Image Open Access
Thalamic Bilateral Lesions Due to Occlusion of the Artery of Percheron
Raquel Rodríguez García*, Carmen Pascual, Lorena Forcelledo and Dolores Escudero
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Central University Hospital of Asturias, Oviedo, Spain
- *Corresponding Author:
- García RR
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Central University Hospital of Asturias
Oviedo, Spain
Tel: 98510800
E-mail: rakel_20r@hotmail.com
Received date: September 15, 2017; Accepted date: September 18, 2017; Published date: September 20, 2017
Citation: García RR, Pascual C, Forcelledo L, Escudero D (2017) Thalamic Bilateral Lesions Due to Occlusion of the Artery of Percheron. J Community Med Health Educ 7:i101. doi:10.4172/2161-0711.1000i101
Copyright: © 2017 García RR, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education
Clinical Image
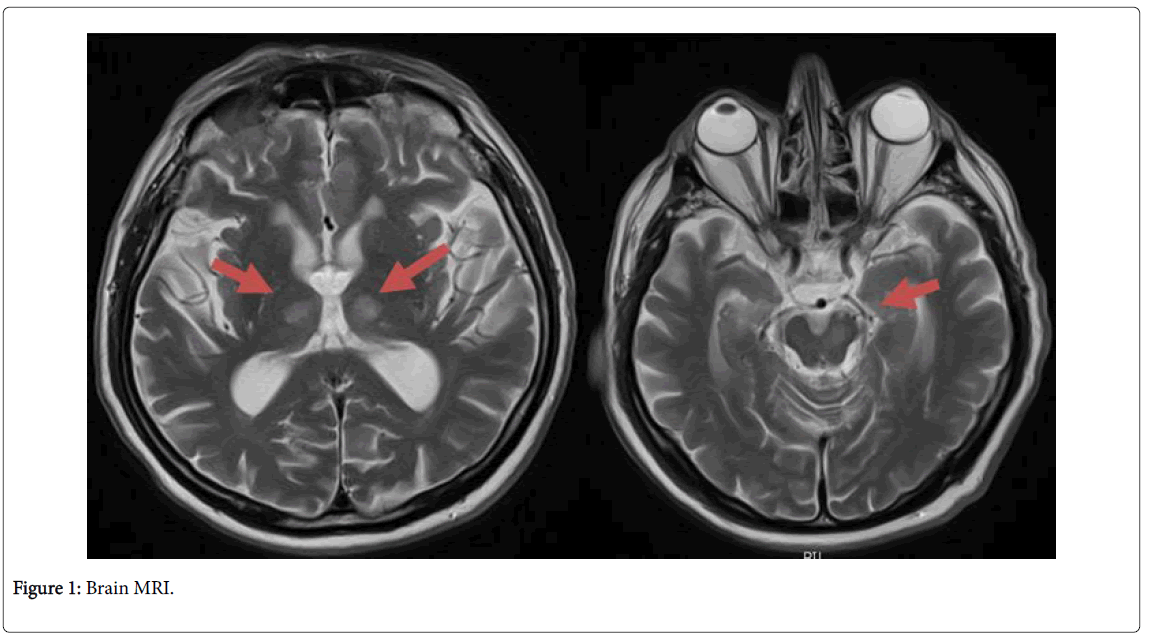
85-year-old man who was admitted to the ICU with a sudden deterioration in the level of consciousness. Once stabilized, a multimodal cranial CT was performed, without an image of ischemic pathology subsidiary of an endovascular treatment. After withdrawal of sedation, the patient presented a fluctuating state of consciousness, accompanied by palpebral ptosis and fluctuating right hemibody motor deficits too. Therefore, a new imaging study (brain MRI: Figure 1) was performed, confirming bilateral thalamic subacute ischemic lesions in the territory of Percherón artery, with possible atherothrombotic etiology.
Percheron's syndrome or synchronous bilateral thalamic infarction is considered infrequent and difficult to diagnose due to its clinical variability. It is necessary to characterize it by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
--Relevant Topics
- Addiction
- Adolescence
- Children Care
- Communicable Diseases
- Community Occupational Medicine
- Disorders and Treatments
- Education
- Infections
- Mental Health Education
- Mortality Rate
- Nutrition Education
- Occupational Therapy Education
- Population Health
- Prevalence
- Sexual Violence
- Social & Preventive Medicine
- Women's Healthcare
Recommended Journals
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 3393
- [From(publication date):
October-2017 - Jul 11, 2025] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 2559
- PDF downloads : 834