Page 27
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education
Community Nursing 2018
November 19-21, 2018
November 19-21, 2018 Cape Town, South Africa
International Conference on
Community Nursing and Public Health
John Kyalo Muthuka, J Community Med Health Educ 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0711-C6-047
Risk predictors for neonatal mortality and its association with HIV infection among postnatal women
attending Pumwani Maternity Hospital (PMH), Kenya
John Kyalo Muthuka
Kenya Medical Training College, Africa
H
IV in pregnancy has contributed to early neonatal deaths. Rate of HIV
among pregnant women is 15-40% in countries with the highest overall
HIV prevalence. Poor pregnancy outcomes are higher among HIV+ women.
PMTCT focus on vertical HIV transmission, but no data on poor pregnancy
outcomes with HIV among postnatal women. The study design was unmatched
case control. The information was extracted from every file records of the
woman and the newborn outcome within the first twenty eight days after
birth randomly and considering age, sex, anthropometric measurements and
other clinical factors of the newborn and mother. A total of 256 records were
reviewed to retrieve the information retrospectively on cases and controls at 1:1
ratio. Mothers’ pregnancy history, clinical and social economic, comorbidities
and health factors were considered for both cases and controls. The data was
analyzed using SPSS version 20.0. Chi-square test was used to establish the
association between the dependent and independent variables and the level
of statistical significance was set at p-value<0.05. Multiple logistic regression
analyses were performed to adjust for confounding. Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR)
with corresponding 95% confidence interval was estimated. Out of 128 cases (neonatal mortalities) 12.5% were born from
HIV-positive mothers compared to 3.9% among 128 controls HIV sero-positive was found to be significantly associated with
neonatal mortality in bivariate analysis [OR=3.51; 95%CI:1.25-9.91; P=0.012] but not sustained after adjusting for other factors
at the multivariate analysis [AOR=2.33; 95% CI:0.76-7.15; P=0.139]. Multiple logistic regression revealed; LBW [AOR=3.97;
95% CI:2.26-6.98; P<0.001], co-morbidities [AOR=3.84; 95% CI:1.32-11.16; P=0.013]. Mother’s hemoglobin level [AOR=3.18;
95% CI:1.19-8.46; P=0.021], unemployment [AOR=0.43; 95%CI: 0.22-0.85; P=0.016]. There’s increased risk of neonatal mortality
with HIV infection among postnatal women.
Recent Publications
1. Mosioma P, Otundo D, Wambura F Muchiri, Chimbevo Mwagandi L, Muthuka J K, Wang’ombe Ann (2017) Association
of pre-antiretroviral treatment body mass index with Cd4+ T-lymphocyte immune reconstitution among HIV-infected
adults and adolescents.
International Journal of HIV/AIDS Prevention, Education and Behavioral Science
; 3(3): 28-35.
Biography
John Kyalo Muthuka has his interest in HIV/AIDS, Maternal, Child and Neonatal (MCNH), reproductive and adolescent health. He is a Health Educator and Promoter
with over 9 years of experience in both local community and national settings. He is Researcher, Trainer, Lecturer and Community Organizer with a strong focus
towards improving the population’s quality of life through innovative health approach and research. He is a health communication expert and social/community
mobilizer. His work on maternal and child health has boosted current health programs and initiatives to determine what areas need improvement in a child’s health
through training, develop new strategies and programs to boost child health, implement educational tools and programs that raise awareness about child health.
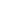
kyamut07@yahoo.co.ukFigure 1:
The conceptual frame work,
Independent variables anddependent variables.