Page 31
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 08
Innovative Energy & Research
ISSN: 2576-1463
Advanced Energy Materials 2019
July 11-12, 2019
July 11-12, 2019 | Zurich, Switzerland
21
st
International Conference on
Advanced Energy Materials and Research
Electrochemically fabricated substrate dependent smart electrocatalysts Ni-Fe double and Ni-Co-Fe triple
hydroxides for efficient water splitting to oxygen and hydrogen
Shahed U M Khan
and
Meron S Metaferia
Duquesne University, USA
W
ater electrolysis is a significant method that can utilize renewable energy to produce hydrogen; a fuel that can
transform earth towards a clean energy future. Activity of electrocatalysts for water oxidation is fundamental
for energy conversion technologies including integrated solar power generating devices and water electrolyzers.
In this study we have electrochemically fabricated the naturally abundant and stable electrocatalysts Ni-Fe-
double hydroxides, Ni-Fe-Co-triple hydroxides, for efficient splitting of water to oxygen and clean fuel hydrogen.
Oxygen-evolution activities of these electrocatalysts were examined in an alkaline solution of KOH. We focused in
determining electro-catalytic activity of these double and triple hydroxides electrodeposited on different substrates
such as Ni-foam, electrodeposited Ni-Co-oxide on Ni-foam and pressed porous Ni-Co oxide under varying
electrodeposition bath composition, electrodeposition time and electrodeposition current and potentials. We found
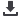
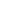
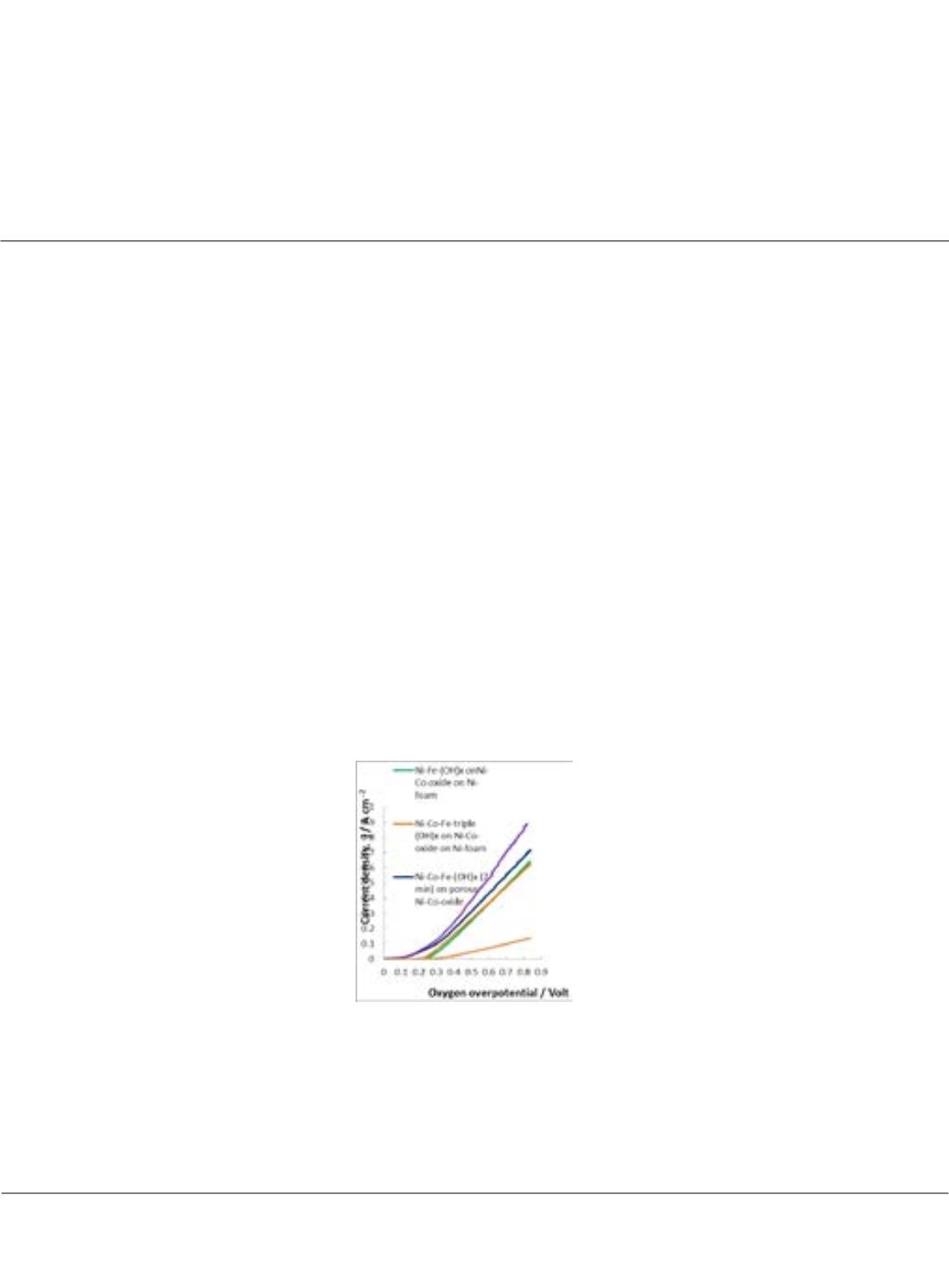
that Ni-Fe-Co triple hydroxide electrodeposited for total of 10 min on pressed porous Ni-Co-oxide sheet acted as a
superior electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction during water splitting reaction. This electrocatalyst generated
a current density of ~ 100.0 mA cm
-2
at an oxygen overpotential of 0.270 volt (= 1.5-volt vs RHE) in 1.0 M KOH at
electrolyte temperature of 25°C. However, this triple hydroxide deposited for 7 min generated 81.0 mA cm
-2
at the
same overpotential, electrolyte concentration and temperature. The synergetic effect of multiple hydroxides and
the substrates was mostly responsible for such enhanced electro-catalytic activity. The effect of higher electrolyte
temperature was also found to have important role in enhancing the current density because of exponential
dependence of reaction rate on temperature. The surface morphology and the composition of these electrocatalysts
were determined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopic (EDS) data.
Recent Publications
1. Khan S U M, Al-Shahry M and Ingler Jr W B (2002) Efficient Photochemical Water-splitting by Chemically
Modified n-TiO
2
. Science 297:2243-2245.
Shahed U M Khan et al., Innov Ener Res 2019, Volume 08
Figure:
The oxygen evolution current density versus oxygen overpotential on Ni-Fe-double hydroxides and Ni-Co-
Fe-triple hydroxides electrodeposited on various substrates such as Ni-foam, Ni-Co-oxide on Ni-foam and on pressed
porous Ni-Co-oxide in 1 M KOH at electrolyte temperature of 25°C measured using the scan rates of 5 mV/sec