Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
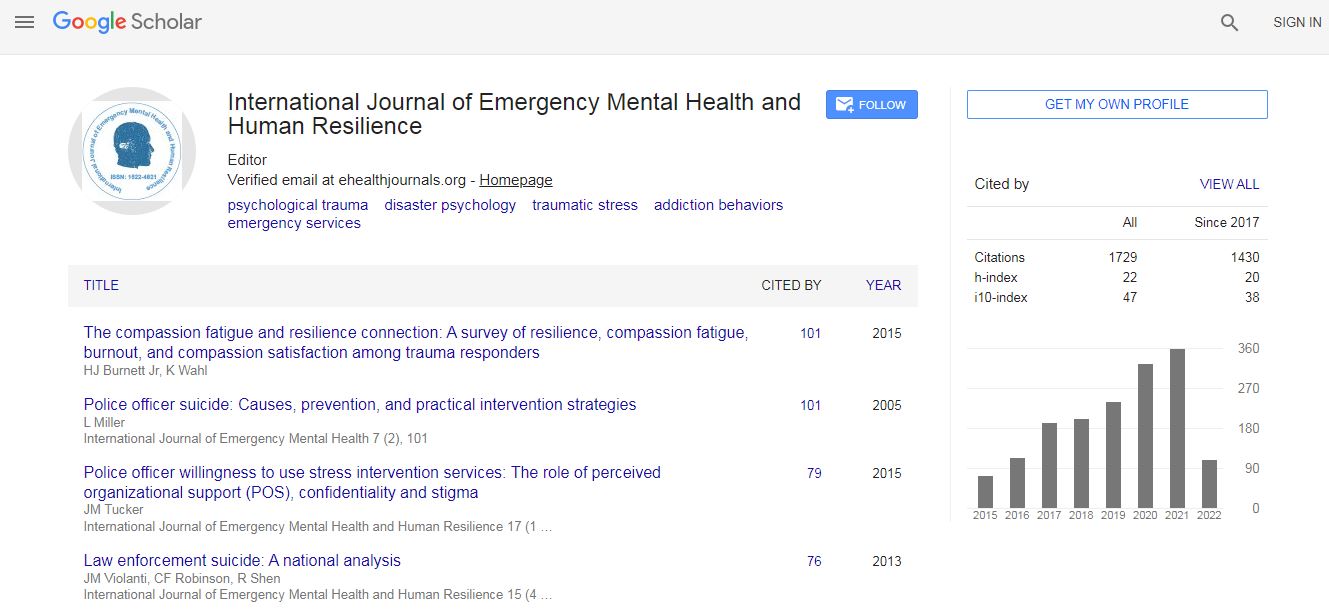
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 4948
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- Publons
- Pubmed
- science Gate
- scispace
- world cat
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
A study to assess personality, psychological distress and adjustment difficulties among nursing students at AIIMS
5th International Conference on Mental Health and Human Resilience
Anita P, Deepika C Khakha and Rachna Bhargava
All India Institute of Medical Sciences, India
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Int J Emerg Ment Health
Abstract
Background: Stress is linked to psychological distress and other adverse consequences on student’s health and wellbeing. Being in a profession closely related to life and death makes nursing students more prone to stress.Aim: To assess personality, psychological distress and adjustment difficulties among nursing students at AIIMS.
Materials & Methods: This cross sectional descriptive study included 292 subjects enrolled in BSc (Hons) Nursing course at College of Nursing AIIMS, New Delhi. Data was collected by using Big Five Inventory, General Health Questionnaire and Adjustment Inventory for college students.
Results: Extrovert and neuroticism was found to be the most dominant type of personality trait among the nursing students. A high level of distress was experienced by 56.2% of the subjects, while low levels of psychological distress was experienced by 43.8%. No subjects belonged to excellent adjustment category while 2.1% of the subjects belonged to good overall adjustment category. Average overall adjustment was seen in 10.3% of the subjects and unsatisfactory and very unsatisfactory overall adjustment was seen in 40.7% and 46.9% of the subjects respectively. There was significant association found between neuroticism personality trait and psychological distress at p<0.05. A significant association also found between neurotic and conscientiousness personality trait with father’s education. Home, health and educational adjustment were found to be positively correlated with mother’s education. Neuroticism and openness to experience personality trait and also educational adjustment was found to have statistically significant relationship with duration of sleep. A significant relationship was also seen between psychological distress and health adjustment with the number of close friends.
Conclusion: Extrovert and neuroticism personality is dominant among the nursing students. Psychological distress is faced by majority of the subjects and majority of the subjects belonged to very unsatisfactory adjustment category. Therefore, student friendly environment is needed in the colleges to decrease to the level of distress faced by the students and to help them in easy adjustment.
Biography
Anita P is a graduate of College of Nursing, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi and has also pursued her MSc in Psychiatric Nursing from the same institute. She has been awarded with second prize for scientific oral paper presentation in the 15th Annual Conference of the Indian Academy of Geriatrics.
E-mail: anita.9.9.1992@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi