Page 50
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 7, Issue 6 (Suppl)
J Nov Physiother
ISSN: 2165-7025 JNP, an open access journal
Physiotherapy 2017
November 27-29, 2017
November 27-29, 2017 Dubai, UAE
5
th
International Conference on
Physiotherapy
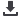
Effects of model of exercise on type-2 diabetes progression
Sub Title:- Exercise is the new pill for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
Castellano Juan
1
, Goyanes S
2
, Ibabe A
2
, Baute D
3
, Prieto H
3
, Diaz-Martinez E
4
, Ubeda N
5
, de Gonzalo-Calvo D
6
, Tomas-Zapico C
7
, Iglesias-Gutierrez E
7
and Fernandez-Garcia B
7
1
Life-Pilates, Spain
2
Servicio de Salud del Principado de Asturias, Spain
3
Servicio Canario de Salud, Spain
4
Consejo superior de Deportes, Spain
5
Universidad Europea de Madrid, Country Name
6
Instituto de Investigaciones Biomedicas de Barcelona, Spain
7
Universidad de Oviedo, Spain
S
troke is a leading cause of disability. There are common motor impairments after
stroke such as hemiparesis in the upper extremity contralateral to the affected
hemisphere.Many stroke patientsmay suffer long termupper limbmotor deficits.This
decrease in hand dexterity could negatively affect the performance of daily activities
that need skilled upper limb use such as grasping force control and coordination as
well as appropriate fine motor skills. Participation, satisfaction and activity of stroke
patients decline and difficulty in using the paretic hand in daily tasks and functional
limitation have been associated with decrease in participation and quality of life. Thus, improving the affected hand function
of chronic stroke patients is vitally important. It has been reported that there is functional re-organization after stroke and that
such cortical plasticity might be correlated with upper limb motor recovery. Understanding the neurophysiological changes
after stroke and how these changes are associated with hand motor recovery as well as how to promote such plastic changes
would assist in developing effective therapeutic interventions that are based on neurophysiological evidence in order to resolve
upper limb motor impairments in stroke patients. During the last two decades, the significant progress in neuroscience has
led to novel concepts for rehabilitation interventions post stroke. The constraint-induced movement therapy (CIMT) has been
shown to improve function and amount of use of the paretic hand of chronic stroke patients and is thought to induce cortical
plasticity. The aim of the speech is to demonstrate and discuss the role of cortical re-organization (plasticity) in motor recovery
of the paretic upper extremity of chronic stroke patients as well as the efficacy of CIMT in improving upper extremity motor
function of chronic stroke patients and its potential underlying mechanism. It also shows the potential cellular mechanisms
that underlie neural plasticity.
Sub Title:- Exercise is the new pill for the prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
P
hysical activity represents a cornerstone in the primary prevention of at least 35 chronic diseases. Today exercise has a role
as therapy in diseases that do not manifest mainly as disorders of the locomotors system. In physiotherapy it is relevant
to train professionals who know how to prescribe exercise effectively based on the theoretical-practical knowledge of the
biological bases. Evidence suggests that in certain cases exercise therapy is as effective as medical treatment and in special
situations more effective or increases its effect. The accumulated knowledge is now so broad that it has to be implemented.
Although there is still a need to define the optimal type and dose of exercise, explore whether high-intensity interval training as
well as low intensity and long-term training or other newer exercise modalities will have a place for specific populations. Health
systems should create the necessary infrastructure to ensure that supervised exercise can be prescribed as a fundamental part
of treatment. Physiotherapists should promote a physical active lifestyle. It is necessary educators who know how to evaluate
globally to each individual the morphological type and the factors of risk not modifiable as those that if can be modified as the
diet and the exercise.
Castellano Juan
et.al., J Nov Physiother 2017, 7:6(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2165-7025-C1-020