Page 38
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
March 22-23, 2017 | Rome, Italy
2
nd
World Congress on
Public Health & Nutrition
Volume 7, Issue 1 (Suppl)
J Community Med Health Educ 2017
ISSN: 2161-0711, JCMHE an open access journal
Public Health 2017
March 22-23, 2017
PREVALENCE OF MAJOR RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASE AMONG
COMMUNITY-DWELLERS ADULTS: RESULTS FROM THE “MESE DEL CUORE 2016 ONSITE”
SURVEY
Emanuele Marzetti
a
, Matteo Tosato
a
, Anna Maria Martone
a
, Elena Ortolani
a
, Sara Salini
a
, Anna Picca
a
, Giulia Savera
a
, Marianna Broccatelli
a
, Maria Elena Delia
a
and
Francesco Landia
a
Catholic University of the Sacred Heart, Italy
Aim:
Primary prevention is essential for reaching cardiovascular (CV) health. This is defined by seven ideal health metrics identified
by the American Heart Association. The aim of the present study is to assess the prevalence and the distribution of these seven ideal
CV health metrics within an unselected population.
Methods:
All the 1206 consecutive individuals (mean age 58.8±14.1 years; 55.6% women) who agreed to be “face-to-face” screened
at the outpatient clinic of Catholic University of Rome, within the context of a national campaign (Mese del Cuore, 2016) of CV
prevention, were included
(www.viaggioalcuoredelproblema.it). The following health metrics have been considered as an ideal:
never/former smoker, regular physical activity (at least two hours per week), body mass index lower than 25.0 Kg/m2, healthy diet
(consumption of at least three portions of fruit and/or vegetables per day), cholesterol lower than 200mg/dl, diabetes absence and a
blood pressure lower than 120/80mmHg.
Results:
Participants presented, on average, 4.1±1.3 ideal CV health metrics (4.3±1.3 and 3.9±1.3 in women and men, respectively,
p<0.001). Only 37.3% covered more than five ideal CV health metrics and 10.0% covered less than three ideal health metrics. Only
4.3% of the study population met all the seven ideal metrics. In particular, only 36.9% (431 subjects) presented normal cholesterol.
The mean cholesterol levels were 206.7 mg/dl and 202.9 mg/dl in women and men, respectively (p=0.08). Interestingly, among those
who thought to have normal cholesterol (n=492), 50% (n=246) had a cholesterol level more than 200mg/dl. Similarly, among those
who did not know their cholesterol level (n=143), 55% (n=79) had an abnormal value. Finally, 451 subjects (37.4%) had not measured
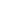
the cholesterol during the last year. Among these subjects, the mean cholesterol level was 203.5±32.3 mg/dl. The figure shows the
percentages of normal and higher cholesterol among subjects who had not previously measured the cholesterol.
Conclusion:
Prevalence of the seven CV health metrics was low in our population, in particular the uncontrolled cholesterol level.
Social initiatives and awareness policies from health care agencies are mandated to promote CV health.
Biography
Emanuele Marzetti is a board certified Geriatrician and Clinical Assistant Professor in Geriatrics at the Teaching Hospital "Agostino Gemelli" (Rome, Italy). He has
a Ph.D. degree in Geriatric Preventive Medicine. His research focuses on frailty and disability in older people. He has authored and co-authored over 150 scientific
publications and serves as associate editor and editorial board member for several biomedical.
emarzetti@live.comEmanuele Marzetti et al., J Community Med Health Educ 2017, 7:1 (Suppl)
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2161-0711.C1.024