Page 66
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Medicinal Chemistry
ISSN: 2161-0444
Medicinal Chemistry 2018
June 14-15, 2018
June 14-15, 2018 | Barcelona, Spain
10
th
World Congress on
Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Design
Development of new polymeric systems with potential applications in chronic wound treatment
Luminita Confederat
1
, Mihaela-Iustina Avram
1
, Amalia Telisca
2
, Mihaela Mosnegutu
2
, Mariana Pinteala
3
, Florica Doroftei
3
and
Lenuta Profire
1
1
"Grigore T. Popa" University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
2
Antibiotice SA Company, Romania
3
P Poni Institute of Macromolecular Chemistry, Romania
Statement of the Problem:
Chronic wounds represent an important issue in medical practice taking into account their impact
on patient’s quality of life, the difficulty of their care and the costs involved. Based on their specific characteristics and biological
properties, chitosan and hyaluronic acid have attracted the researchers’ interest in developing new systems with medical
applications. The purpose of this study was the development of some new polymeric systems, hydrogel type, with potential use
in chronic wounds treatment.
Materials & Methods:
The developed systems were obtained using chitosan hydrogel 5%, bentonite 5% and hyaluronic acid
solution 1%. The proportion of chitosan-bentonite hydrogel and hyaluronic acid solution ranged between 95%-5% and 40%-
60%. In these formulations the arginine 2% was included. The obtained hybrid hydrogels were characterized in terms of pH
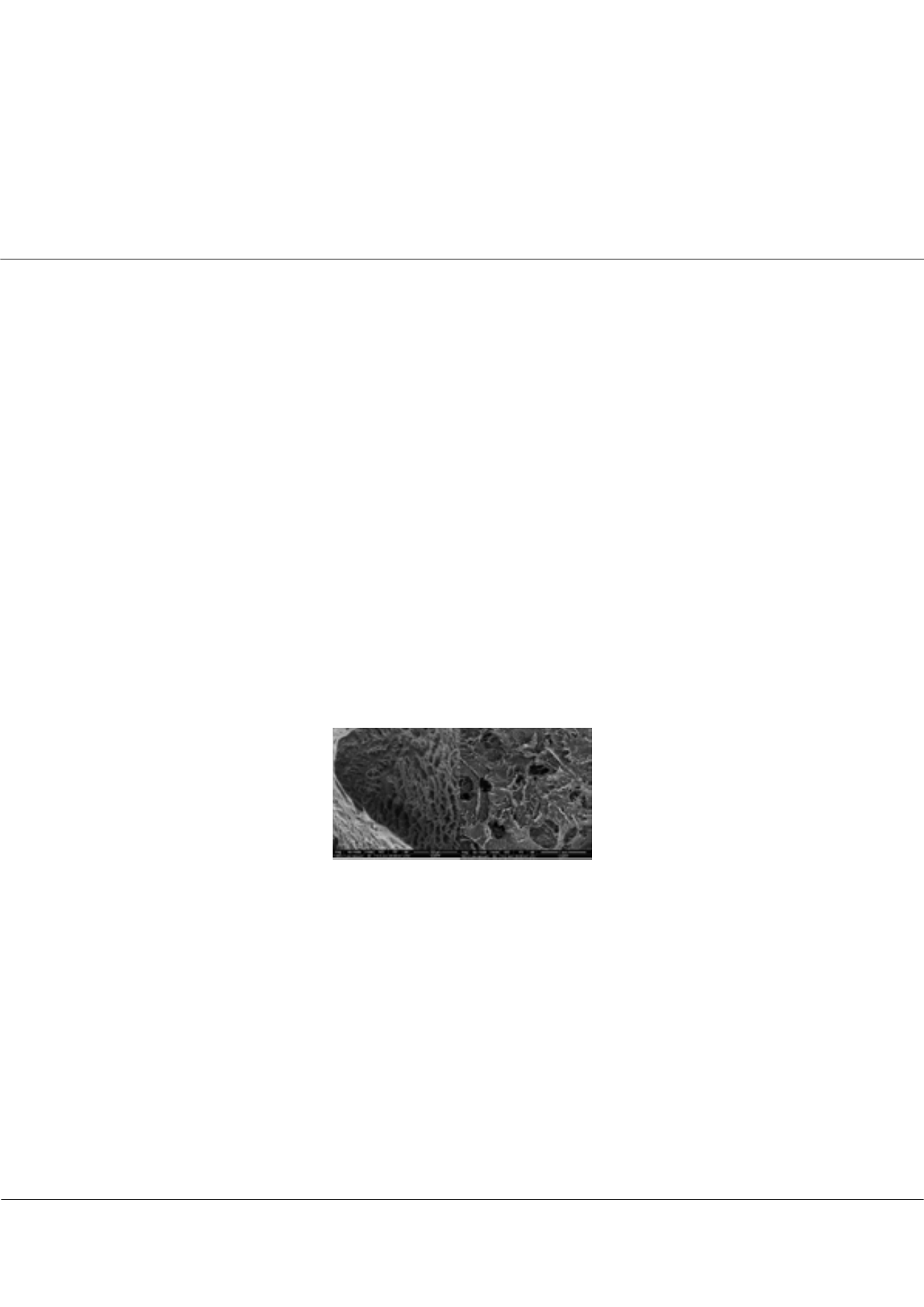
and morphology using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM). The presence of arginine in the polymer matrix was proved by
Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR).
Findings:
There were obtained seven new hybrid hydrogels based chitosan-bentonite-hyaluronic acid-arginine, whose pH
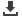
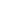
varied between 4.72 and 5.33. The presence of the active substance was proved by IR spectroscopy and the morphology was
analyzed by SEM.
Conclusion & Significance:
The systems developed represent a step in the attempt to improve chronic wound management,
targeting the tissue regeneration and the risk of local infections.
Fig SEM images of hydrogels obtained
Recent Publications
1. Giri T K, Thakur A, Ajazuddin A A, Badwaik H and Tripathi D K (2012) Modified chitosan hydrogels as drug delivery
and tissue engineering systems: present status and applications, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2 (5):439-449.
2. Debats I B J G, Wolfs T G A M, Gotoh T, Cleutjens J P M, Peutz-Kootstra CJ and Van der Hulst R (2009) Role of
arginine in superficial wound healing. Nitric Oxide 15:147-156.
3. Mogoşanu GD and Grumezescu (2014) AM Natural and synthetic polymers for wounds and burns dressing,
International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 463 (2):127-136.
4. Stern R and Maibach H I (2008) Hyaluronan in skin: aspects of aging and its pharmacologic modulation, Clinics in
Dermatology, 26: 106-122.
5. Mayet N, Choonara Y E, Kumar P, Tomar L K, Tyagi C, Du Toit LC and Pillay V (2014) A Comprehensive Review of
Advanced Biopolymeric Wound Healing Systems, Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 103 (8): 2211-2230.
Luminita Confederat et al., Med chem (Los Angeles) 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444-C1-040