Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
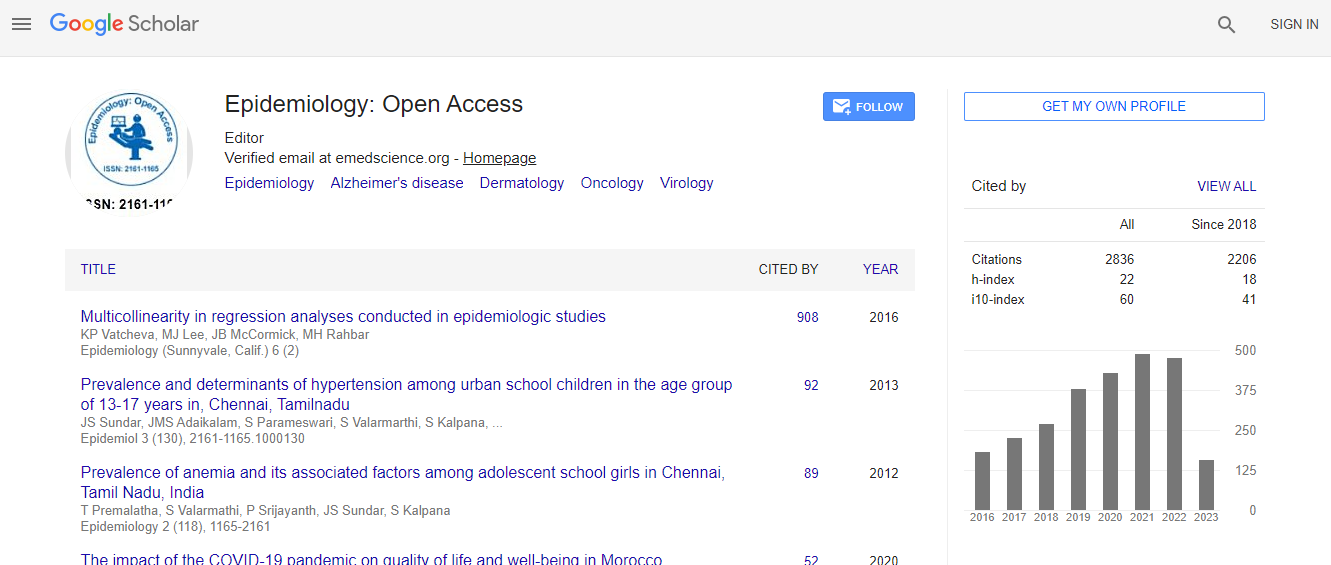
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3864
Epidemiology: Open Access received 3864 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
A comparison of samplers for inhalable welding fumes and laboratory analysis for manganese
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Verpaele Steven1, Jouret Jonathan1, Vanoirbeek Jeroen2, Poels Katrien2, Godderis Lode2, Haegeman Martine3, Martens Frank4 and Lepla Bart4
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Welding fumes are a major domain of interests among occupational hygienist. Sampling these fumes demand great skill of
the occupational hygienist, with important considerations such as the use of samplers, filters, sampling time and laboratory
analysis. This study focused on the differences that may occur while sampling and analyzing welding fumes. The comparisons
were done by using the Workplace Atmosphere Multisampler (WAM). The device was earlier validated for the comparison of
respirable dust, but could also be validated for inhalable welding fumes (5.5% average variation) in this study. At the same time,
the necessity of the use of a simplified torso for inhalable dust sampler comparisons was evaluated. The study shows that the
use of a simplified torso was unnecessary to use in the selected workplace conditions (calm air conditions), since the variation
between the WAM and the Torso was not more than 4.9%. Mixed Cellulose Esters filters (MCE) were used as reference filters
and compared to polycarbonate (PC), polyvinylchloride (PVC) and glass fiber filters (GF). Gravimetric analysis found that the
MCE filters were under sampling, compared to the PVC (y=0.88x), the PC (y=0.82x) and the GF (y=0.91x), while there were
no significant differences found in between the other types of filters. The IOM conductive plastic sampler was tested against
the IOM stainless steel sampler, and no significant differences were found between the two types of samplers. Three different
laboratories performed the analysis of manganese on the different filters by using their own in-house method. The analyzing
techniques used where Inductive Coupled Plasma (ICP)-Mass Spectroscopy (MS) and Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy
(AAS). For the manganese percentage in the gravimetric determined welding fume the same approach was used to compare
the differences. Manganese analysis found that the MCE filters were equally sampling compared to the PVC (y=1.02x) and the
GF (1.06) and is slightly oversampling compared to the the PC (y=1.13x). Compared with the gravimetric analysis it seems that
MCE filters retain more Manganese than the other filters tested in this study.
Biography
Verpaele Steven is President at Belgian Center for Occupational Hygiene –BeCOH, Belgium.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi