Volume 2
Environment Pollution and Climate Change
ISSN: 2573-458X
Climate Change 2018 &
Global ENVITOX 2018
October 04-06, 2018
Page 66
conference
series
.com
October 04-06, 2018
London, UK
16
th
Annual Meeting on
Environmental Toxicology and Biological Systems
&
5
th
World Conference on
Climate Change
JOINT EVENT
Volker M Arlt, Environ Pollut Climate Change 2018, Volume 2
DOI: 10.4172/2573-458X-C1-001
Modelling mutational signatures of environmental carcinogens in cultured human cells
W
hole genome sequencing (WGS) of human tumors has revealed distinct patterns of mutation that hint at the causative
origins of cancer.The Catalogue of SomaticMutations in Cancer (COSMIC) is a global resource for information on somatic
mutations in human cancer and currently lists 30 distinct mutational signatures. Some signatures are correlated with known
environmental exposures, but the causative origins of many signatures remain unknown. We have developed an experimental
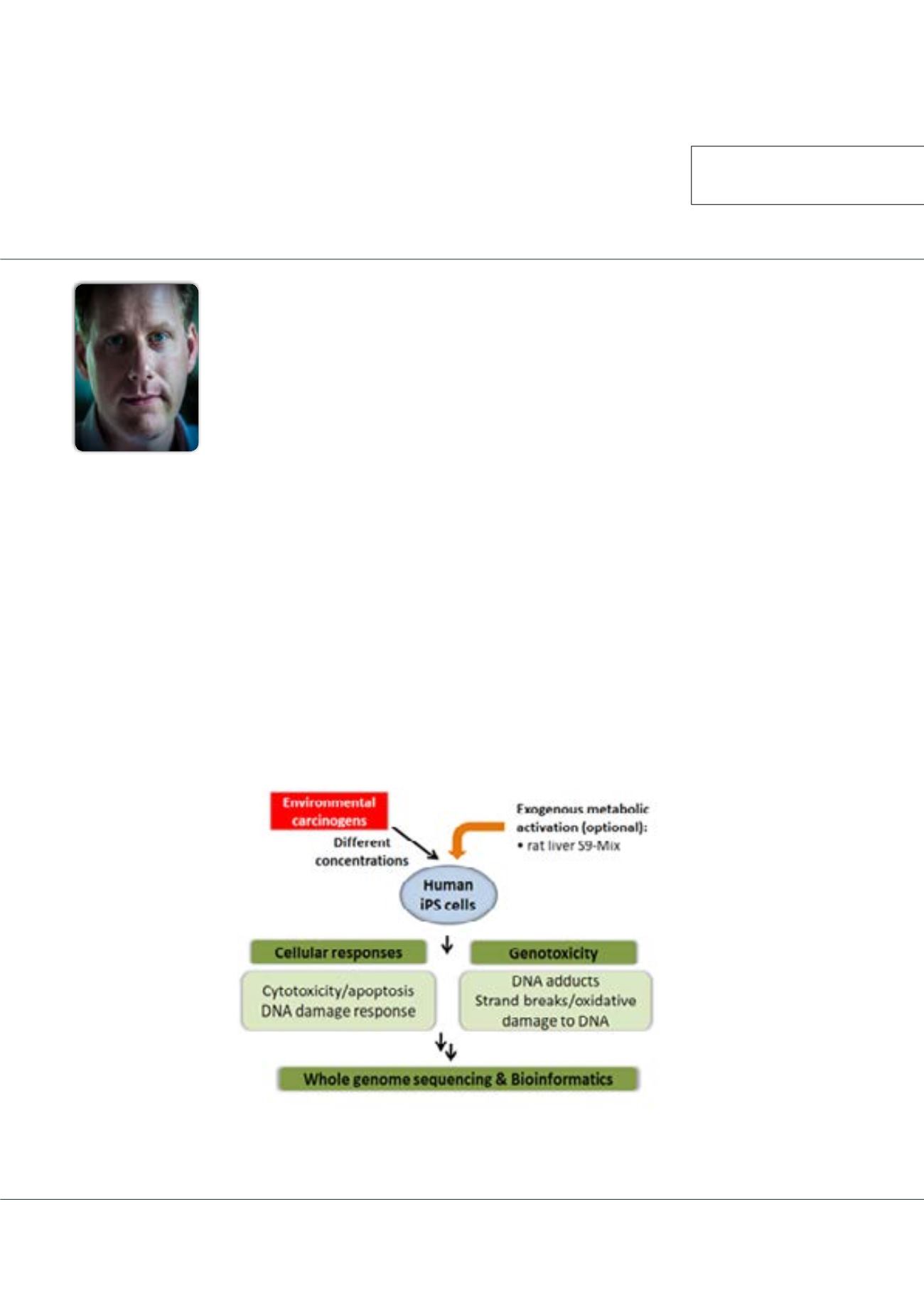
approach using human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells to definemutational signatures of environmental carcinogens byWGS.
Treatment conditions (e.g. concentration) for WGS were optimized by assessing cytotoxicity, DNA damage response signaling
and the formation of premutagenic DNA adducts. After WGS, a ubiquitous background mutational signature was extracted in all
clones showing similarities with COSMIC Signature 18 which has been reported in other cultured human cells. Specific signatures
were identified in human iPS cells, following exposure to benzo[a]pyrene (BaP), simulated sunlight aristolochic acid I (AAI) and
aflatoxin B1 (AFB1), revealing characteristic mutation pattern for each carcinogen that were highly similar to COSMIC signatures
of mutations found in tumors of individuals who were exposed to the agent of interest: predominantly G to T mutations for BaP
were linked to COSMIC Signature 4; C to T for simulated sunlight was linked to COSMIC Signature 7; A to T for AAI was linked
to COSMIC Signature 22; and G to T for AFB1 was linked to COSMIC Signature 24. Thus, human cell-based systems and WGS
can be used to study the genome as a record of environmental exposure.
Volker M Arlt
King’s College London, UK
Figure 1:
Experimental design for modelling the mutational signatures of DNA damaging agents
in human induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by whole genome sequencing.