Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
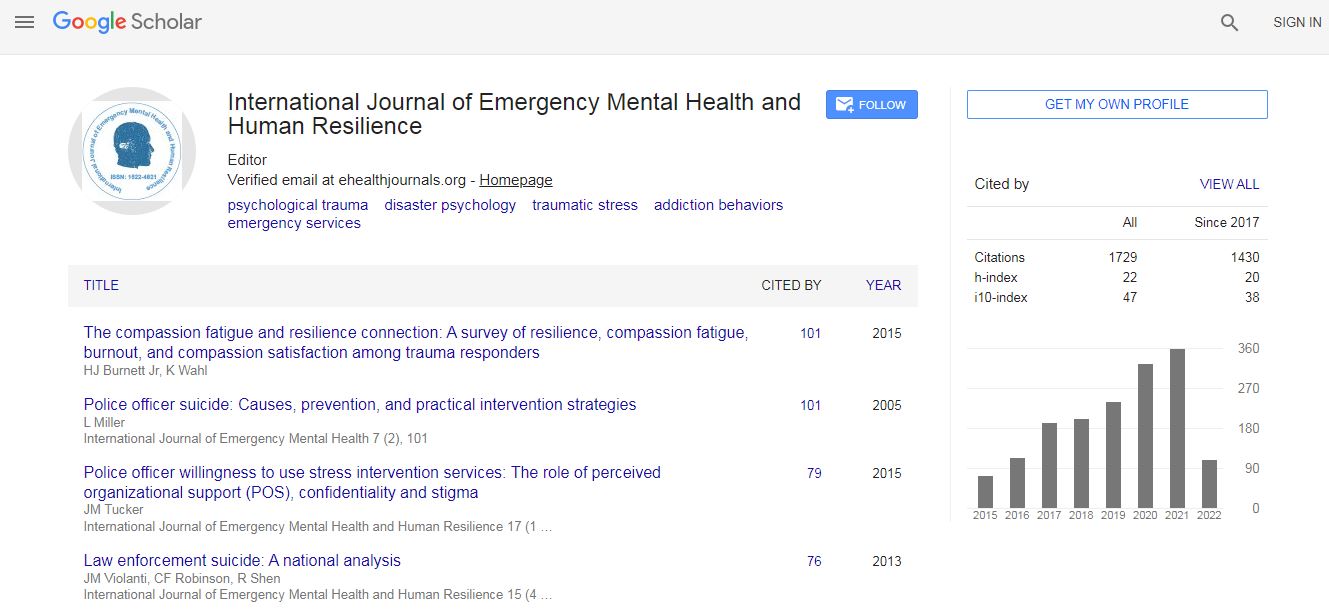
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 4948
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- CiteFactor
- Publons
- Pubmed
- science Gate
- scispace
- world cat
Useful Links
Related Subjects
Share This Page
A study of female adolescent depression in rural areas of India
6th World Congress on Mental Health, Psychiatry and Wellbeing
Soumen Acharya
National Institute of Public Co.operation and Child Development, Indai
Posters & Accepted Abstracts: Int J Emerg Ment Health
Abstract
The study sought to identify the role of cognitive distortion and parental bonding in depressive symptoms among Female adolescents l in rural India. The study also aims to ascertain the extent to which parent-child relationship, specifically father care and mother care; and, father overprotection and mother overprotection differ in the way they contribute to depressive symptoms of adolescents. Materials and Methods: A total of 150Fe male adolescents aged 18- 19 were drawn through random sampling. The educational institution was randomly selected from a list of higher educational institutions in India. The subject chosen for the study were also randomly selected from a class of 40-50 students. All tests were administered in the group of 20- 30 students. Stepwise multiple regression analysis was carried out to ascertain the contribution of cognitive distortion (selfcriticism, self-blame, helplessness, hopelessness, and preoccupation with danger); parent-child relationship (mother care, mother overprotection, father care, father overprotection) towards depressive symptoms. Survey Instrument: Reynolds Adolescent Depression Scale (RADS-2) was developed by William Reynolds (2010) to measure the severity of depressive symptoms in adolescents in clinical settings. The RADS-2 is a brief, 30-item self-report measure that includes subscales which evaluate the current level of an adolescent’s depressive symptoms along four basic dimensions of depression: (1) dysphoric mood; (2) anhedonia; (3) negative self-evaluation; and, (4) somatic complaints. In addition to the four subscale scores, the RADS-2 yields a depression total score that represents the overall severity of depressive symptoms. The reliability and validity of the test are well-established with an internal consistency of 0.86, test-retest of 0.80, and a validity criterion of 0.83. Cognitive Distortion Scales (CDS) was developed by John Briere (2000). It measures distorted or negative cognitions and consists of 40 items. Each symptom item is rated according to its frequency of occurrence over the preceding month; using a five-point scale range from never to very often. The five subscales are selfcriticism, self-blame, helplessness, hopelessness, and preoccupation with danger. The score on each dimension can be added to 9, which is the total score. The reliability and validity of the test are well-established, with the reliability of 0.89 and validity of 0.94. Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI) was developed by Parker, Tupling, and Brown (1979). PBI is a 25-item instrument designed to assess the children’s perception of the parent-child relationship in terms of parental behaviors and attitudes. The authors identified two variables that are important in developing parent-child bonding: (1) care and, (2) overprotection. Out of 25 items, 12 items measure children’s perception of their parents as caring with the opposite end of the spectrum being indifference or rejection, the remaining 13 items assess children’s overprotectiveness with the extreme opposite being encouragement and independence. The care subscale allows a maximum of 36 and overprotection a score of 39. The scale yields information on four dimensions, namely: mother care, father care, mother overprotection, and father overprotection. The participants’ responses are scored on a fourpoint scale ranging from “very likely” to “very unlikely”. Some of the items are reverse scored. The PBI demonstrated high internal consistency with split-half reliability coefficients of 0.88 for care and 0.74 for overprotection. The instrument shows good concurrent validity and correlated significantly well with the independently rated judgment of parental care and overprotection.Biography
E-mail: drsoumenacharya@gmail.com

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi