Tumor Report Imaging: Vascular Adrenal Cyst
Received: 04-Jul-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-70941 / Editor assigned: 06-Jul-2022 / PreQC No. roa-22-70941 (PQ) / Reviewed: 20-Jul-2022 / QC No. roa-22-70941 / Revised: 22-Jul-2022 / Manuscript No. roa-22-70941 (R) / Published Date: 29-Jul-2022 DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000393
Image Article
The primary instance of a burst vascular adrenal cyst was reported by Greiselius in 1970, Viena Later in 1837, France; Rayers described the second case [1-3]. Since then up to date, around 600 cases have been reported [4].
Majority of them stay quiet long time or have a slow growth; nonetheless, they can likewise introduce a great variety of side effects and signs: stomach pain, distress, mass impact, feelings of queasiness, vomits, and so on. In the last decades, the development in imaging strategies has caused an expansion in the quantity of adrenal incidentalomas, and thus, the quantity of vascular adrenal cysts analyzed as coincidental finding. Before of the period of the inescapable of radiologic imaging strategies, these lesions were analyzed when arrived at an extraordinary size or caused side effects [4].
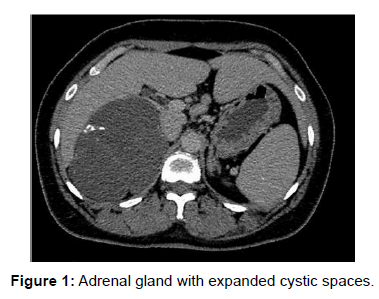
Their rate goes from 0.06 to 0.18%. Around, 6% of all adrenal incidentalomas are cystic lesions. Ladies are more regularly impacted than men with a proportion of 3:1 with a pinnacle occurrence in their fifth to sixth decade of life. Most cases have a good prognosis (Figure 1).
Adrenal cysts are an uncommon element. Their presentation differs from coincidental finding to symptomatic lesions causing stomach torment or mass impact when they arrive at a great size. It is essential to separate them from other retroperitoneal growths. Valuable devices are CT and MRI. Surgical treatment is required when side effects are present, lesions having an extraordinary size or when malignancy cannot be precluded. At long last, histological review will confirm the diagnosis.
References
- Cavallaro G, Crocetti D, Paliotta A, De Gori A, Tarallo MR, et al. (2015) Cystic adrenal lesions: clinical and surgical management. The experience of a referral centre. Int J Surg 13: 23-26.
- Sebastiano C, Zhao X, Deng FM, Das K (2013) Cystic lesions of the adrenal gland: our experience over the last 20 years. Hum Pathol 44: 1797-1803.
- Carvounis E, Marinis A, Arkadopoulos N, Theodosopoulos T, Smyrniotis V (2006) vascular adrenal cysts: a brief review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 130: 1722-1724.
- Wedmid A, Palese M (2010) Diagnosis and treatment of the adrenal cyst. Curr Urol Rep 11: 44-50.
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Indexed at, Google Scholar, Crossref
Citation: Patel P (2022) Tumor Report Imaging: Vascular Adrenal Cyst. OMICS J Radiol 11: 393. DOI: 10.4172/2167-7964.1000393
Copyright: © 2022 Patel P. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Share This Article
Open Access Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 2569
- [From(publication date): 0-2022 - Mar 29, 2025]
- Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views: 2161
- PDF downloads: 408