Mini Review Open Access
Synthesis of 1,3,2-Dioxoazaphospholanes
Aimakov OA1, Belgara A2* and Maksimov AG31Kazakh Agro-Technical University after S Seifullin, Astana, Kazakhstan
2Eurasian National University after LN Gumilyev, Astana, Kazakhstan
3Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia
- *Corresponding Author:
- Belgara A
Eurasian National University after L. N. Gumilyev
Astana, Kazakhstan
Tel: +77078061706
E-mail: akadil.belgara@gmail.com
Received date: March 10, 2017; Accepted date: April 18, 2017; Published date: May 25, 2017
Citation: Aimakov OA, Belgara A, Maksimov AG (2017) Synthesis of 1,3,2-Dioxoazaphospholanes. Biochem Physiol 6:216. doi:10.4172/2168-9652.1000216
Copyright: ©2017 Aimakov OA, et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Visit for more related articles at Biochemistry & Physiology: Open Access
Introduction
The chemistry of phospholanes gained broad development first of all due to their many useful properties as the intermediate readily available monomeric substances with functional groups and various heteroatoms and also having particular biological properties [1,2]. Phospholane cycle is a part of the biologically active synthetic material. In addition, it is a structural basis of many antimicrobic tools, thus researchers are interested in these systems [3-5].
With the purpose of obtaining new 1,3,2-dioxoazaphospholanes, the following compounds are used as starting reagents: ethylene glycol, phosphorus trichloride, alcohols, monoethanol amine vinyl ether. These substances are readily available monomers of chemical production. They are not waste products, but are monomers for obtaining different chemicals. The novelty of this work is that in order to obtain new phospholanes for the first time we used vinyl monoethanol amine ether. For the first time we obtained 1,3,2-dioxoazophospholanes.
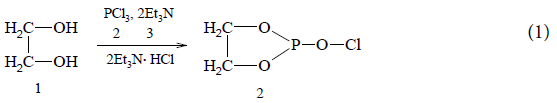
The aim of this work was to develop preparative aspects of the formation reactions of phospholane series compounds at interaction of chlorine-containing phospholanes with monoethanolamine vinyl ether, which would extend preparative capabilities using a known method and obtain previously unknown 1,3,2-dioxoazaphospholanes. Chlorides of ethyleneglycolphosphorus acid were taken as initial reagents. They were obtained by phosphorylation of ethylene glycol by means of phosphorus trichloride according to the scheme:
In the series of phosphorous organic compounds, 1,3,2-dioxoazaphospholanes have a huge potential as a synthetic materials, and are interesting objects to study different types of biological activities.
In the course of the experiment, we have successively obtained the compounds indicated in the article.
Experimental Section
O.O-Dipropyl - {N-2-(vinyloxy), ethylamido}thiophosphate
4.55 g (0.025 mol) of thiophosphite O,O-dipropyl was added to benzene solution of 2.17 g (0.025 mol) of monoethanolamine vinyl ether, 2.5 g (0.025 mol) of triethylamine and 3.84 g (0.025 mol) of CCL4 under stirring and a temperature of 18ºC. Hydrochloride of triethylamine precipitated in process of cooling of a reaction mixture. The sediment was filtered, then the filtrate was boiled out in vacuo, the rest was investigated on a chromatograph with a column with a silica gel, eluent-hexane-acetone (3:1).
O,O-diisopropyl-, O,O-dibutyl-, O-isopropyl (piperidyl) [N-2- vinyloxyethylamido]thiophosphate and O-butyl (piperidyl) [N-2- vinyloxyethylamido]thiophosphate were received similarly.
The purity of the compounds and the reactions were monitored by TLC on Silufol UV 254 plates in specified eluents systems. The manifestation was carried out with iodine vapor.
31P NMR spectra was recorded on the “Bruker WP-200SY” device with an operating frequency on nuclei 31P 81.01 MHz; external standard - 85% solution of H3PO4.
Synthesis of 2-chloro-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane
50 ml of anhydrous ether, 9.3 g of ethylene glycol and 22.0 g of pyridine were placed in the reaction flask. 20.62 g of phosphorus trichloride was added to the reaction mixture with stirring at a temperature of -16 to -17ºС. After the addition of phosphorus trichloride at room temperature, the solution was left with stirring for about 1.5 h. During the reaction, the pyridine hydrochloride formed. The ether solution of 2-chloro-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane was isolated by filtration. Further desired product 2-chloro-1,3,2-dioxaphospholane was obtained by simple distillation. Boiling point=56ºC, 1.4917; Molecular Weight=126.49; Gross formula: С2Н4Р�?2Сl.
a. Synthesis of 2-alkoxy-1,3,2-dioxaphospholanes
b. Synthesis of 2-ethoxy-1,3,2-dioxaphospholanes
30 l of absolute diethyl ether, 1.72 g of ethanol, 2.96 g of pyridine were placed in a reaction flask.
Results and Discussion
The foundation of researches in the field of 1,3,2-dyoxaphospholane is laid in Arbuzov and Kabachnik’s works [6,7].
We investigated reactions of alkyl-1,3,2-dioxophospholanes with monoethanolamine vinyl ethers, which, in the result, leads to formation of series of 1,3,2-dioxophospholanes vinyl ethers derivatives. Firstly we synthesized the phosphorous acid ethyleneglycol chloride [8] and further corresponding alkyl-1,3,2-dioxaphospholanes were obtained on its basis according to the following scheme:

In order to obtain polyfunctional derivatives of phosphorous acid diols, in our investigations we used the chemical monomer of series of amino alcohols vinyl ethers-monoethanolamine vinyl ether. Due to the presence of amino- and vinyloxy groups these compounds have a great synthetic potential of amines and vinyl ethers. Vinyl ethers and their derivatives are of great interest as monomers for synthesis of polyfunctional compounds, which are widely used as chemotherapeutic drugs, polymer materials, pesticides, plant growth stimulators.
In the industry, ethoxyethylamine were obtained by catalytic hydrogenation on the basis of monoethanolamine vinyl ether. Ethoxyethylamine were used in synthesis of anti-diabetic medicines. The scheme of this medicinal preparation is given below:

The synthesized vinyl ethers of Schiff ’s bases are of interest as polyfunctional monomer compounds for the development of the theory and practice of functionally substituted vinyl ethers of amino alcohols, and for the further development of targeted methods of new biologically active derivatives synthesis on their basis having a set of properties that are important for practical applications. The researches of properties of a number of Schiff ’s bases containing amino groups, various on character [8-14] were conducted in order to clarify the relationship between the structure and reactivity of vinyl ethers of amino alcohols. Studying the properties and synthetic opportunities of amino alcohols vinyl ethers and their derivatives, the research on properties of a monoethanolamine vinyl ether monomer in reaction with phosphoric-acid-diols were continued.
Earlier we studied condensations of monoethanolamine vinyl ether with various carbonyl compounds, the corresponding Schiff ’s bases were received [15-23].
With a view to expand the series of polyfunctional and heteroatom-containing derivatives of amino alcohols vinyl ethers, including monoethanolamine vinyl ether, the series of derivatives of 1,3,2-dioxophospholanes vinyl ethers was synthesized in the result of interaction between alkyl-substituted diols of phosphorous acid with monoethanolamine vinyl ether:
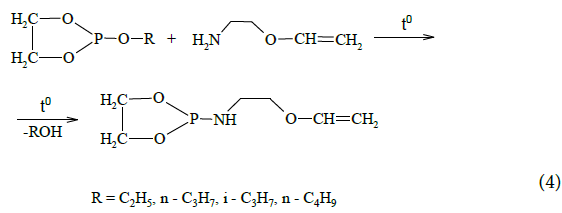
Molecules of 1,3,2-dioxaphospholane vinyl ethers derivatives contain reactive secondary amino groups and vinyloxy group. The presence of trivalent phosphorus of dioxaphospholane cycle and the double bond in vinyloxy group cause high reactivity. Thus, organic phosphorus compounds containing R-C-N, P-O-C fragments deserve attention as effective bioactive agents, flotation agents and complexing agents. These compounds possess unique reactivity due to the mutual influence of geminal nitrogen and phosphorus atoms.
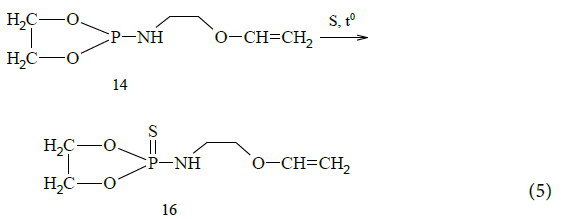
Due to our research interests in the field of organophosphorus compounds chemistry [8-10], we conducted the reaction of N-vinyloxiethyl-1,2,3-dioxaphospholane with elemental sulfur, which resulted in the corresponding synthesized thiophospholane:
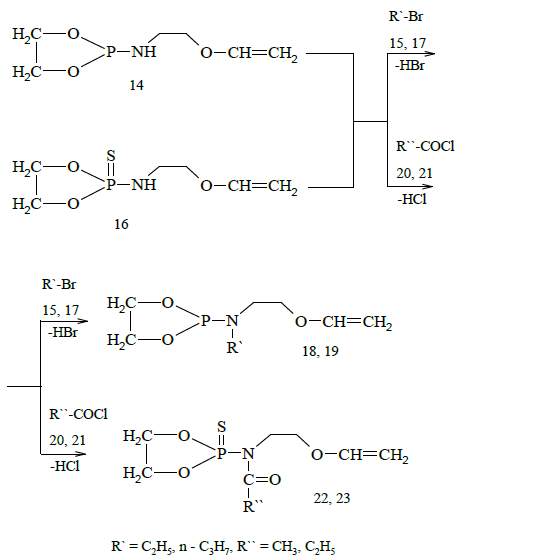
Reactions of alkylation and acylation were carried out in order to elucidate the reactivity of synthesized 1,3,2-dioxathio-phospholanes. As a result, the corresponding alkyl and acyl derivatives of phospholanes were obtained:
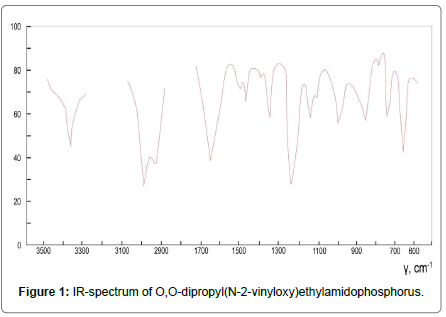
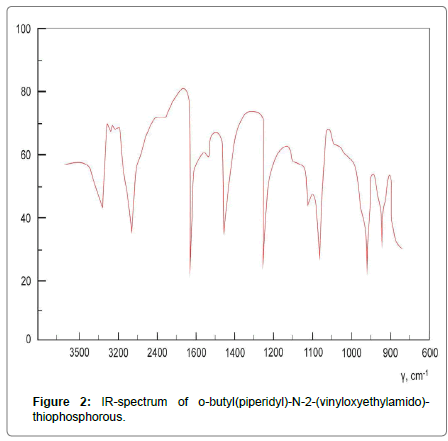
The structure of the obtained substances was confirmed by 31P-NMR and IR spectroscopy. IR spectra (δ): P=S (630-650), Р-N (890-920), Р-�?-С (1135-1180), С=С (1605-1625), N-H (3260-3280) (Figures 1-3).
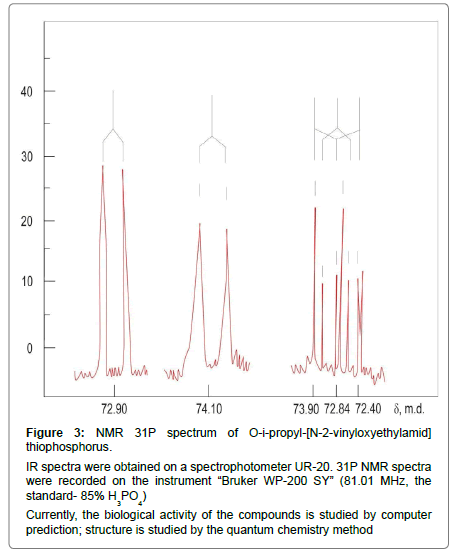
Figure 3: NMR 31P spectrum of O-i-propyl-[N-2-vinyloxyethylamid] thiophosphorus. IR spectra were obtained on a spectrophotometer UR-20. 31P NMR spectra were recorded on the instrument ��?Bruker WP-200 SY� (81.01 MHz, the standard- 85% H3PO4) Currently, the biological activity of the compounds is studied by computer prediction; structure is studied by the quantum chemistry method.
31P NMR spectra -(1Н) [m.d.[:Pr n 72.40 (c), Pr iso 72.84(c), Bu n 72.90(c), Pr iso РР piperidyl- 74.10(c), Bu n PP piperidyl 73.90(c).
Conclusion
In the process of phosphorylation of ethylene glycol in the presence of phosphorus trichloride and alcohols, cyclic alkyl derivatives of phospholanes were synthesized. On the basis of cyclic phospholanes and vinyl ether monoethanol amine, amine derivatives of phospholanes were first obtained. Subsequently, cyclic amino derivatives of phospholanes undergo an acylation reaction. In the result, acyl derivatives of cyclic phospholanes and their thio derivatives were synthesized.
The importance from the theoretical point of view of the amino derivatives of cyclic phospholanes are promising chemical monomers. Since the molecule contains vinyloxy and a secondary amine group. 1,3,2-dioxoazophospholanes form a class of biologically active substances and can have antibacterial properties.
References
- Aiswarya KSB, Rao PJ, Spoorthy YN, Begum DI, Ravindranath LK (2012) Synthesis and anti-microbial activity of novel mannich bases containing 2-phenoxy-1,3,2-dioxa phospholanes and indole systems. J Chem Pharm Res 4: 4052-4059.
- Mazzacurati M, Baccolini G, Boga C (2007) Advanced studies on the synthesis of organophosphorus compounds. Alma Mater Studiorum, Università Di Bologna 59: 1-215.
- Bernd W, Elena VK, Wolfgang M (2014) Novel 1,3-dichalcogeno-2-phospholanes with an annelated 1,2-dicarba-closo-dodecaborane(12) unit. Athens Journal of Natural and Formal Sciences 1: 83-95.
- Sridhar SK, Ramesh J (2001) Synthesis and pharmacological activities of hydrazones, Schiff and mannich bases of isatin derivatives. Biol Pharm Bull 24: 1149-1152.
- Shamsiyeva AV (2011) Synthesis of pyridyl-containing phospholanes, Kazakh Agro-Technical University.
- Arbuzov BA, Vizel AO (1963) News of SA of USSR, GCN 749.
- Kabachnikov MI (1957) Chemistry and use of phosphorous organic compounds, Moscow, p: 18.
- Aimakov OA (2002) Materials of the Republican scientific-practical conference "State and prospects of development of chemistry and chemical technologies in Central Kazakhstan". Karaganda, pp: 140-145.
- Aimakov OA, Mastruykova TA (1998) Synthesis and esters of the phosphoric acids. MS RK, Chemical Series 1: 68-72.
- Aimakov OA, Erjanov KB (1998) New amidoesters of thiphossporic acids. Russ Chem Rev 47: 1189-1192.
- Aimakov OA (2002) News of ENU after LN Gumiliev, Astana, pp: 246-249.
- Aimakov OA (2002) Mastriukova TA, News RSA, Moscow 12.
- Aimakov OA, Lugovickaia TN, Svincickaia NI (2004) Proceedings of the VII Youth Scientific Conference on Organic Chemistry. Yekaterinburg, Russia, p: 99.
- Aimakov OA, Medetova LK (2006) Materials of the Republican scientific-practical conference "Valikhanov readings". Kokshetau 11: 148-155.
- Aimakov OA (1981) Collection ��?Synthesis and study of functionally-substituted unsaturated compounds�. Karaganda, pp: 93-98.
- Aimakov OA, Mastriukova TA, Erzhanov KB (1996) News of ME-SA RK. Chem ser 4: 7-9.
- Aimakov OA, Seitkalieva DK, Svincickaia NI (2003) Chemistry, chemical engineering and biotechnology at the turn of the millennium. Tomsk 1: 193-194.
- Aimakov OA (2013) Proceedings of the scientific conference devoted to the 185th anniversary of the St. Petersburg State Technical Institute, Saint-Petersburg, Russia, pp: 68-70.
- Aimakov OA, Zubova NM (2003) Scientific collection "Problems of development of new drugs". Guillem Ufa, pp: 35-37.
- Aimakov OA, Erzhanov KB, Mastriukova TA (2003) News of RSA. Chem ser 1: 2276-2279.
- Aimakov OA, Erzhanov KB, Mastriukova TA (1998) News of RSA. Che ser 8: 1876-1878.
- Aimakov OA, Duisembaev SA, Mastriukova TA, Erzhanov KB, News of MS-SA RK (1996) Chem ser 5: 68-717.
- Aimakov OA, Erzhanov KB, Mastriukova TA (2002) Scientific collection "State and Prospects of Development of Organic Chemistry". Almaty, pp: 31-32.
Relevant Topics
- Analytical Biochemistry
- Applied Biochemistry
- Carbohydrate Biochemistry
- Cellular Biochemistry
- Clinical_Biochemistry
- Comparative Biochemistry
- Environmental Biochemistry
- Forensic Biochemistry
- Lipid Biochemistry
- Medical_Biochemistry
- Metabolomics
- Nutritional Biochemistry
- Pesticide Biochemistry
- Process Biochemistry
- Protein_Biochemistry
- Single-Cell Biochemistry
- Soil_Biochemistry
Recommended Journals
- Biosensor Journals
- Cellular Biology Journal
- Journal of Biochemistry and Microbial Toxicology
- Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
- Journal of Biological and Medical Sciences
- Journal of Cell Biology & Immunology
- Journal of Cellular and Molecular Pharmacology
- Journal of Chemical Biology & Therapeutics
- Journal of Phytochemicistry And Biochemistry
Article Tools
Article Usage
- Total views: 3062
- [From(publication date):
June-2017 - Nov 21, 2024] - Breakdown by view type
- HTML page views : 2351
- PDF downloads : 711