Unveiling Earth's Secrets: A Journey into Geochemistry
Received: 03-Oct-2023 / Manuscript No. jee-23-116113 / Editor assigned: 05-Oct-2023 / PreQC No. jee-23-116113 / Reviewed: 19-Oct-2023 / QC No. jee-23-116113 / Revised: 21-Oct-2023 / Manuscript No. jee-23-116113 / Accepted Date: 27-Oct-2023 / Published Date: 27-Oct-2023 DOI: 10.4172/2157-7625.1000450
Abstract
Geochemistry, a fascinating branch of Earth science, delves into the study of the chemical composition and processes of the Earth and other celestial bodies. By scrutinizing the distribution of elements and their isotopes,geochemists unlock the mysteries of planetary formation, evolution, and the interconnected systems that shape our world. This article explores the fundamental concepts of geochemistry, its diverse applications, and the pivotal role it plays in understanding the Earth's dynamic processes
Keywords
Geochemistry; Earth science; Isotopes.
Introduction
At its core, geochemistry investigates the distribution and behavior of chemical elements in the Earth's crust, mantle, and core. Understanding the abundances of elements and their isotopes provides insights into the processes that have shaped our planet over billions of years. Geochemists utilize analytical techniques such as mass spectrometry and X-ray spectroscopy to unravel the chemical fingerprints embedded in rocks, minerals, and fluids [1,2].
Methodology
Isotopes, with their unique atomic structures, act as tracers of geological processes. For instance, the study of isotopic ratios in rocks helps geochemists decipher the age of rocks and provides a timeline for Earth's geological history. Isotopic analyses also contribute to the understanding of climate change, as certain isotopes can serve as indicators of past environmental conditions [3].
The water cycle and geochemistry
Geochemistry plays a crucial role in elucidating the intricate processes of the water cycle. By analyzing the chemical composition of surface water, groundwater, and precipitation, geochemists can trace the movement of water through various geological formations. This knowledge is invaluable for managing water resources, predicting the behavior of contaminants, and understanding the factors influencing water quality [4-6].
Mineral exploration and resource management
In the realm of economic geology, geochemistry is an indispensable tool for mineral exploration. Geochemical surveys help identify anomalies associated with valuable mineral deposits beneath the Earth's surface. By analysing soil, rock, and water samples, geochemists can map out areas with high mineral potential, guiding exploration efforts and minimizing environmental impact [7 ].
The study of geochemistry is not confined to Earth alone. Planetary geochemistry extends our understanding of other celestial bodies, such as the Moon and Mars, through the analysis of meteorites and spacecraft data. This interdisciplinary approach sheds light on the formation and evolution of our solar system [8,9].
Environmental geochemistry
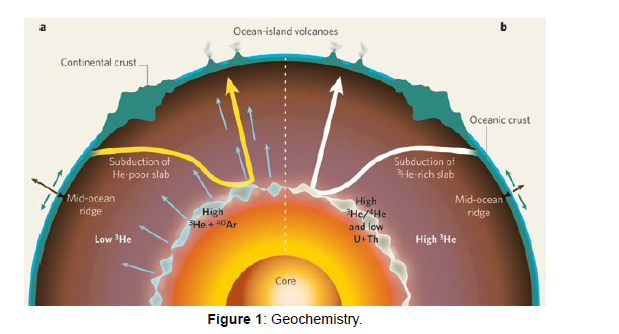
In the face of contemporary environmental challenges, geochemistry plays a pivotal role in assessing and mitigating the impact of human activities on the Earth. Whether studying the dispersion of pollutants in soil and water or monitoring the effects of climate change on ecosystems, geochemists contribute to the development of sustainable environmental management strategies (Figure 1) [10].
Conclusion
Geochemistry stands as a cornerstone in unraveling the mysteries of our planet. From understanding the formation of the Earth to addressing contemporary environmental issues, geochemistry's broad scope encompasses geological, biological, and atmospheric processes. As technology advances, the field continues to evolve, providing increasingly sophisticated tools for exploring the chemical intricacies of our dynamic planet. As we look to the future, the contributions of geochemistry will undoubtedly play a crucial role in fostering a deeper understanding of Earth's past, present, and future.
References
- Andrew RM (2018) Global CO2 emissions from cement production. Earth Syst Sci Data 10:195-217.
- Metz B, Davidson O, de Coninck H (2005) Carbon Dioxide Capture and Storage. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Umar M, Kassim KA, Chiet KTP (2016) Biological process of soil improvement in civil engineering: A review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 8:767-774.
- Li M, Fang C, Kawasaki S, Achal V (2018) Fly ash incorporated with biocement to improve strength of expansive soil. Sci Rep 8:2565.
- Choi S-G, Wang K, Chu J (2016) Properties of biocemented, fiber reinforced sand. Constr Build Mater 120:623-629.
- DeJong JT, Mortensen BM, Martinez BC, Nelson DC (2010) Bio-mediated soil improvement. Ecol Eng 30:197-210.
- Chang I, Im J Cho G-C (2016) Introduction of microbial biopolymers in soil treatment for future environmentally-friendly and sustainable geotechnical engineering. Sustainability
- Ashraf MS, Azahar SB, Yusof NZ (2017) Soil Improvement Using MICP and Biopolymers: A Review. Mater Sci Eng 226:012058.
- Chang I, Prasidhi AK, Im J, Cho G-C (2015) Soil strengthening using thermo-gelation biopolymers. Constr Build.Mater 77:430-438.
- Aguilar R (2016) the potential use of chitosan as a biopolymer additive for enhanced mechanical properties and water resistance of earthen construction. Constr Build Mater 114:625-637.
Crossref
Citation: Colhert S (2023) Unveiling Earth's Secrets: A Journey into Geochemistry.J Ecosys Ecograph, 13: 450. DOI: 10.4172/2157-7625.1000450
Copyright: © 2023 Colhert S. This is an open-access article distributed under theterms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricteduse, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author andsource are credited.
Select your language of interest to view the total content in your interested language
Share This Article
Recommended Journals
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2193
- [From(publication date): 0-2023 - Dec 22, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 1793
- PDF downloads: 400