Page 36
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Joint Conference
July 17-18, 2017 Chicago, USA
International Conference on
DIAMOND AND CARBON MATERIALS & GRAPHENE AND SEMICONDUCTORS
Volume 6, Issue 6 (Suppl)
J Material Sci Eng, an open access journal
ISSN: 2169-0022
Diamond and Carbon 2017 & Graphene 2017
July 17-18, 2017
The control of pore sizes in porous carbon fiber and its enhanced microwave absorption
Guang Li
Donghua University, China
A
s one of the carbon materials, the porous carbon fiber has played a great role as catalyst support, separation by absorption;
gas storage etc. based on its high aspect ratio. Among related publications, few studies focused on themicrowave absorption
characteristics of porous carbon fibers, although a great number of papers concerned carbon materials such as carbon black,
fiber, tube as microwave absorbents. In this study, porous carbon fibers were prepared through carbonization of the blend
fibers composed of poly (acrylonitrile) (PAN) and poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) with 70 wt % of PAN. The pore size
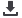
in porous carbon fibers could be controlled by changing the average molecular weight of PAN. The pores of 1-10μm and 0.1-
1μm in diameter were obtained from the blend fibers where the average molecular weight of PAN is 51000 and 83000 g/mol,
respectively (Figure 1). The obtained porous carbon fibers were used as absorbents to make epoxy composites with addition of
2-6 wt%. The microwave absorption properties were stimulated based on a model for a single-layer plane wave absorber. The
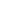
results explained the porous carbon fiber showed much better microwave absorption than carbon nanofiber, and the porous
carbon fiber with small size of pores showed much better microwave absorption than that with large size of pores, as shown
in figure 2. It is believed that the enhanced microwave absorption from the porous carbon fibers is due to a combination of
the dielectric-type absorption and the interference of multi-reflected microwaves. When the pore size in porous carbon fibers
is large, the air-absorber interfaces could be reduced at the same pore volume. Therefore, the superior microwave absorption
of composites filled by porous carbon fiber with smaller pore size may be ascribed to the combination of absorption and
interference of microwaves.
Biography
Guang Li has received her MSc degree in Chemistry from China Textile University in 1985 and PhD in Material Science and Engineering from Donghua University
in 2006, respectively. She has worked as an Assistant Professor, a Lecturer and an Associate Professor at China Textile University from 1986 to 1999. She
was a Senior Visiting Scholar in the University of Twente (Netherlands). She was promoted to be a full Professor at Donghua University (China) in 1999, and is
continuously working on high performance polymer synthesis, porous carbon fibers and their associated processing for energy applications including PEM fuel
cells. She has led more than 20 projects supported by Chinese National Natural Science Foundation, Ministry of Education of China, Shanghai Municipal Science
and Technology Commission, etc. She has published more than 100 scientific papers in high-impacting peer-reviewed journals. She has given more than 24
keynote/invited/oral presentations in international conferences, co-authored 4 books and owns 26 patents. She has been awarded several prizes for recognizing
her great contributions to science and technology, including the second prize of Science and Technology Progress in Shanghai, the second prize from Ministry of
Education of China, the second prize from China Textile Industry Association, etc.
lig@dhu.edu.cnGuang Li, J Material Sci Eng 2017, 6:6(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2169-0022-C1-076