience scale (CD-RISC) for assessing the resilience of caregivers and Brief psychiatric rating scale (BPRS) to assess the psychopathology of patient. The collected data was analyzed using STATA 14.0 software. Ethical clearance was obtained from ethics committee of the selected hospital, New Delhi.
Result: The mean age of caregivers and patients were 47.7(±11.5) and 29.8(±9.3) respectively. Sixty five percent of the family caregivers were male. Most of the caregivers were having high score on resilience scale, with mean scores of 72.14(±16.1). Caregivers who were spouse were found to be more resilient as compared to other caregivers who were giving care to patient having schizophrenia and related disorders (p=0.0006).The caregivers who had only one child are more resilient than those who had more than two children (p=0.04). A significant association was found between the resilience levels of caregivers with the age of the patients (p=0.003), marital status of the patients (p=0.002), occupation of patients (p=0.0002) and with monthly income of the patients (p=0.008).
Conclusion: A family caregiver caring for mentally ill patient constantly experience various challenges, be it in caring issues or in meeting their own needs. Most of the study subjects have shown good levels of resilience which is a protective factor for their own mental health. However the mental health care workers need to counsel and guide the family caregivers to enhance their resilience level whenever they visit the clinics for follow ups.
Biography
Bobby Syiemlieh has completed his graduation from College of Nursing, NEIGRIHMS, Meghalaya, India, as well as Post-Graduation in Psychiatric Nursing from AIIMS, New Delhi, India. He is currently working as Nursing Officer at AIIMS, Raipur, India. His area of interest includes Preventive Psychiatry, Addiction Psychiatry, and Severe Mental Illness.He has attended and presented scientific papers in national and international conferences.
E-mail: bobbysyiemlieh8@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi