Review Article Open Access
White Spot Lesions in Orthodontic Patients: Formation, Prevention and Treatment
Irena Gavrilovic*
Faculty of Dental Medicine, University “St Cyril and Methodious”, Denal Clinical Centar, Orthodontic Deparment, Vodnjanska 17 Skopje, Macedonia, Europe
- *Corresponding Author:
- Irena Gavrilovic
Faculty of Dental Medicine
University “St Cyril and Methodious”
Denal Clinical Centar, Orthodontic Deparment
Vodnjanska 17 Skopje, Macedonia, Europe
Tel: 39871438398
Fax: 38923075333
E-mail: i.gavrilovic@yahoo.com
Received Date: May 23, 2014; Accepted Date: July 30, 2014; Published Date: August 05, 2014
Citation: Gavrilovic I (2014) White Spot Lesions in Orthodontic Patients: Formation, Prevention and Treatment. J Oral Hyg Health 2:154. doi: 10.4172/2332-0702.1000154
Copyright: © 2014 Gavrilovic I. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Oral Hygiene & Health
Abstract
During fixed orthodontic treatment, white spot lesions (WSLs) may arise on the teeth as undesirable situation. The white spot lesions are defined as areas of demineralization of tooth enamel that can occur during the treatment with fixed orthodontic appliances, around brackets, tubes or orthodontic rings. Their location is mostly on the labino-gingival part of the tooth crown. The white spots can be seen even after 1 month of setting fixed appliances and in some patients after 6 or 12 months. This state of demineralization of enamel is a complication of orthodontic treatment and represents a major clinical problem that can compromise the results of successfully treated case. Orthodontic wont to improve not only function but also the aesthetic appearance of patients, so during the treatment these complications should be minimized. The most common reason for this phenomenon is inappropriate and poor oral hygiene. In this paper there is the contemporary review of risk factors for the formation, prevention and successful treatment of WSLs. For avoiding side effects of wearing orthodontic braces, for each patient, before setting fixed orthodontic appliances, training is require for maintaining excellent oral hygiene. In literature there are numerous studies for the prevention and treatment of white spot lesions. The use of fluoride (in toothpaste, gels and solutions for the mouth, in bonding materials for orthodontic braces, fluoride varnish), Casein phosphopeptide-amprphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP0 in topical crème and microabrasion can greatly contribute to the process of remineralization of enamel and successful treatment of WSL.
Keywords
White spot lesions; Demineralization; Fluoride
Introduction
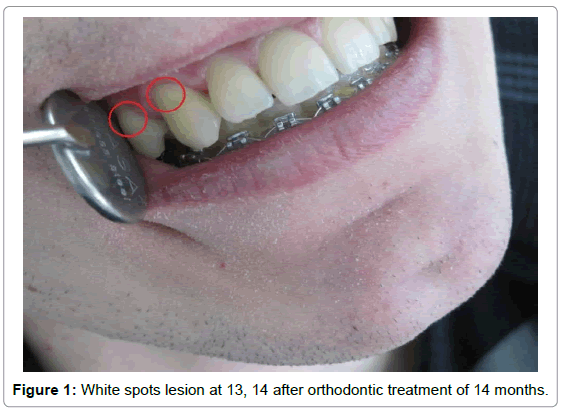
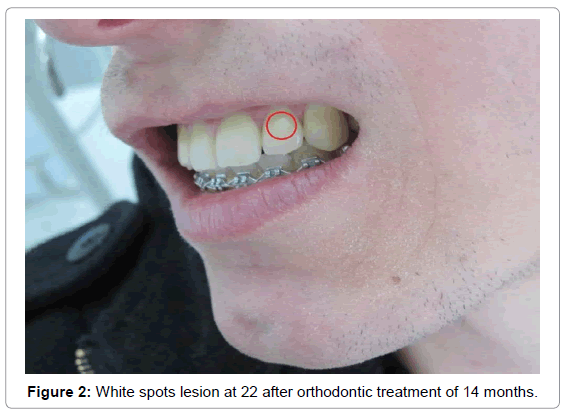
The appearance of white spot lesions on labial surface of the teeth during orthodontic treatment is the most common clinical problem that occurs as a complication of orthodontic treatment. Increased and prolonged accumulation of plaque is one of the reasons that these unwanted changes occur. The presence of brackets, attachments, wires, rings and ligatures and their uneven surface in the oral cavity increases the accumulation of plaque on the labial surface of crowns. In patients with poor oral hygiene comes to the accumulation of plaque and its prolonged effect, which results with demineralization of enamel (Figures 1 and 2).
According to [1] white spots are defined as “the first sign of decay, which is seen as a lesion of the enamel and can be detected with the naked eye”. Tufekci E et al. [1] defined WSLs as “subsurface enamel porosity from carious demineralization, which we can see as milky opacity when located on smooth surface”. Appearance of white spot lesions after orthodontic treatment ranges from 2-96% [2]. The most commonly affected teeth are maxillary central and lateral incisors and canines and mandibular caninesand bicuspids [3]. Management of white spots includes the methods of prevention, demineralization and methods used for remineralization of lesions that are already formed [4]. Remineralization is the process of restoring minerals in the form of mineral ions in dental enamels [4]. Demineralization is the process of removing minerals, in the form of mineral ions, from dental enamel [4].
Etiology of the Demineralization
The appearance of white lesions is the result of a process that occurs between dietary carbohydrate and bacteria found in saliva. This results with imbalance in the process of demineralization and remineralization that takes place on the surface of the enamel [5]. Due to loss of minerals below the surface of the enamel comes to appearance of opaqe white spot on the tooth. This increases the porosity of the enamel surface of the tooth and it looks like a chalk. If the surface of the tooth remains intact, it is possible to stop the process of demineralization and can become spontaneous reversible remineralization of the lesion [5-7]. For this spontaneous remineralization requires a combination of fluoride that can be inserted for therapeutic purposes and minerals found in salivata. If there is prolonged loss of minerals below the surface of the enamel spontaneously remineralization can not occur and cavities can appear. Major role at the formation of these lesions have change of pH of saliva and the presence of bacteria in plaque [4,8].
Bacteria
From literature data we found that in caries lesions there are increased presence of Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilus [4]. Sudjalim TR et al. suggested that acid bacteria are increasing when orthodontic appliances are present in the mouth. In period of 6-15 weeks after the removing orthodontic appliance reduction of bacteria have been found [2].
Saliva
Saliva plays an important role in the process of remineralization of enamel. With the help of saliva, fluoride ions can rich to the enamel. It regulates the exposure of the teeth at carbohydrate from the food and acidity of the plaque, which have acid bacteria. Its flow provides mechanical self-cleaning surface of the teeth [3,5,6]. Teeth that are less exposed to the flow of saliva are frequently exposed to the appearance of white spot lesions. These are the teeth in the anterior segment of maxillary dental arch on their buccal side. Gingival third of the crown, between the place where was the bracket placed and the cervical side of the crown is most commonly affected. Lingual surface of mandibular teeth is least susceptible to demineralization due to plentiful flushing by saliva. Therefore, in patients with lingual retainers at the mandible from canine to canine can often encounter formation of calculi. It tells us of increased mineralization due to saliva [9]. PH of saliva is important because it can reduce acidic products from the dental plaque. PH of saliva depends on the amount of secretion. In unstimulated saliva pH equals less than 6, while in stimulated saliva PH is about 8. Low or acidic PH stimulated the growth of acid bacteria.
Factors that Affect the Prevention of WSLs
There are several factors that can contribute to prevent WSLs. These are primarily educating patients for proper maintenance of oral hygiene before setting fixed appliances and the use of fluoride during orthodontic treatment [6]. If due to improper hygiene WSLs appear, there are methods who are contributing to relieve their visibility and satisfying aesthetic component, like use of CPP-ACP crème and the method of microabrasion.
Patient education and oral hygiene
The presence of fixed orthodontic appliances complicates maintenance of oral hygiene. It further results with the accumulation of dental plaque located more on cervical enamel edge , the edge between brackets and the gingiva. Because of that, this part of the tooth crown considered to be place where WSLs often occurrence [6]. Before the start of orthodontic treatment in patients who do not maintain good oral hygiene, should be aware of the consequences that may arise due to improper hygiene. Every patient needs to know techniques and methods for proper brushing the teeth.
Dental assistant should pay attention to the technique of brushing teeth. It is recommended at least twice a day to brush the teeth to avoid the accumulation of plaque and for better results after every meal.
Fluoride
Fluoride have important role in preventing the formation of WSLs. They can incorporate at the hydroxyapatite grid of the enamel of the tooth and thus increase tooth’s strength. Calcium fluoride is the main product that occurs during treatment with fluoride on enamel and has an important cariostatic [2,6,10]. During orthodontic treatment fluoride can be used in various ways: mouth rinse, fluoride in toothpaste, gels and varnishes which are used for coating the teeth. Multiple studies have shown that regular use of fluoride in toothpaste does not inhibit the development of lesions around brackets [9]. Using solvents mouth (mouth rinse) with sodium fluoride (0,05% or 0.2%) during orthodontic treatment could reduce the demineralization process. Using glass ionomer cement for bonding orthodontic brackets and rings, gave significant reduction of demineralization of 16.5 % compared to composite resin cements [2,11-13]. Duraphat (5% NaF), fluorprotector (1% difluorosilane and 0.1% F), duraflor (5% NaF) are the commonly used fluoride varnishes.
Casein phosphopeptide-amprphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)
This cream should be used after brushing the teeth twice a day. After applying the cream, patient should be with open mouth for 3 minutes. After 30 minutes of application, eating and drinking is prohibited. During this period, the cream can act on teeth at repairing the WSLs (CPP-ACT-GC Tooth Mousse).
Microabrasion
This technique is implemented with 18% hydrochloric acid which is a mix of fine pumice powder to obtain a slurry form. Teeth which started the formation of white spots, carefully cleaned with pumice and water. For isolating surrounding tissues we can use rubber dam. This procedure is repeated 3-4 times for a period of 2 weeks. In the literature [4] found that microabrasion technique gave a dramatic cosmetic results. They achieved 99% success for mild and moderate white spot lesions and 94% for severe lesions.
Recommendations
Based on the literature data and our own experience we can suggest some recommendations that will lead to prevention of WSL:
• To motivate patients with fixed orthodontic appliances for normal maintenance of oral hygiene
• To instruct patients to brush teeth properly
• Minimum brushing teeth to be twice a day
• To use daily fluoride mouth rise (0.05% NaF)
• To use the glass ionomer cements for rings and brackets bonding
• If white spot lesions appear Tooth Mouth paste or microabrasion should be used
Conclusion
Demineralization which occurs during orthodontic treatment is a major clinical problem for dentist and for the patients. The appearance of white spot lesions during orthodontic fixed treatment can be prevented. Maintaining oral hygiene and mechanical removal of plaque is essential for preventing the occurrence of WSLs. The presence of fluoride even in small concentrations is necessary to inhibit cavities. If white spot lesions appear using tooth mouse and mikroabrasion can enhance cosmetic effect.
References
- Tufekci E, Dixon JS, Gunsolley JC, Lindauer SJ (2011) Prevalence of white spot lesions during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances. See comment in PubMed Commons below Angle Orthod 81: 206-210.
- Sudjalim TR, Woods MG, Manton DJ (2006) Prevention of white spot lesions in orthodontic practice: a contemporary review. See comment in PubMed Commons below Aust Dent J 51: 284-289.
- Maxfield B, Hamdan A, Tufekci E, Shroff B, Best A, et al. (2012) Development of white spot lesions during orthodontic treatment: Perceptions of patients, parents, orthodontists, and general dentists, Am Journal of Orthod and DentofacOrthop 141: 337 - 343.
- Srivastava K, Tikku T, Khanna R,Sachan K (2013) Risk factors and management of white spot lesions in Orthodontics. J OrthodSci 2: 43-49.
- O'Reilly MM, Featherstone JD (1987) Demineralization and remineralization around orthodontic appliances: an in vivo study. Am J OrthodDentofacialOrthop 92: 33-40.
- Hamdan AM, Maxfield BJ, Tüfekçi E, Shroff B, Lindauer SJ (2012) Preventing and treating white-spot lesions associated with orthodontic treatment: a survey of general dentists and orthodontists. J Am Dent Assoc 143: 777-783.
- Shungin D. Long-term changes of white spot lesions after orthodontic treatment. Masther Thesis in Publis Health, Epidemiology and Public. Health Sciences Department of Public Health and Clinical Medicine Umeå University 1-37.
- BasaranG,Veli I, Basaran EG (2011) Non-Cavitated Approach for the Treatment of White Spot Lesions: A Case Report. International Dental Research 1: 65.
- Chang HS, Walsh LJ, Freer TJ (1997) Enamel demineralization during orthodontic treatment. Aetiology and prevention. Australian Dental Journal 42:322-7.
- Akin M, Basciftci FA (2012) Can white spot lesions be treated effectively? Angle Orthod 82: 770-775.
- O'Brien KD, Read MJ, Sandison RJ, Roberts CT (1989) A visible light-activated direct-bonding material: an in vivo comparative study. Am J OrthodDentofacialOrthop 95: 348-351.
- Thiyagarajah S, Spary DJ, Rock WP (2006) A clinical comparison of bracket bond failures in association with direct and indirect bonding. See comment in PubMed Commons below J Orthod 33: 198-204.
- Wilson RM, Donly KJ (2001) Demineralization around orthodontic brackets bonded with resin-modified glass ionomer cement and fluoride-releasing resin composite. Pediatr Dent 3:255-259.
Relevant Topics
- Advanced Bleeding Gums
- Advanced Receeding Gums
- Bleeding Gums
- Children’s Oral Health
- Coronal Fracture
- Dental Anestheia and Sedation
- Dental Plaque
- Dental Radiology
- Dentistry and Diabetes
- Fluoride Treatments
- Gum Cancer
- Gum Infection
- Occlusal Splint
- Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
- Oral Hygiene
- Oral Hygiene Blogs
- Oral Hygiene Case Reports
- Oral Hygiene Practice
- Oral Leukoplakia
- Oral Microbiome
- Oral Rehydration
- Oral Surgery Special Issue
- Orthodontistry
- Periodontal Disease Management
- Periodontistry
- Root Canal Treatment
- Tele-Dentistry
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 24308
- [From(publication date):
November-2014 - Nov 21, 2024] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 18960
- PDF downloads : 5348