Wind Energy Potential in Sindh Region
Received: 28-May-2022 / Manuscript No. iep-22-63143 / Editor assigned: 01-Jun-2022 / PreQC No. iep-22-63143 (PQ) / Reviewed: 15-Jun-2022 / QC No. iep-22- 63143 / Revised: 21-Jun-2022 / Manuscript No. iep-22-63143 (R) / Published Date: 28-Jun-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2576-1463.1000291
Abstract
Electricity performs an essential position inside the socioeconomic boom and social prosperity of any country. It is to be taken into consideration because of the fundamental need for human improvement. Nowadays, the low production of power is extreme trouble in Pakistan, which immediately restricts the improvement of the country. 1/3 of Pakistan’s populace does not have any electricity inside, the rural regions, and approximately eight to ten hours of load shedding in city regions and is pretty common. Although Pakistan constantly indicates a deficit with inside the conventional sources, however, no development becomes additionally is being made inside the renewable sources consisting of the wind. Therefore, it's far higher to make use of these natural assets on the way to satisfy the power to deliver Pakistan. In this manuscript, our important goal is to study the potential of wind energy in the Sindh region and how much potential we use for our country.
Keywords: Electricity; Load Shedding; Potential; Renewable Sources; Wind
Introduction
This portion assesses the value of the wind sources inside the Sindh region. The authorities of Pakistan have taken firm measures to provoke wind power projects in Pakistan mainly Sindh. Satellite mapping carried out with the aid of using the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) in collaboration with the National Renewable Energy Laboratories (NREL), USA anticipated a gross capability in Sindh province is 43.8 GW out of which 11 GW is usable. Wind power as renewable sources is greater favourable nowadays due to the fact these are surroundings pleasant with zero emissions compared to standard power assets. It is better to make use of those natural assets to meet the power delivery to the country. In this manuscript, my major goal is to observe and outlooks the country's electricity profile scenario vis-à-vis wind power capability characteristics of the most crucial wind corridor with inside the Sindh province [1]. Sindh has around 350 kilometres (km) coastal line for the wind power capability. In this paper, I attempted to estimate the wind power capacity of the Sindh region and what number of wings power makes use of in Sindh with the assist of IPPs.
Due to the depletion of a power source like fossil fuels, there's a multiplied usage inside the non-traditional reasserts including wind power, solar power, and biogas power. Wind Energy is the conversion of wind to electric power. Wind energy is a less expensive form of electricity as compared with coal, fuel line, or fossil gasoline powered plants [2]. Wind power exists over huge geographic areas. Increased deployment of wind strength and energy-efficient strategies has ended in substantial energy security, weather alternate mitigation, and financial benefits. The wind has the capability to generate far more than 1 percent of the entire power of the word. Pakistan generates 6% of power from the wind and 80% of wind power produce from Sindh regions due to the fact air velocity of Sindh is 6 to 11 ms that is efficient for generating energy for a complete year. The bulk of this wind useful resource is derived from the power of the extremely good southwest monsoon system which blows over Pakistan. The wind electricity power plant in Pakistan begins operating with 50 MW ability in Sindh in 2012.
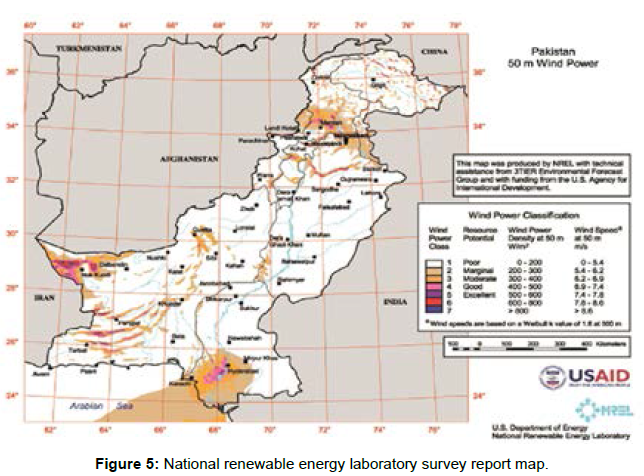
Alternative Energy Development Board (AEDB) and Pakistan Meteorological Department measure the velocity of the wind and introduce regions for wind electricity plant [3]. Initial surveys executed in the past due to the nineties and early years of this century indicated that coastal regions of Sindh the respectable reviews pick out that in Sindh Province, district Thatta, Karachi, Hyderabad, and Badin potential sites for development, set up, and commissioning of wind farm projects [4]. Sindh has the ability to produce about forty-three GW of wind energy, says the latest United States Agency for International Development (USAID) report (Figure 1).
Potential Calculation
Wind Potential is one of the technologies to count the wind to be used full work the most wind potential may be received from the subsequent equation.
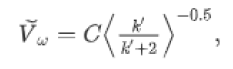
Where Ṽω is the maximum wind power k′, C is the dimensionless element and Weibull factor respectively
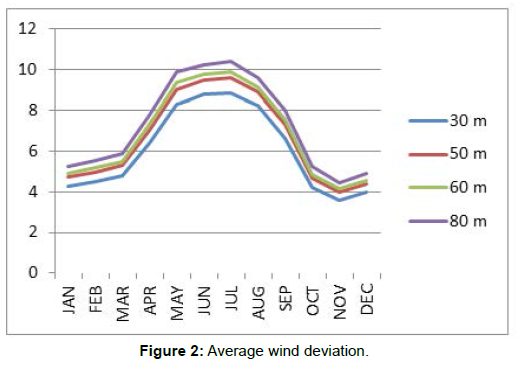
Average Wind Deviation
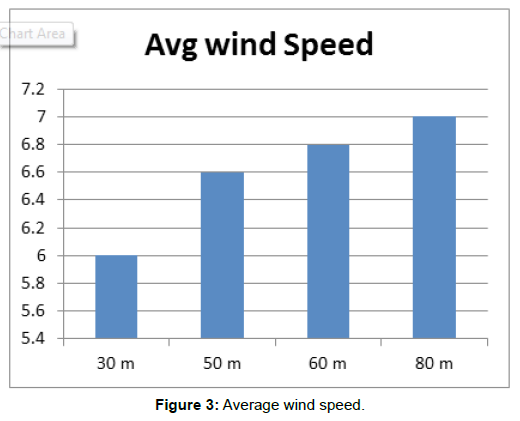
As regarding the maximum of the locations, the wind speed constantly changes with altitude, which basically relies upon on parameters terrain roughness and combining of the environment (Figures 2 and 3). The wind velocity deviation with altitude relation is defined as follows:
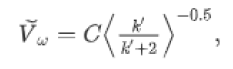
Where, Ṽavg2, Ṽavg1, are the common wind speeds at h2′ and h1′ altitudes respectively, and the exponent energy is the land surface roughness environment stability, and its most and minimum limits are the “0.5” and “0.05” respectively
The annual wind velocity at 30 m and 50 m, 60 m, and 80 m, respectively as proven in (Table 1).
| S.No | Company Name | Project Capacity (MW) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FFC Energy Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 2 | Zorlu Enerji Pakistan (Pvt.) | 65.4 | Completed |
| 3 | Three Gorges Pakistan First Wind Farm (Pvt.) Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 4 | Foundation Wind Energy II (Pvt.) Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 5 | Foundation Wind Energy –I Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 6 | Sapphire Wind Power Company Limited | 52.8 | Completed |
| 7 | Metro Power Company Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 8 | Yunus Energy Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 9 | Master Wind Energy Pvt. Limited | 52.8 | Completed |
| 10 | Act Wind (Pvt.) Ltd. (Tapal Wind Energy Pvt. Limited) | 30 | Completed |
| 11 | Gul Ahmed Wind Power Ltd | 50 | Completed |
| 12 | Tenega Generasi Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 13 | Hydro China Dawood Power Pvt. Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 14 | Sachal Energy Development Pvt. Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 15 | UEP Wind Power Pvt. Limited | 99 | Completed |
| 16 | Jhampir Wind Power (Pvt.) Limited | 50 | Completed |
| 17 | Hawa Energy Pvt. Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 18 | Hartford Alternative Energy Pvt. Limited | 49.3 | Completed |
| 19 | Three Gorges Second Wind Farm Pakistan Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 20 | Three Gorges Third Wind Farm Pakistan (Pvt.) Limited | 49.5 | Completed |
| 21 | Tricon Boston Consulting Corporation Pvt. Limited – A | 49.6 | Completed |
| 22 | Tricon Boston Consulting Corporation Pvt. Limited – B | 49.6 | Completed |
| 23 | Tricon Boston Consulting Corporation Pvt. Limited – C | 49.6 | Completed |
| 24 | ACT 2 Wind Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 25 | Artistic Wind Power Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 26 | Din Energy Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 27 | Gul Ahmed Electric Ltd | 50 | Under construction |
| 28 | Indus Wind Energy Ltd | 50 | Under construction |
| 29 | Lakeside Energy Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 30 | Liberty Wind Power-1 Pvt. Ltd | 50 | Under construction |
| 31 | Liberty Wind Power-2 Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 32 | NASDA Green Energy Pvt. Limited | 50 | Under construction |
| 33 | Metro Wind Power Ltd | 60 | Under construction |
| 34 | Transatlantic Energy Pvt. Limited | 48.3 | Under construction |
Table 1: The status of company project capacity (MW)
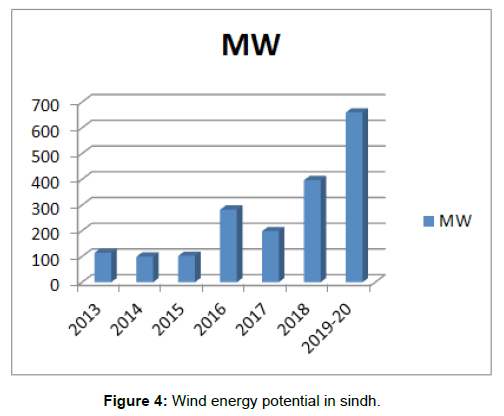
Sindh Wind Energy Projects Status
Sindh became assigned a project to the Alternative Energy Development Board (AEDB) to put in force renewable electricity projects especially wind and sun electricity projects. With the contribution of AEDP, there are numerous renewable electricity projects (Figure 4).
Wind Energy Potential in Sindh
Pakistan has a coastal line of 1046 km, of which the Sindh coastal line is almost 250 km that's wealthy withinside the wind electricity source up to 20 GW. The wind velocity reaches around five to twelve m/s in wind corridors of Sindh [5]. A general coastal place of Sindh 9749 km2. The common capability factor is 25%, the ability which may be acquired from 1 km2 is 18 MW. Thus, the gross capability in Sindh province is 43.8 GW out of which 11 GW is usable.
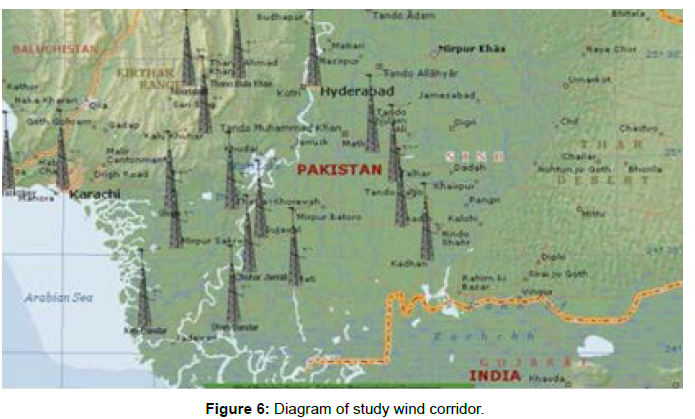
Alternative Energy Development Board (AEDB) has assigned the land to 23 Independent Power Producer (IPPs) for the production of wind energy. Those projects generate common 50 MW at every location, namely Jhimpir, Lakha, Gharo, Bhambhor, and kuttikun operational wind energy projects in sindh which are with the cumulative potential of 1199MW withinside the winding corridor of Jhimpir and Gharo, Keti Bandar, the sites of Sindh province (Figures 5 and 6).
Results
The market for wind energy in Pakistan is predicted to grow at a CAGR of greater than 5% within side the forecast duration of 2020- 2025. Factors which include supportive government rules and efforts to fulfil power demand the use of renewable to decrease dependency on fossils are predicted to be massive participants to the growth of the marketplace [6]. The declining expenses of renewable technology are getting competitive with fossil fuel sources, and further subsidies on renewable are driving the renewable marketplace further. On the opposite hand, due to the significant scale of dependency on fossil fuel-based power technology, very much less improvement within side the renewable energy sector in Pakistan, and limited power capability by variable renewable energy sources, there may be a bad effect at the increase of wind electricity.
• Wind power has an enormous capacity in Pakistan. Because of this, Pakistan has proven a CAGR of greater than 40% from 2014- 2018, in phrases of set up capability of wind energy, ensuing in greater than a thousand MW of operational wind farms in 2019.
• The authorities of Pakistan is aiming to gain 6% of its electricity generation from renewable via way of means of 2030, aside from hydroelectricity, which turned into predicted at 3% in 2018. Solar and wind are going to be the most important markets within side the coming years.
• In 2019, the Alternative Energy Development Board of Pakistan accorded approval for eleven different wind projects together comprising greater than 500 MW, which can be predicted to be operational within side the forecast duration, using the wind marketplace of Pakistan
Concluding Remarks Renewable energy sources evaluation and electricity output estimation from a hypothetical wind turbine at Gharo have proven that commonly in the course of summertime season six months April-September, there are strong sustainable winds basically from Southwest and in the course of this excessive ability factor of 32- 50% might be achieved. Normally in the course of summertime season, warm months nearby power call for are also predicted to be high. However, during the remaining six months the typically slight winds are experienced and commonly during this era local power needs is also low. Annual ability factor of 27% suggest that summertime season six months energy production remains compensating the low electricity output in the course of the last six months and the location is appropriate for setting up commercially viable wind farms
Acknowledgment
The author is grateful to Mr. Mansoor Ali Zaheer assistant professor of Mechanical Department, University Of Sargodha who assisted in data analysis and typing etc.
References
- Akpinar EK, Akpinar S (2004) Determination of the wind energy potential for Maden-Elazig, Turkey. Energy Convers Manag 45: 2901–2914.
- Bagiorgas HS, Assimakopoulos MN, Theoharopoulos D, Matthopoulos D, Mihalakakou GK( 2007)Electricity generation using wind energy conversion systems in the area of Western Greece. Energy Convers Manag 48: 1640–1655.
- Baloch MH, Kaloi GS, Wang J (2015) Feasible wind power potential from costal line of Sindh Pakistan. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 10: 393–400.
- Lam JC, Lun IYF(2000) A Study of Weibull parameters using Long-term Wind Observations. Renewable Energy 20:145-153.
- Chaudhry Qamar Z, Hussain A, Wang J (2003) Preliminary Investigation of Wind Power Potential of Gharo-Sindh. PMD Tech Report 6:1-11.
- Celik A (2003) Weibull representative compressed wind speed data for energy and performance calculations of wind energy systems. Energy Convers Manag 44: 3057–3072.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Awais M (2022) Wind Energy Potential in Sindh Region. Innov Ener Res, 11: 291. DOI: 10.4172/2576-1463.1000291
Copyright: © 2022 Awais M. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2654
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Jul 08, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 2211
- PDF downloads: 443