Use of RPMI in Vitreous Cytology: The Case for Sterile, Single Use Aliquots
Received: 17-Jan-2018 / Accepted Date: 31-Jan-2018 / Published Date: 02-Feb-2018 DOI: 10.4172/2161-0681.1000336
Abstract
Importance: Sterile aliquots of Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) are necessary in obtaining uncontaminated vitreous biopsies.
Background: To report a case of RPMI medium contamination in diagnostic pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) to exclude vitreoretinal lymphoma.
Design: Interventional case report.
Participants: One patient.
Methods: Diagnostic pars plana vitrectomy, vitreous biopsy.
Main outcome measures: Diagnostic, clinical, and histopathologic features of granulmoatous vitritis.
Conclusion: A case for single use, sterile aliquots of refrigerated RPMI for vitreoretinal surgeons.
Keywords: Vitreoretinal lymphoma; Vitreous haemorrhage; vitreous biopsy; RPMI contamination; Vitreous cells
Introduction
Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) medium is composed by inorganic salts, amino acids and vitamins, utilizing a bicarbonate buffering system [1]. It was developed in 1966 by Moore and his coworker at Roswell Park Memorial Institute and has been used for the culture of normal and neoplastic leukocytes [2].
In vitreous biopsies, the addition of RPMI to neat vitreous and vitreous washings improves the preservation of any cellular constituents and is particularly helpful in the diagnosis of vitreoretinal lymphoma. RPMI is also invaluable for preserving cytomorphology in the assessment of therapeutic par plana vitrectomies (PPVs). However, RPMI, a tissue culture medium, is usually purchased by diagnostic laboratories in 500 ml or 1000 ml containers. Since a 1:1 ratio of RPMI to vitreous provides excellent cytological preservation in our experience, a 500 ml bottle of RPMI is typically adequate for at least three PPV procedures. Bottles of opened RPMI are kept in operating theatre refrigerators at 4 degrees, in keeping with manufacturer recommendations. Here we report on a case of diagnostic PPV to exclude vitreoretinal lymphoma.
Case Report
A 68-year-old Caucasian male was referred for a history of floaters and blurring of vision in his right eye with suspected vitreous hemorrhage.
Systemic history included hypertension, cholecystectomy, osteoarthritis and previous transurethral resection of the prostate. Past ocular history included a previous foreign body which was removed 30 years ago in his right eye. On examination, best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was OD 6/12 and OS 6/6 respectively. Intraocular pressure was 10 mmHg in the right and 11 mmHg in the left eye.
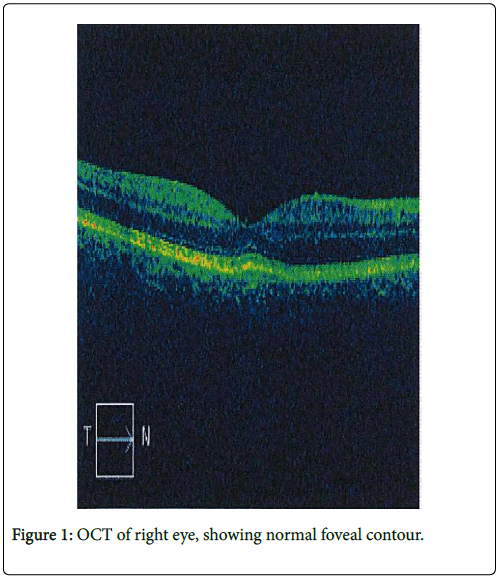
On slit lamp examination, the patient had some anterior chamber and vitreous cells in the right eye with no tears, holes or detachment. Optical coherent tomography (OCT) scans showed a normal foveal contour in both eyes and flourescein angiogram did not reveal any active disc or vascular leakage in the right eye (Figure 1). Left eye examination was unremarkable.
Laboratory tests showed an increase of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) of 14 mm/h, serum angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) was 26, liver enzymes were elevated (ALT, 42 U/L; AST 32 U/L and GGT 43 U/L), venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test was negative, C-reactive protein was normal, ANA was positive with a titer of 1/80, ANCA and Quanti Feron gold were indeterminate.
High resolution Computed tomography (HRCT) of the chest did not reveal any masses, lymphadenopathy or interstitial lung disease and this were confirmed with Magnetic resonance scan (MRI).
To assess the presence of vitreous cells the patient had a right vitectomy and biopsy 8 days after initial presentation. Refrigerated, but previously opened RPMI was added to neat vitreous and washings prior to submission to the cytology laboratory.
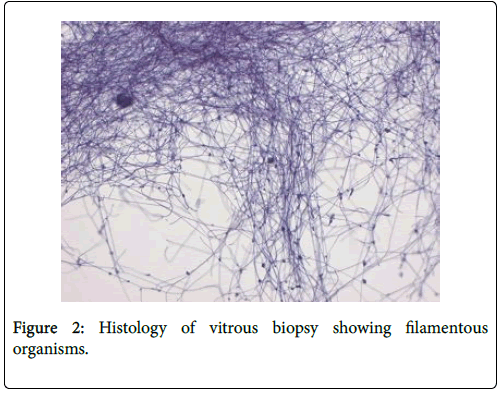
Cytomorphology and multichannel flow cytometry excluded lymphoma and a diagnosis of granulomatous vitritis was made. However, fine filamentous organisms were seen on cytospin slides from both neat vitreous and washings (Figure 2).
Microbiological culture yielded no growth. Consultation with the microbiology team suggested these were likely actinomyces or nocardia-like species based on morphology.
Discussion
The gold standard for diagnosing primary intraocular lymphoma or infection is through cytologic examination by means of a vitreous biopsy. In our case, this was performed under anesthesia using a vitreous cutter which “chops” the vitreous and aspirates the fluid. The vitreous sample was placed in 2 ml to 5 ml of RPMI. This media prolongs cell viability by preventing cell death which may improve biopsy results [3].
The challenge in diagnosing primary intraocular lymphoma or intravitreal inflammation arises from a paucity of cells obtained during sampling as well as the fragility of cells.
Factors which ensure the diagnostic yield are to use a low cute rate and gentle aspiration during vitrectomy, immediate placement of the vitreous sample into ice and attempts to decrease the chance of contamination [4].
In the above case, it was difficult to determine whether the organisms were a contaminant (probable) or an infectious agent and the cause of the granulomatous vitritis (less likely, since both actinomyces and nocardia organisms do not classically elicit a granulomatous response).
As such, this case raises the illustrates the importance of making available single use, sterile aliquots of refrigerated RPMI for vitreoretinal surgeons when submitting diagnostic samples to the laboratory in an attempt to reduce the risk of contamination in the diagnosis during vitreous biopsies.
Declaration
All authors declare: no support from any organization for the submitted work; no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
References
- Cote RJ (2009) Media composition, microbial, laboratory scale. Encyclopedia of Bioprocess Technology.
- Ranty ML, Laurent C, Aziza J, Mahieu L, Olle P, et al. (2015) Improving the cytological diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma from vitreous fluid. Histopathology 67: 48-61.
- Davis JL (2004) Diagnosis of intraocular lymphoma. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 12: 7-16.
- Huang JS, Russack V, Flores-Aguilar M, Gharib M, Freeman WR (1993) Evaluation of cytologic specimens obtained during experimental vitreous biopsy. Retina 13: 160-165.
Citation: Ting RJE, Keller J, Franzco HI, Cherepanoff SF (2018) Use of RPMI in Vitreous Cytology: The Case for Sterile, Single Use Aliquots. J Clin Exp Pathol 8: 336. DOI: 10.4172/2161-0681.1000336
Copyright: ©2018 Ting RJE, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 4762
- [From(publication date): 0-2018 - Apr 07, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 3964
- PDF downloads: 798