Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
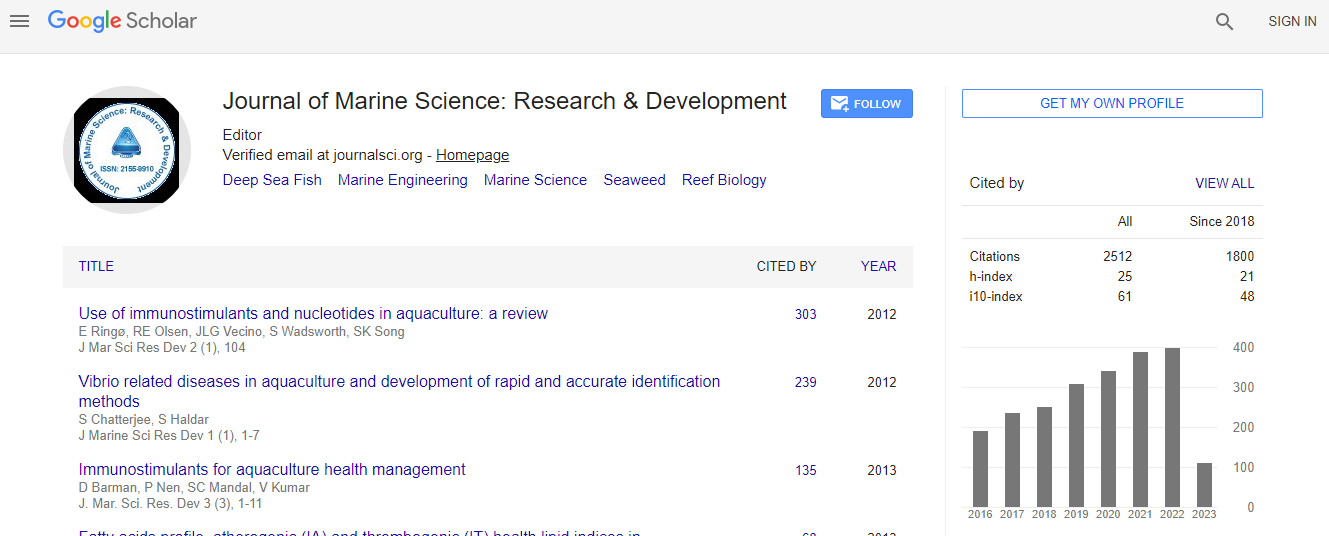
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 3189
Indexed In
- CAS Source Index (CASSI)
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Open J Gate
- Genamics JournalSeek
- Academic Keys
- ResearchBible
- Ulrich's Periodicals Directory
- Electronic Journals Library
- RefSeek
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- Scholarsteer
- SWB online catalog
- Virtual Library of Biology (vifabio)
- Publons
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Deep Sea Mining
Deep sea mining is a relatively new mineral retrieval process that takes place on the ocean floor.Ocean mining sites are usually around large areas of polymetallic nodules or active and extinct hydrothermal vents at about 1,400-3,700 m below the ocean’s surface.The vents create sulfide deposits, which contain valuable metals such as silver, gold, copper, manganese, cobalt, and zinc.
Among the impacts of deep sea mining, sediment plumes could have the greatest impact. Plumes are caused when the tailings from mining (usually fine particles) are dumped back into the ocean, creating a cloud of particles floating in the water. Two types of plumes occur: near bottom plumes and surface plumes.[1] Near bottom plumes occur when the tailings are pumped back down to the mining site.
Related Journals of Deep Sea Mining
Fisheries & Livestock Production, Fisheriessciences, Hydrogeology & Hydrologic Engineering, Ecosystem & Ecography, Journal of Aquatic Ecosystem Stress and Recovery, Journal of Ocean University of China, Marine Biotechnology, International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology.